Table of Contents
ToggleHair loss behind the ears can seem minor at first but often signals deeper follicle or scalp problems. It may result from tension, poor circulation, hormonal changes, or inflammation that weakens the surrounding area. Early evaluation helps prevent spreading and supports faster recovery.
At Kopelman Hair, specialists identify the exact causes and design custom treatments to restore density and balance. With over 40 years of experience, Dr. Ross Kopelman combines advanced medical techniques with surgical artistry to help patients regain strong, healthy hair and lasting confidence.
Key Takeaways
- Hair loss behind the ears may result from genetics, traction, or scalp inflammation.
- Retrograde alopecia is a common pattern that starts at the sides or nape instead of the temples.
- Inflammation, friction, and hormonal imbalance can weaken follicles and slow growth.
- Early diagnosis through scalp imaging and medical evaluation improves treatment outcomes.
- Targeted therapies such as PRP, medication, and FUE restore balance and long-term density.
Why Hair Loss Behind the Ears Happens
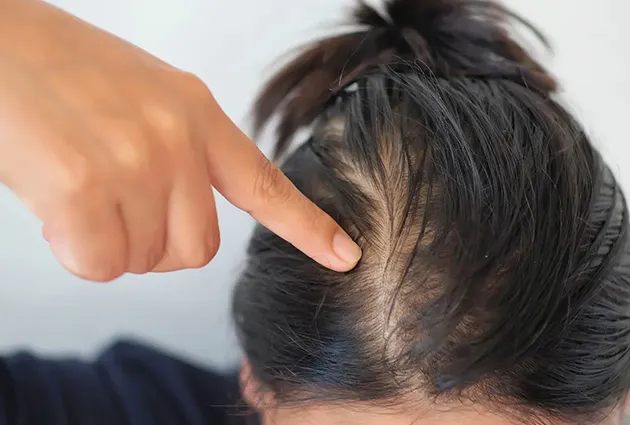
Hair thinning or patchy loss behind the ears is less common than crown or frontal loss, but it can still spread if untreated. The follicles in this area are delicate and react quickly to hormonal shifts, tension, or irritation.
A frequent pattern is retrograde alopecia, where the hairline recedes upward from the neckline or sides. Because it develops slowly, many notice it only once the scalp becomes visible. Early medical care prevents progression and supports healthy regrowth.
Main Reasons for Hair Loss Behind the Ears
Several underlying conditions can weaken follicles and lead to loss near the ears. Identifying the cause ensures proper care and recovery.
1. Retrograde Alopecia
A variation of genetic hair loss that starts along the lower scalp and sides. Sensitivity to DHT (dihydrotestosterone) causes follicles to shrink, producing thinner strands until growth stops.
2. Traction and Friction
Repeated pulling from tight hairstyles, headbands, or mask straps irritates follicles and leads to thinning. Constant tension may eventually cause permanent damage.
3. Scalp Conditions
Dermatitis, psoriasis, or fungal infections inflame the scalp and disrupt circulation. Chronic inflammation shortens the growth phase and damages follicle roots.
4. Autoimmune or Hormonal Disorders
Alopecia areata, lupus, or thyroid imbalance can cause smooth, circular bald patches behind the ears. Medical evaluation is necessary to prevent recurrence.
5. Nutrient Deficiencies and Poor Circulation
Low levels of iron, zinc, or vitamin D weaken follicles. Reduced blood flow also limits the nutrients needed for new hair growth.
Recognizing Early Signs
Early symptoms include thinning strands, visible scalp patches, or increased shedding when brushing. Some people experience redness or itching before visible loss.
At Kopelman Hair, high-resolution scalp imaging helps detect these changes early, allowing for targeted, minimally invasive treatment.
Understanding the Pattern of Hair Loss
Hair loss behind the ears usually follows a distinct pattern. In retrograde alopecia, thinning progresses symmetrically along the sides or nape.
It can occur alongside androgenetic alopecia but advances more slowly. Without treatment, affected follicles shrink and stop producing strong hair. A precise diagnosis ensures effective intervention.
When to Seek Medical Advice
You should see a specialist if:
- Patches or thinning appear near the ears
- Shedding continues for months
- Itching, redness, or flaking develops
- Family history suggests hereditary or autoimmune hair loss
Prompt diagnosis prevents irreversible damage and improves recovery potential
Diagnosis at Kopelman Hair
A detailed consultation and scalp evaluation determine the exact cause of loss.
Scalp Analysis and Imaging
Advanced magnification allows Dr. Ross Kopelman to study follicle health, density, and inflammation.
Medical History Review
Lifestyle factors, stress, medications, and hormonal fluctuations are examined for contributing patterns.
