Table of Contents
ToggleKopelman Hair has helped many women address hair loss due to menopause through expert diagnosis and personalized treatment plans. Menopause can cause significant changes in hair health, and understanding the causes and solutions is the first step toward restoring confidence.
With over 40 years of combined expertise, Dr. Kopelman and his team provide effective, medically sound options tailored to each patient.
Key Takeaways
- Menopause-related hair loss is driven by hormonal changes, particularly reduced levels of estrogen and increased androgen activity, which can shorten the hair growth cycle and thin hair over time.
- Early intervention with medical treatments, lifestyle adjustments, and proper nutrition can slow shedding and promote hair growth, especially with guidance from a specialist like Dr. Kopelman.
- Solutions may include topical minoxidil, PRP therapy, gentle hair care practices, and targeted vitamins, each with benefits and potential side effects.
- Recognizing early signs such as diffuse thinning, reduced volume, or widening parts allows for faster action and better results.
Preventing Hair Loss Before and During Menopause
Taking steps early can help reduce the severity of hair loss during menopause. A balanced diet rich in protein, vitamins, and minerals supports healthy hair and follicles. Managing stress through exercise or meditation helps stabilize hormones.
Women with a family history of androgenic alopecia or thinning hair should seek early evaluation to discuss preventive treatment options.
Causes of Menopause Hair Loss
Which hormone causes hair loss in females
Estrogen helps keep hair in its growth phase. During menopause, levels of estrogen drop and male hormones (androgens) may rise, shortening the growth cycle. This hormonal shift can directly affect hair density and volume.
Losing hair due to menopause
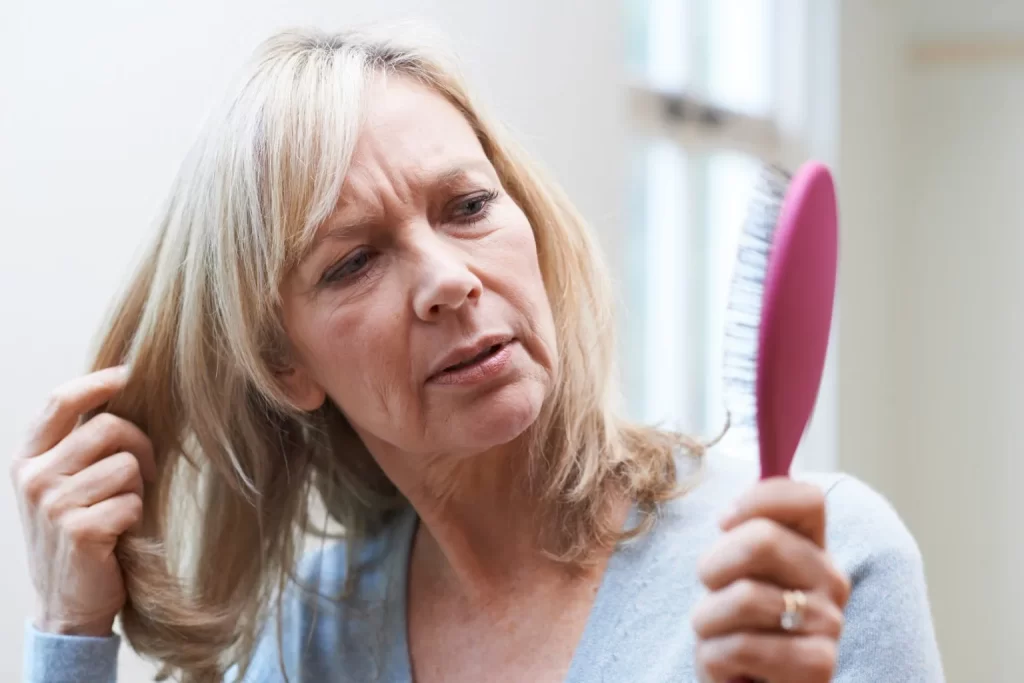
Hair fall in menopause often develops gradually. Many women first notice hair collecting in the shower drain or on their pillow. Increased hair shedding signals hormonal influence, but stress, nutrition, and health conditions can also contribute to hair loss.
Hormonal changes, DHT, and thinning
Lower estrogen lets dihydrotestosterone (DHT) shrink follicles, causing thinning hair in menopause. This resembles androgenic alopecia in men but is more diffuse in menopausal women. Treatments targeting DHT may help stimulate hair growth.
