Table of Contents
ToggleKopelman Hair understands how distressing hair thinning on the crown of the head can be for both men and women. With over 40 years of experience, Dr. Kopelman and his team provide personalized, medically backed solutions to restore density and confidence.
This guide explains the causes, signs, and proven treatments for crown hair loss – helping you make informed decisions about your hair health.
Key Takeaways
- Hair thinning on the crown of the head is often caused by genetics, hormonal sensitivity to DHT, or medical conditions like thyroid disorders and alopecia areata.
- Recognizing early signs – such as a widening part, reduced volume, or a small thinning patch – greatly improves the chances of slowing or reversing loss.
- Effective treatments range from topical medications and PRP therapy to surgical options like FUE transplants, supported by at-home scalp care strategies.
- A professional evaluation, including scalp examination and medical testing, ensures the underlying cause is correctly identified and treated.
- Long-term prevention focuses on consistent scalp hygiene, balanced nutrition, and addressing stress to help maintain density and prevent further hair loss.
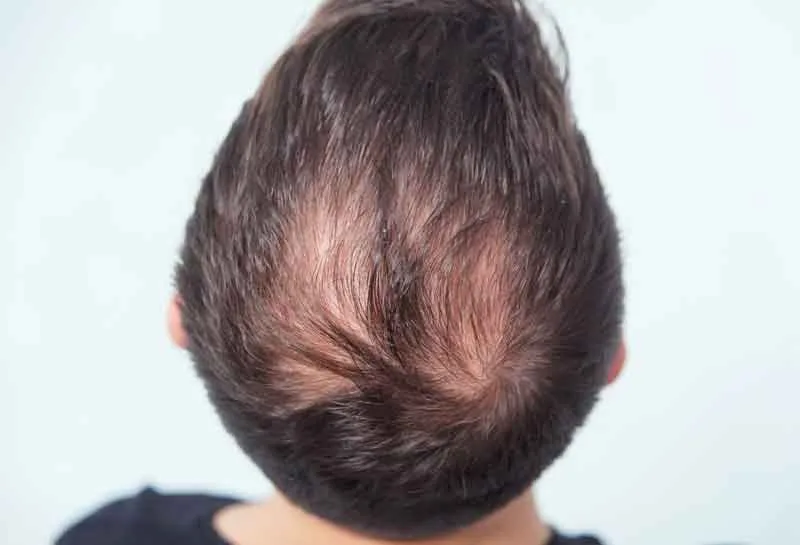
How to Spot Hair Thinning at the Crown
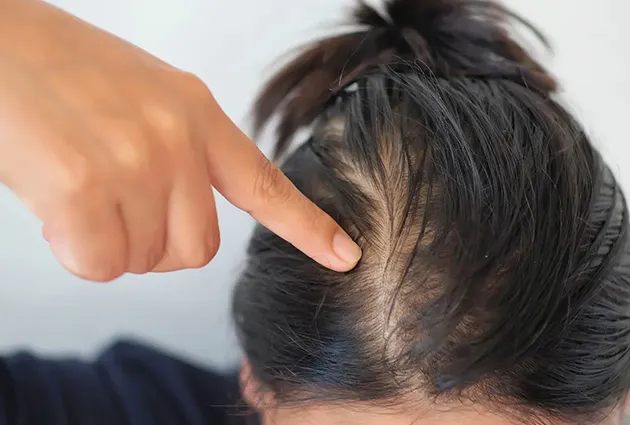
Identifying thinning early improves the chances of slowing or reversing it. The crown area can be hard to monitor without assistance. A trusted friend or clear photographs taken over time can reveal gradual changes.
Quick Recognition Checklist for Crown Hair Loss
Noticing early signs can make a difference in preserving hair at the crown:
If you see these changes, visit a hair restoration specialist promptly.
Signs in Women and Men
Women may notice a widening part line or reduced volume at the crown. Men often see a circular thinning patch that expands. In both, styling may become harder.
Hair Thinning on Top of Head
When thinning spreads beyond the crown, it may indicate advanced hair loss. Look for reduced coverage and a visible scalp under bright lighting.
Why Hair Loss Happens at the Crown
The crown is vulnerable to certain forms of alopecia. Understanding the cause helps determine the right intervention.