Scalp Biopsy
In more complex cases, a biopsy clarifies whether hair loss is autoimmune, hormonal, or scarring in nature. Findings guide safe, personalized treatment planning.
Treatment Options for Hair Loss Behind the Ears
Once the cause is known, treatment focuses on restoring hair strength, repairing follicles, and preventing recurrence.
1. Medical Therapies
Topical Medications: Minoxidil reactivates dormant follicles.
- Oral Treatments: Finasteride lowers DHT and slows shrinkage in men.
- Anti-Inflammatory Formulas: Medicated shampoos and topical steroids soothe irritation and promote healing.
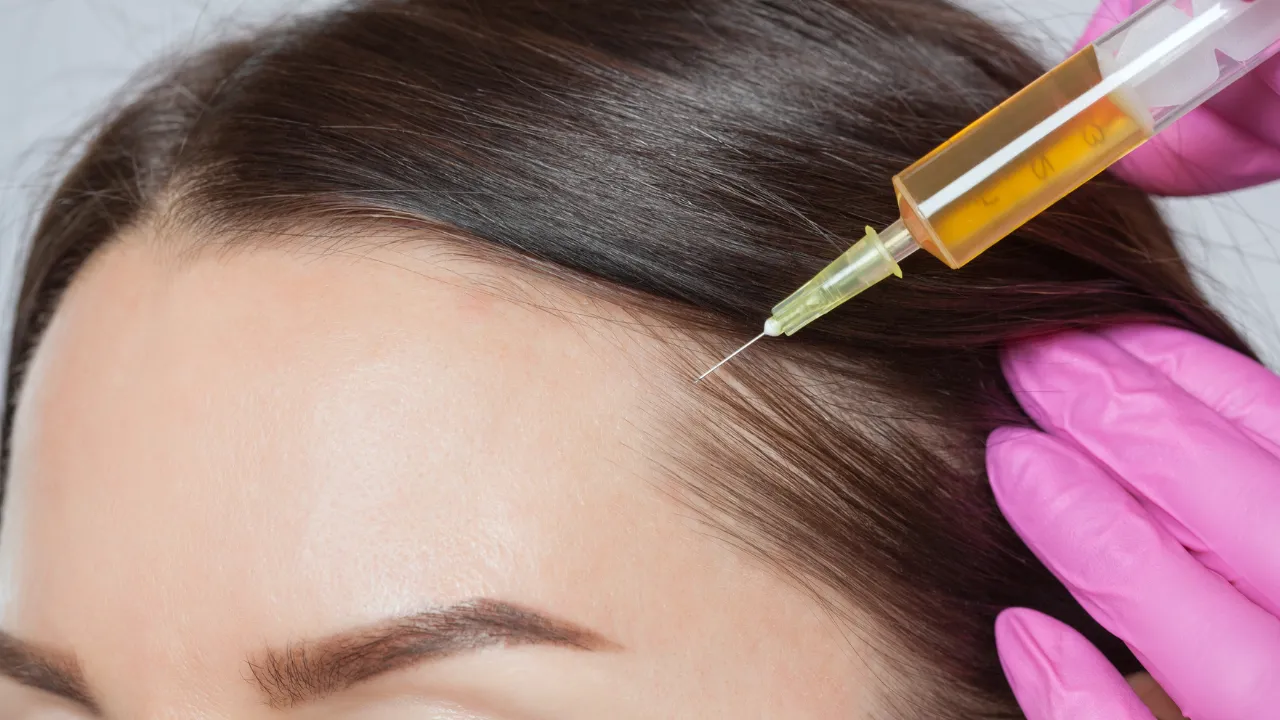
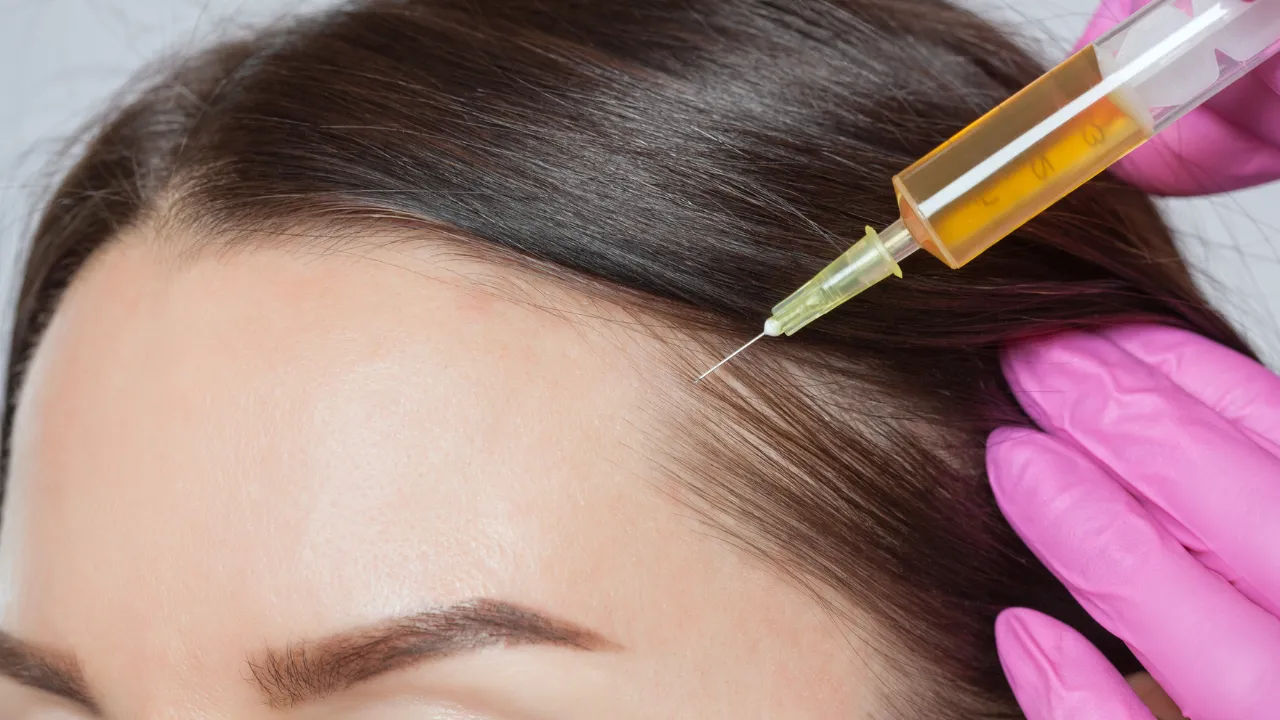