Reduced estrogen and progesterone shorten the growth phase, letting androgens weaken follicles. Some ask, does menopause cause hair thinning? the answer is yes, mainly due to hormonal imbalance. Telogen effluvium, a stress-related shedding, can occur alongside these changes.
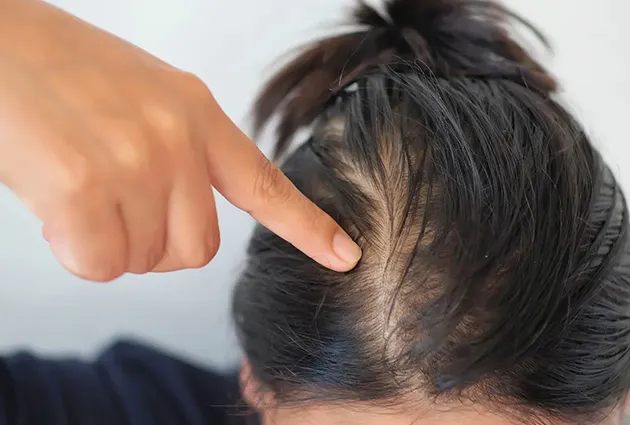
Signs of Menopause Hair Loss
Thinning hair in menopause
Early signs include reduced hair volume, thinner ponytails, or more visible scalp, often without heavy daily shedding.