Broader Medical Causes of Crown Hair Loss
Beyond genetics and hormones, some cases are linked to medical conditions. Autoimmune disorders like alopecia areata can cause sudden loss. Thyroid imbalances, lupus, and certain medications such as chemotherapy drugs may trigger hair loss at the crown of the head.
A thorough evaluation can identify these causes early and sometimes reverse the loss without invasive procedures.
Why Is My Hair Thinning at the Crown?
Thinning at the crown is often linked to androgenetic alopecia – also called androgenic alopecia – a hereditary condition causing gradual hair miniaturization. Hormonal changes and scalp sensitivity to dihydrotestosterone (DHT) – especially rising DHT levels – play key roles.
Why Is Hair Loss Only on Top of the Head?
Follicles in the crown and top regions are more sensitive to hormonal effects. The sides and back often retain thicker hair, making them ideal donor areas in transplants.
Pattern Hair Loss vs Other Causes
While pattern hair loss is common, other triggers include nutritional deficiencies, stress, or scalp conditions. In women, this may present as female pattern hair loss, which often includes crown thinning without a receding hairline.

Role of DHT, Genetics, and Scalp Health
DHT can shrink follicles, producing thinner strands until growth stops. Genetics determines sensitivity, while scalp issues like buildup or inflammation can speed up loss. Good scalp health can help promote hair growth.
Can Thinning at the Crown Grow Back?
Regrowth is possible in many cases, depending on the cause, severity, and timing of treatment.
Hair Regrowth Potential and Limitations
Early-stage crown hair loss often responds to topical minoxidil or oral medications. Advanced balding at the crown may require surgical restoration.
Factors That Affect Results
Results depend on age, how long thinning has been present, overall health, and treatment consistency. Genetics are also a key factor.
Treatment Options for Crown Hair Thinning
Dr. Kopelman tailors each hair loss treatment plan to the patient’s needs, combining medical, procedural, and lifestyle strategies.
Hair Thinning on the Crown of the Head Treatment
Options include medications, targeted procedures, and preventive care. The goal is to slow hair loss, encourage regrowth, and maintain scalp health.
How to Fix Thin Hair on Top of Head