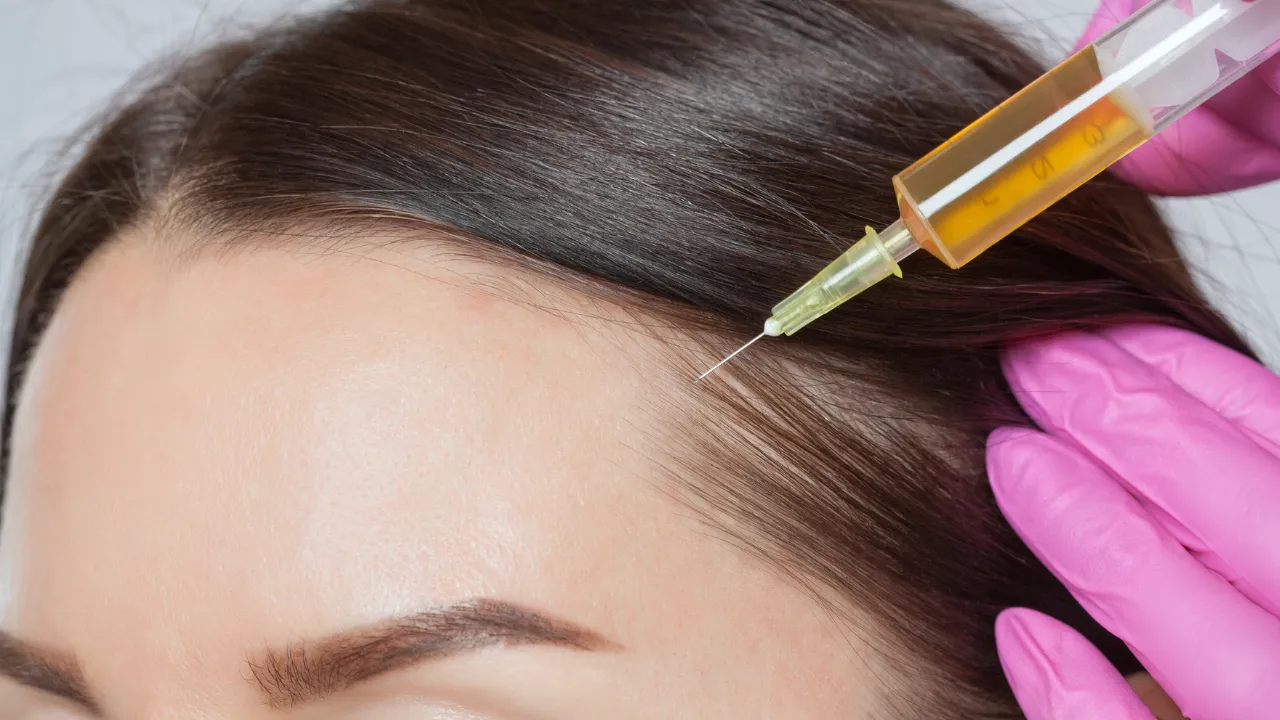
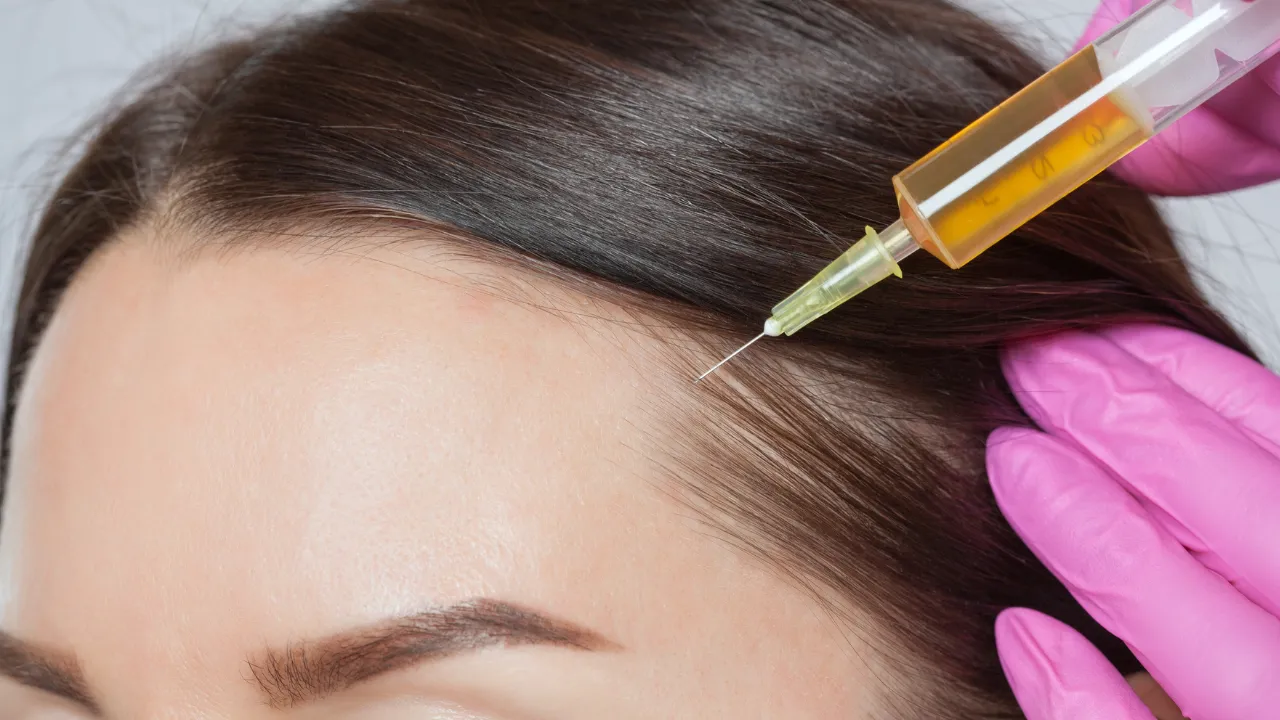
2. Regenerative Treatments
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP): Growth factors from the patient’s own blood stimulate repair and renewal.
- Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT): Red-light devices improve circulation and cellular activity.