Post-menopausal hair loss patterns
Hair becomes sparse across the top of the head, while the hairline usually remains intact. This type of hair loss can be subtle at first.
Hair loss with white bulbs: what it means
White bulbs mean the hair has completed its growth cycle. Frequent shedding with bulbs during menopause may indicate thinning or bald spots that need evaluation.

Psychological Impact of Menopause Hair Loss
Hair loss during menopause can affect confidence and daily life. Stress from appearance changes may further contribute to hair loss. Emotional support and professional help can assist women while they address physical causes.
Treatment and Prevention Options
Stopping and treating menopause hair loss
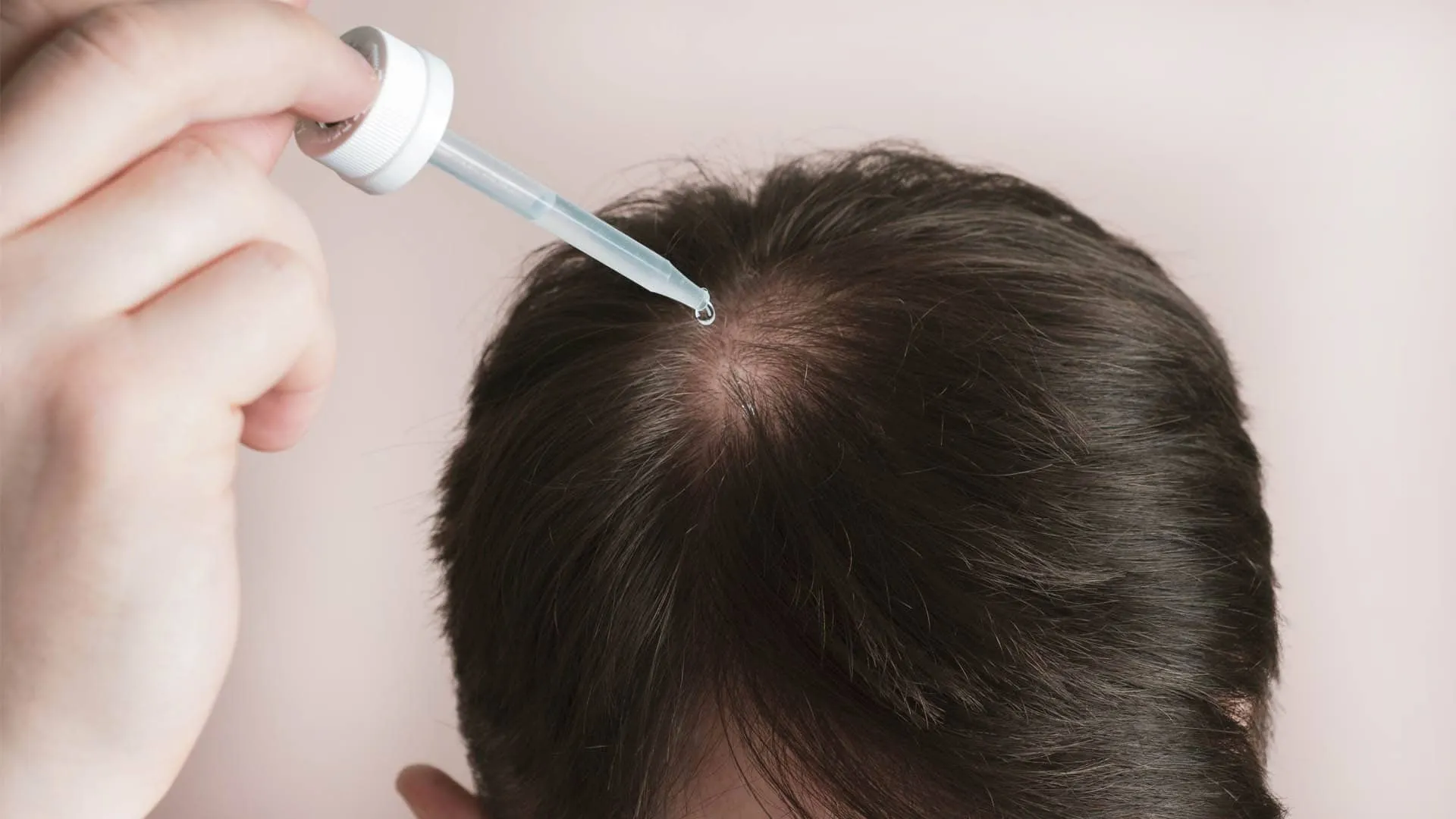
Stopping hair loss during menopause means addressing causes and improving follicle health. This may include hormone checks, scalp treatments, medications, and lifestyle adjustments.