Improving density may involve similar strategies to crown treatments, including platelet-rich plasma therapy, microneedling, or hair transplantation for more advanced cases.
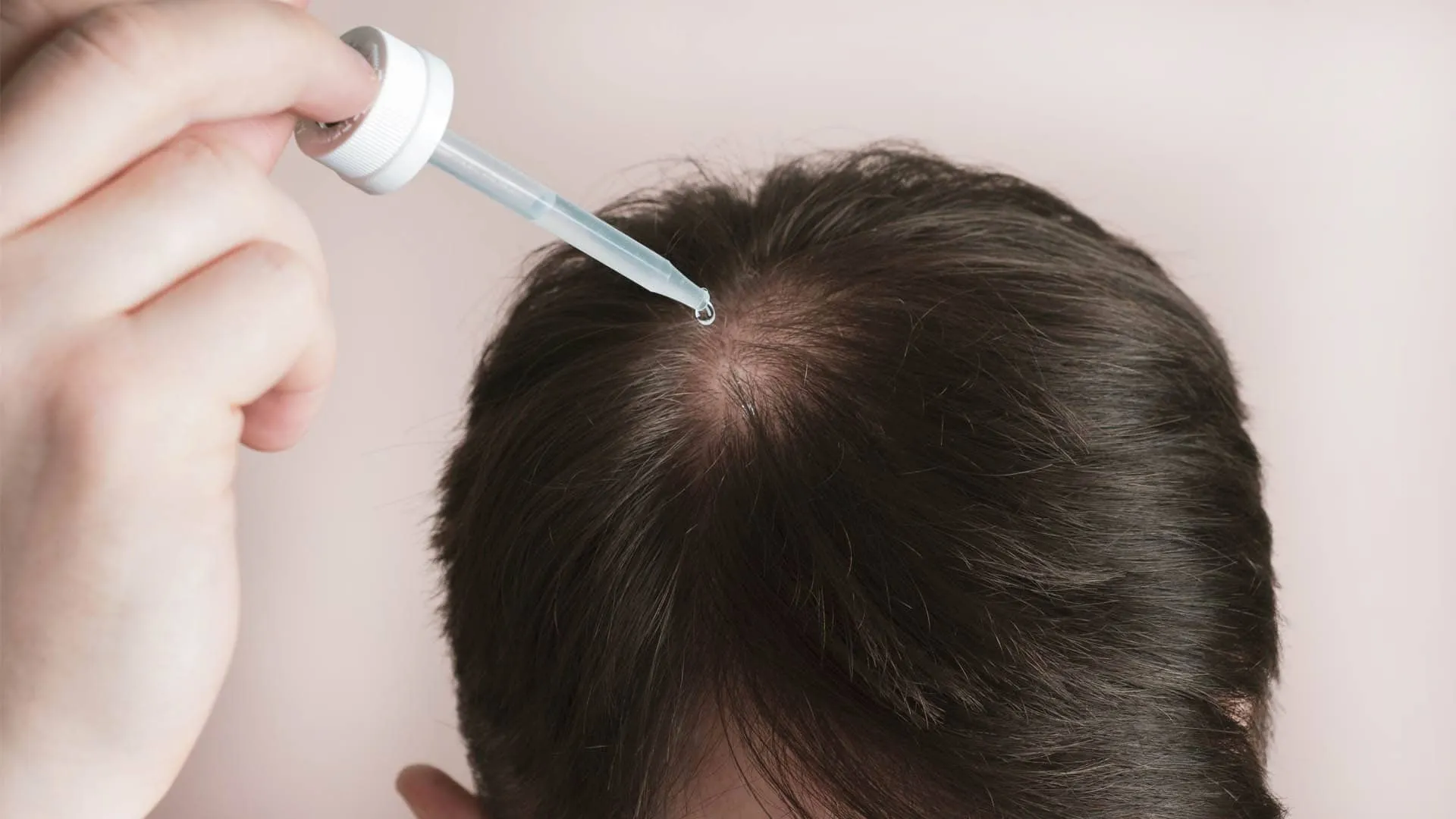
Topical Treatments: Minoxidil and Anti-Androgens
Minoxidil boosts blood flow to follicles, extending the growth phase. Anti-androgens reduce DHT’s local effects, making them useful for thinning at the crown of the head.
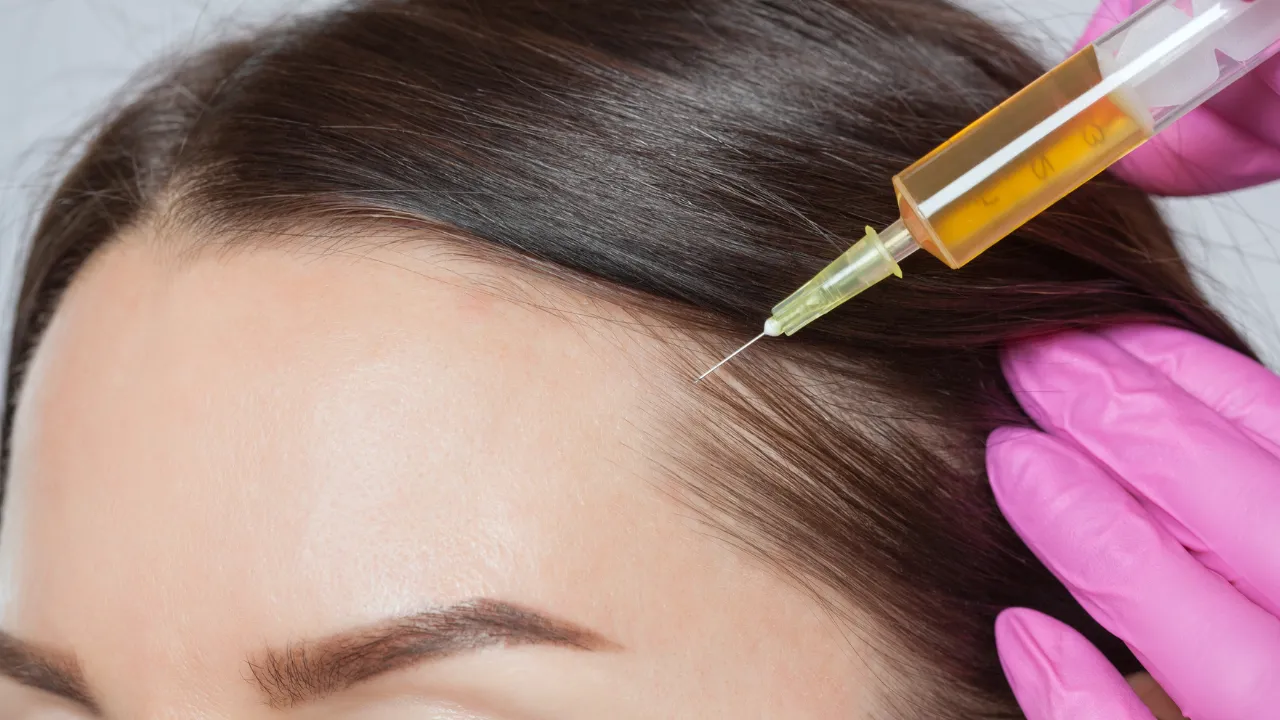
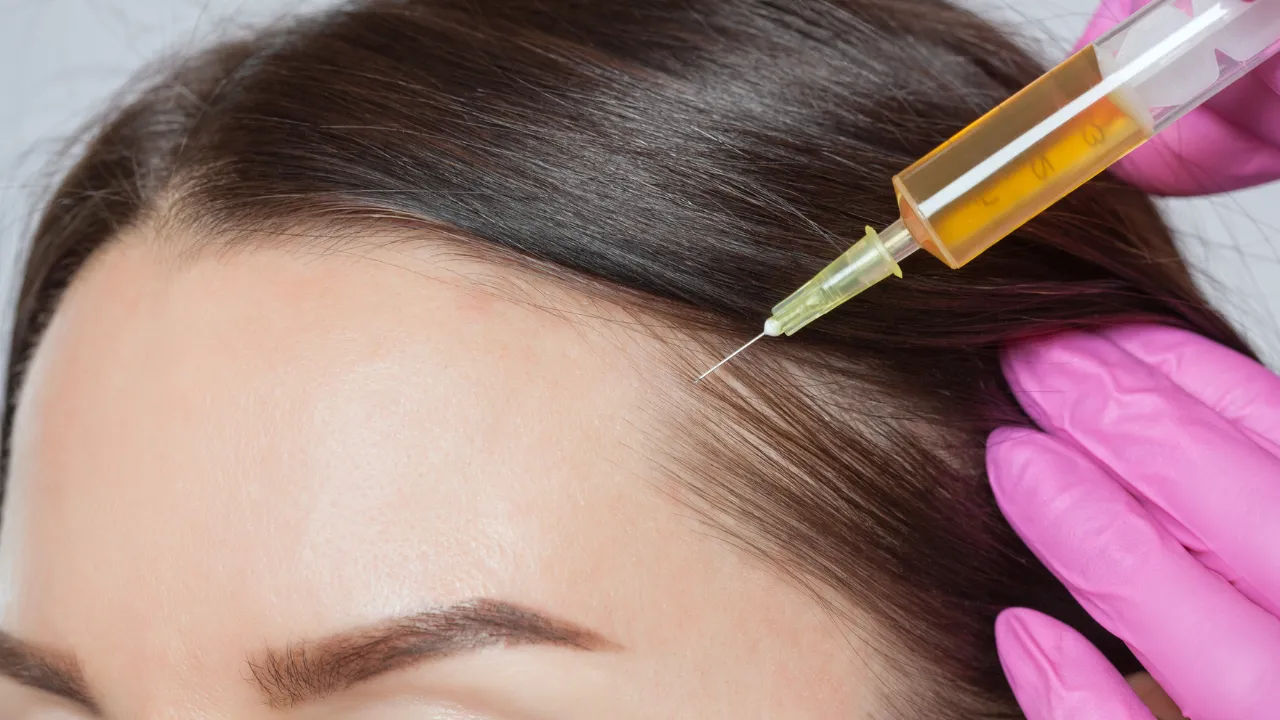
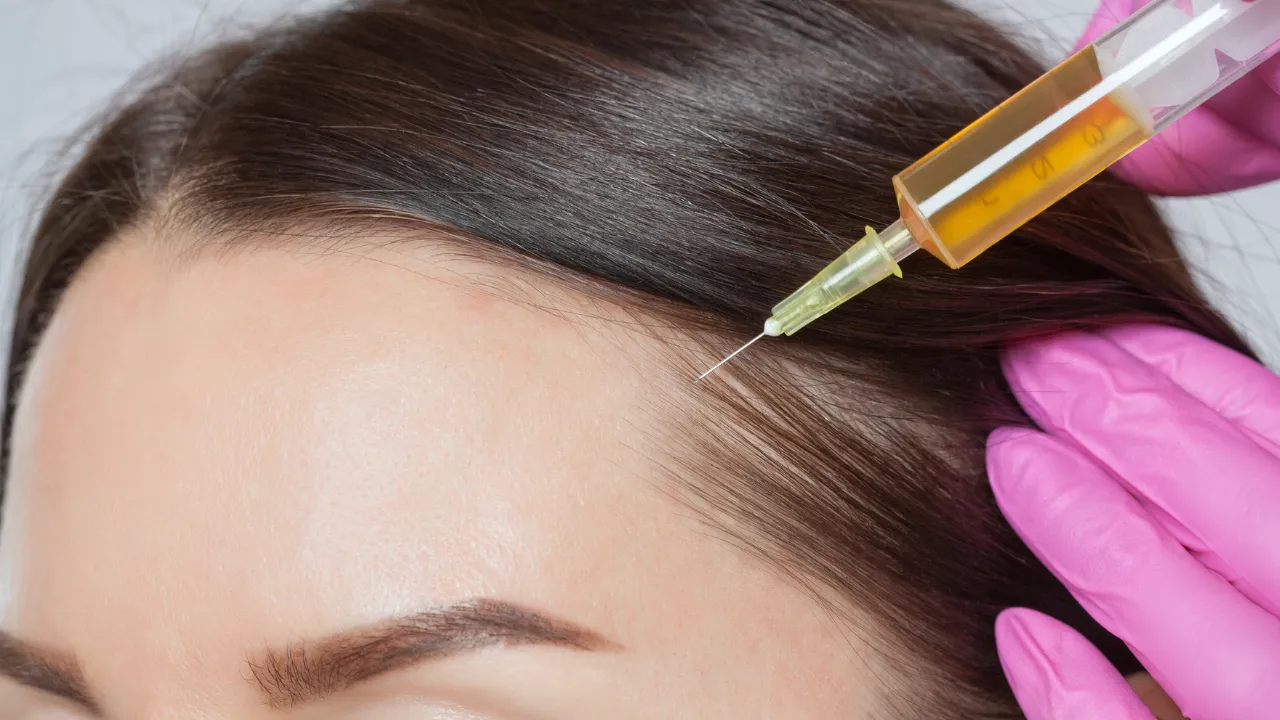
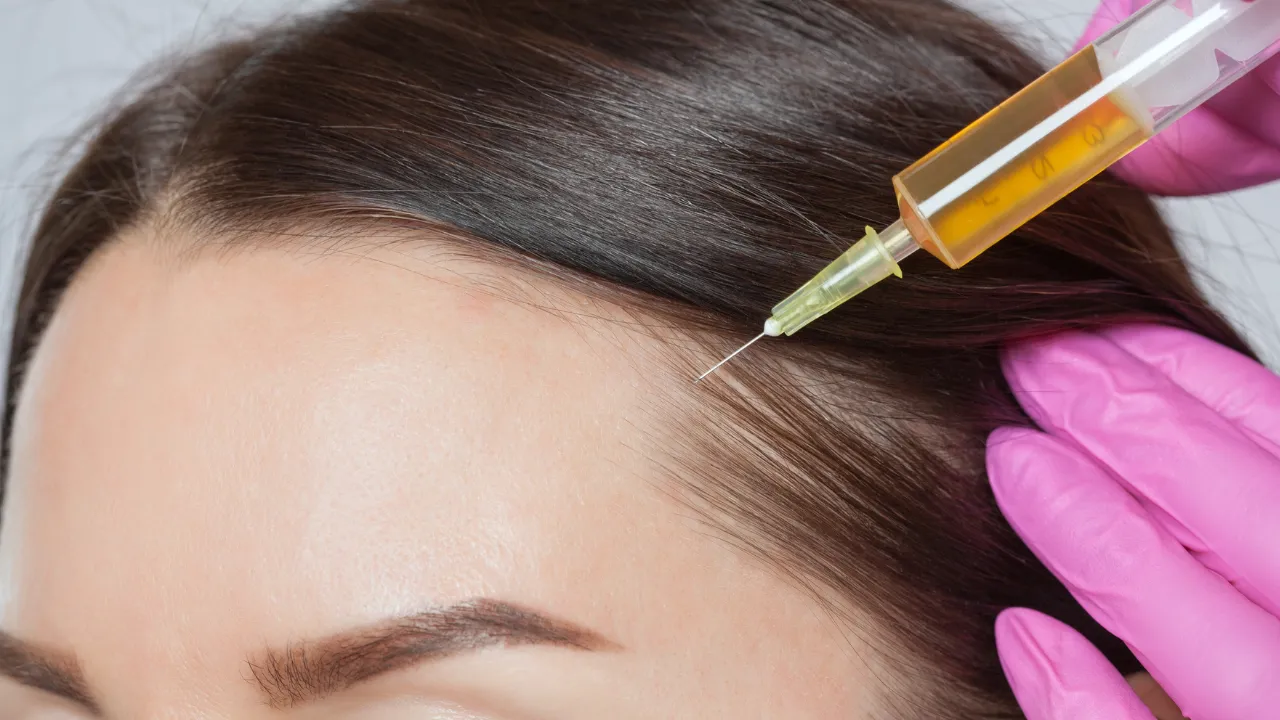
Advanced Procedures: PRP, Microneedling, FUE Transplants
- PRP Therapy – Uses growth factors from your blood to stimulate follicles.
- Microneedling – Improves absorption of treatments and stimulates repair.
- FUE Hair Transplant – Moves healthy follicles to thinning or balding areas.
At-Home Management Tips for Crown Thinning
Non-clinical strategies can improve appearance while deciding on treatments. Layered hairstyles, part changes, or hair fibers can reduce scalp visibility.
These changes do not treat the cause but can boost confidence. They work best when combined with care from a medical professional.
Lifestyle and Scalp Care