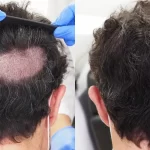
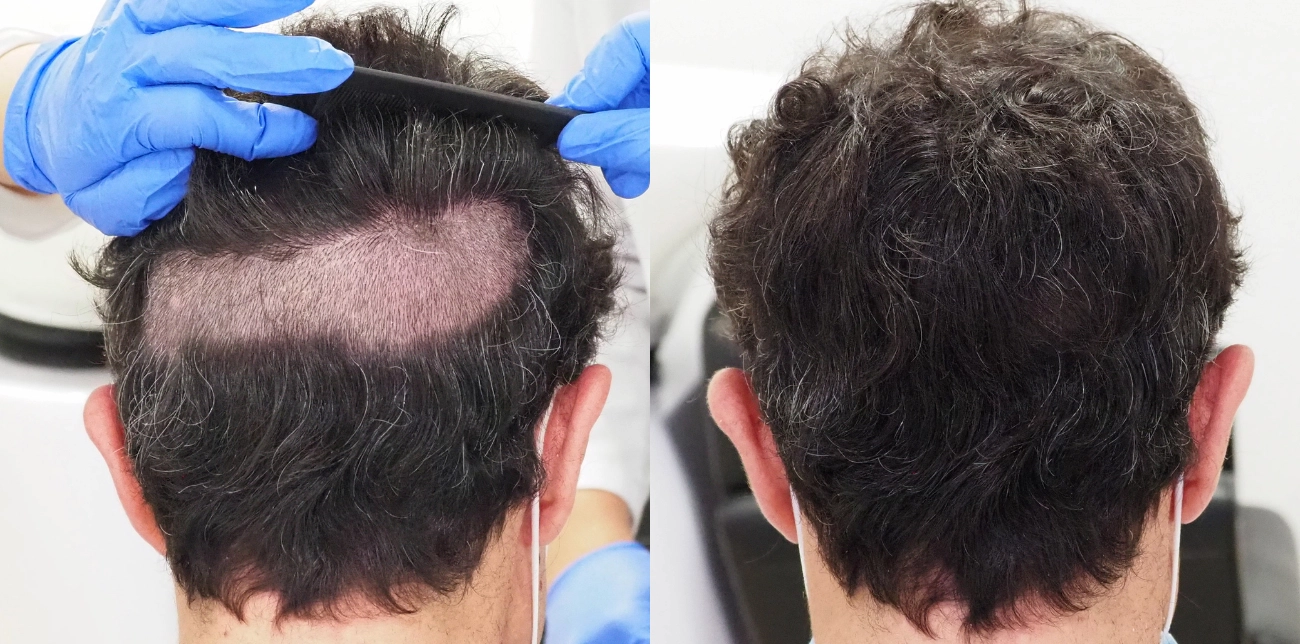
3. FUE Hair Transplant Surgery
When follicles are permanently damaged, Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) offers lasting results. Dr. Ross Kopelmanensures the scalp is stable before surgery, protecting grafts and achieving natural regrowth.
Autoimmune Causes of Patchy Hair Loss
Autoimmune diseases like lupus or alopecia areata can cause sudden, recurring loss behind the ears. The immune system mistakenly attacks healthy follicles, leading to patchy baldness.
At Kopelman Hair, treatments may include corticosteroid injections, topical immunotherapy, or regenerative approaches that restore immune balance and encourage natural regrowth.
Maintaining Healthy Hair Through Lifestyle
Daily care supports medical treatments and protects follicles from new damage.
Practical steps include:
- Use gentle, sulfate-free shampoos.
- Eat foods rich in protein, omega-3s, and vitamins.
- Stay hydrated and manage stress.
- Avoid tight hairstyles or accessories near the ears.
- Massage the scalp to enhance circulation.
Consistent care keeps follicles healthy and prevents recurring loss.
Hair Loss Behind the Ears in Women
Women may experience patchy thinning behind the ears from traction, hormonal changes, or scalp irritation. While men often see defined bald spots, women usually experience diffuse thinning.
For female patients, Dr. Ross Kopelman recommends non-invasive options such as PRP, nutritional optimization, and topical therapy. Because female follicles often stay active, early care helps restore full growth and density.
The Importance of Early Treatment
Treating early signs of hair loss yields better outcomes. Ignoring irritation or thinning allows follicle shrinkage to worsen.
At Kopelman Hair, early diagnosis helps protect active follicles and speed recovery. Using dermoscopy and biopsy data, Dr. Ross Kopelman tailors every treatment plan for precise, lasting improvement.
Recent Research and Innovations
Modern studies confirm that chronic inflammation, DHT sensitivity, and poor blood flow are key drivers of localized hair loss.
Emerging treatments include:
- Exosome Therapy: Repairs and rejuvenates follicles at the cellular level.
- Stem Cell Growth Factors: Stimulate dormant follicles and encourage regeneration.
- Enhanced FUE Technology: Improves graft survival and density for more natural coverage.
These innovations allow safer, faster restoration with minimal downtime.
Expert Oversight and Lasting Results
With decades of expertise, Kopelman Hair continues to lead in medical and surgical hair restoration. Dr. Ross Kopelman combines precision, artistry, and compassionate care to achieve natural, permanent outcomes for each patient.
Final Thoughts
If you’ve noticed patchy thinning or shedding behind your ears, act early. Kopelman Hair offers comprehensive diagnostic testing and tailored treatments designed to restore scalp health and hair density. With expert evaluation, evidence-based care, and consistent follow-up, patients can regain strong, natural-looking hair and lasting confidence.