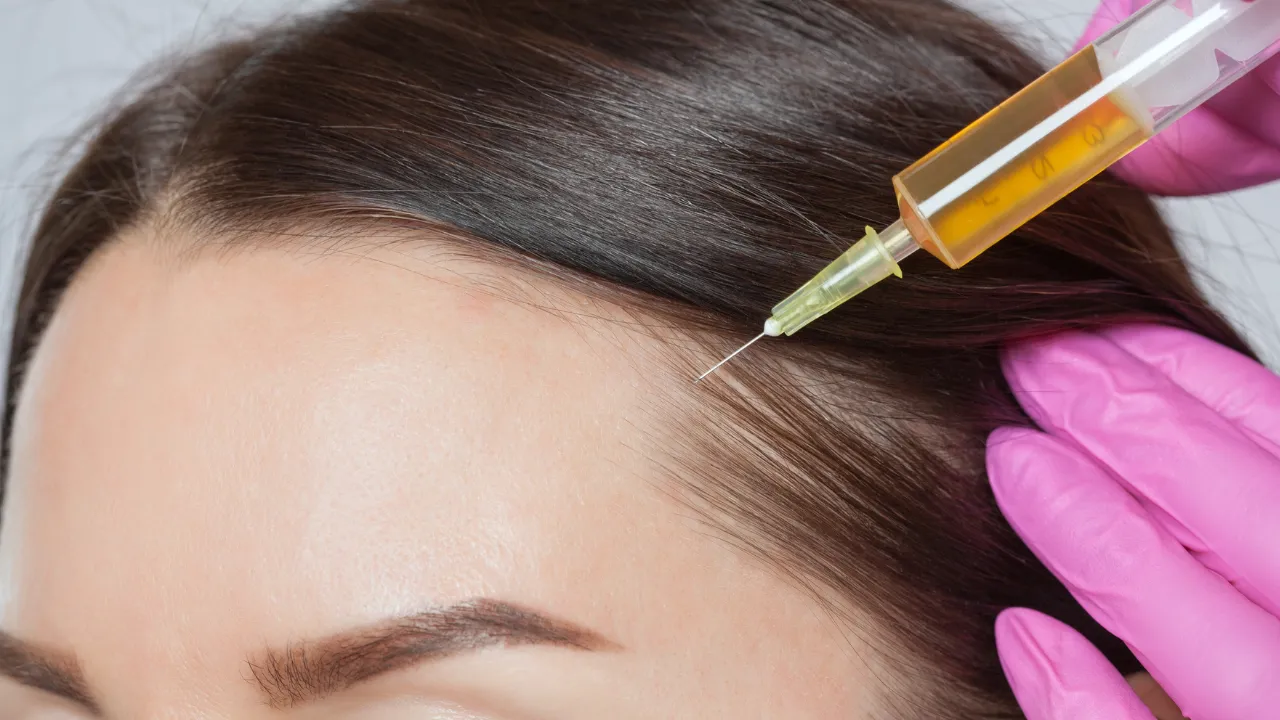
Medical treatments for female hair loss after menopause
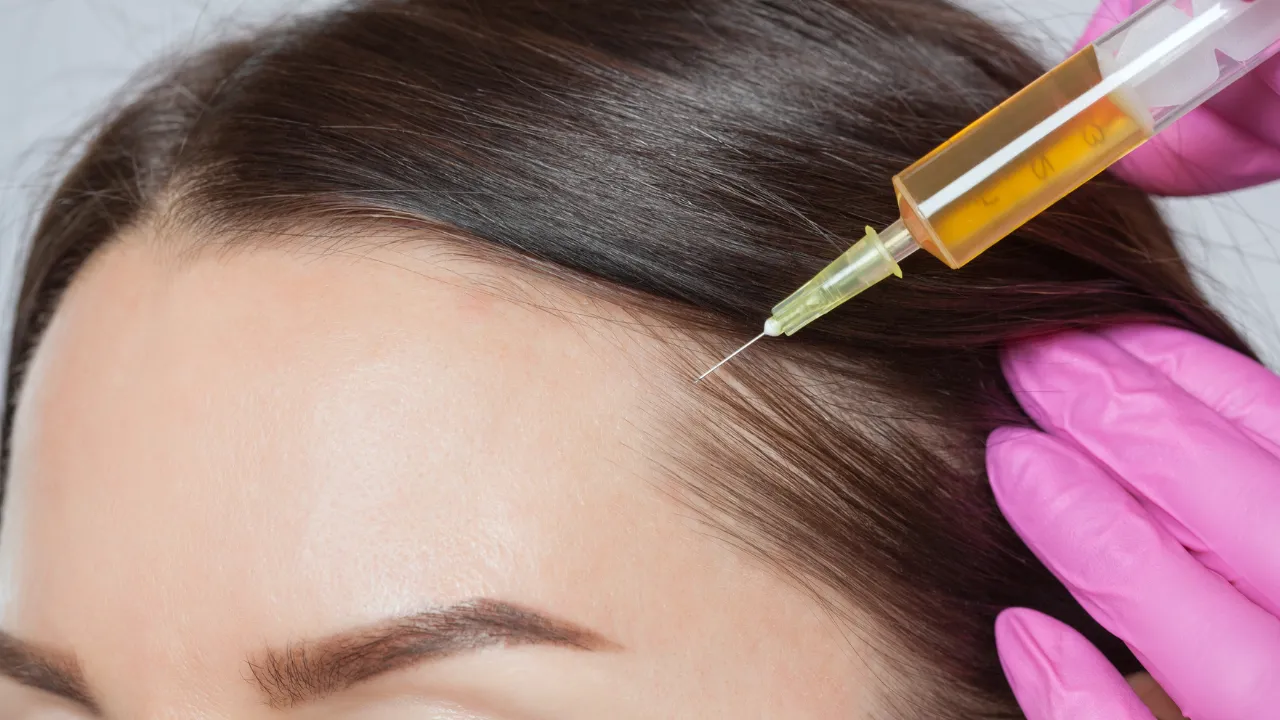
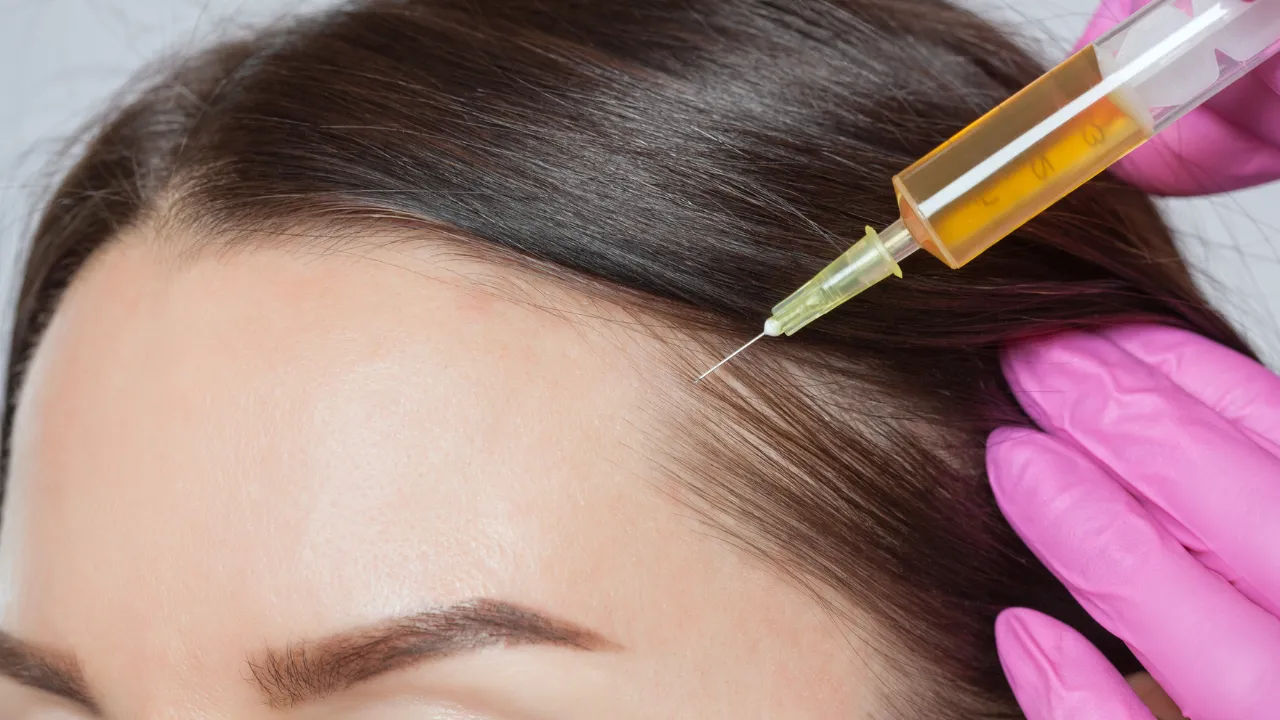
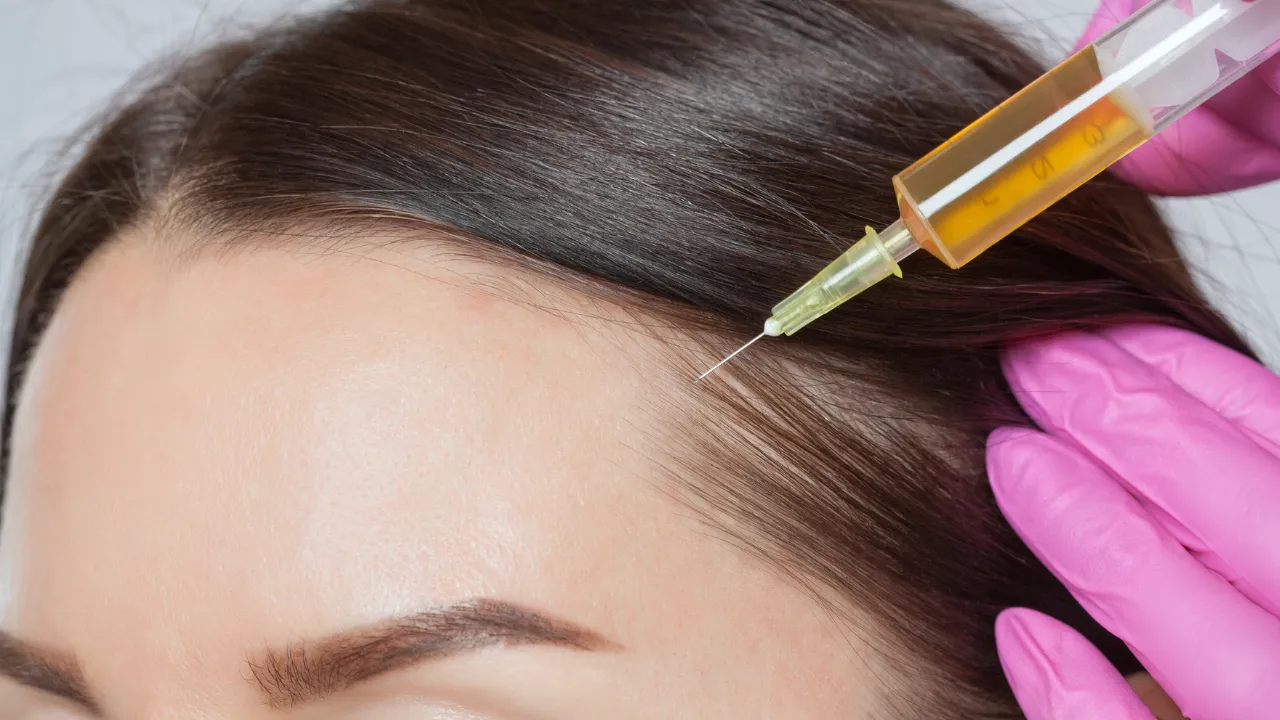
Topical minoxidil, low-level laser therapy, and hormone therapy are common. At Kopelman Hair, Dr. Kopelman may recommend PRP therapy or, for advanced cases, a hair transplant. Each plan is based on the patient’s health and needs.