A diet rich in protein, iron, and vitamins supports hair health. Gentle scalp massage can improve circulation. Avoid harsh chemicals and heat styling.
Risks and Limitations of Treatments
Results vary between individuals, and some may experience temporary shedding. Guidance from a medical professional ensures realistic expectations and safety.
Patient Case Examples from Dr. Kopelman’s Practice
At Kopelman Hair, a male patient in his early 30s regained density within eight months after PRP therapy and topical treatment.
In another case, a female patient with thin hair at the crown improved through nutritional adjustments, scalp care, and low-level laser therapy.
When to See a Hair Specialist
If thinning progresses or shedding is sudden, consult a specialist early.
Signs of Underlying Health Issues
Rapid hair loss, unusual patterns, or scalp pain may indicate hormonal or autoimmune conditions needing medical attention.
When to Seek Urgent Medical Review
Seek urgent review if you notice sudden patchy loss, sores, redness, or pain. These may signal infections, autoimmune activity, or other serious conditions.
Prompt action can protect scalp health and prevent further hair loss.
What to Expect at a Consultation
Dr. Kopelman conducts a full history, scalp exam, and sometimes imaging. For those with crown thinning and a receding hairline, the plan may address both for balanced results.
Recommendations in this guide follow established dermatological principles. Organizations like the American Academy of Dermatology and peer-reviewed journals confirm the role of DHT, genetics, and scalp health in crown thinning.
By using evidence-based guidance, Dr. Kopelman ensures patients receive safe and effective solutions.
Preventing Future Crown Hair Loss
While genetics cannot be changed, steps can be taken to protect existing hair and slow loss.
Daily Scalp Maintenance
Wash with a mild shampoo, avoid tight hairstyles, and protect from excessive sun exposure.
Nutrition and Stress Management
A nutrient-rich diet supports growth, while stress control can reduce shedding triggers. Healthy habits help prevent losing hair at the crown and include hair in overall wellness strategies.
Take the Next Step Toward Restoring Your Hair
If you’re noticing hair thinning on the crown of your head, early action can make a big difference. Schedule a consultation with Dr. Kopelman and the team at Kopelman Hair to receive a personalized, evidence-based plan designed to address your needs and promote lasting results.