Minoxidil boosts blood flow to follicles, while PRP delivers growth factors to the scalp. Hormone therapy can help balance estrogen and androgens when appropriate.
Possible side effects:
- Minoxidil: mild scalp irritation or facial hair growth
- PRP: temporary soreness at injection sites
- Hormone therapy: health risks requiring close monitoring
Best products for menopausal hair loss
Specialized shampoos, conditioners, and leave-in treatments with biotin, caffeine, or ketoconazole may help maintain healthy hair.
Best shampoo for thinning hair due to menopause
Choose sulfate-free formulas enriched with strengthening compounds. While shampoo alone cannot reverse hair loss, it can create a better scalp environment to promote hair growth.
Home remedies for menopause hair loss
Gentle handling, reduced heat styling, and scalp massage can help. Some menopause hair loss remedies include natural oils or herbal rinses, though results vary. Combining home care with professional treatments offers the best results.
Key treatment tips:
- Address hormone changes medically
- Combine treatments with healthy habits
- Use gentle, nourishing hair products
- Avoid tight hairstyles and heat damage
Patient Experience at Kopelman Hair
One woman in her early 50s came to Dr. Kopelman after a year of thinning hair in menopause. Her plan combined PRP therapy, nutrition changes, and a topical solution. Within six months, shedding decreased and volume improved, showing targeted care can reverse hair loss in some cases.
Nutrition and Supplements for Hair Health
Vitamins for hair loss in menopause
Biotin, vitamin D, and B-complex support hair health. Low levels can contribute to shedding and slower regrowth.
Which vitamin deficiency causes hair loss
Iron deficiency is a leading cause of female hair loss after menopause. Zinc and vitamin D deficiencies also affect follicle health. Correcting deficiencies can stimulate hair growth and maintain healthy hair.
Diet and lifestyle tips for prevention
Balanced meals, hydration, stress control, and enough sleep help reduce the risks associated with menopause and thinning hair.
Regrowth Expectations
Will hair loss from menopause grow back?
If follicles remain active, treatments can promote regrowth. Early treatment improves results.
Is menopausal hair loss permanent?
Some thinning may be permanent if follicles shrink beyond repair, making early evaluation vital to discuss all treatment options.
Factors that affect regrowth
Genetics, age, hormone balance, and health play a role. Consistent treatment and lifestyle changes can improve outcomes.
Realistic timelines for recovery
Improvements may appear in 3–6 months, with full results in up to 12 months.
Self-Assessment Checklist
See a doctor if you notice hair changes such as:
Tip: Check any signs you’re experiencing to track changes over time.
Seek urgent care for sudden loss, scalp pain, redness, sores, or systemic symptoms like weight loss or fatigue.
When to See a Doctor
What is the blood test for hair loss
Tests may check thyroid function, iron, vitamin D, and hormone levels to find treatable causes and guide treatment options.
Evaluating treatment results and expectations
Follow-ups track progress and adjust plans. Dr. Kopelman works closely with patients to refine their treatment for the best outcome.
FAQ about Hair Loss Due to Menopause
How do you treat menopause hair loss?
Will hair grow back after menopause?
Is menopausal hair loss reversible?
Does diet alone stop hair loss?
How long should I use treatment before seeing results?
Take the Next Step
If you are experiencing hair loss due to menopause, early action can make a real difference. Schedule a consultation with Dr. Kopelman and the team at Kopelman Hair to receive a personalized assessment and treatment plan designed to protect and restore your hair.