Table of Contents
ToggleHair loss is a common concern for many men, especially those with a family history of balding. You might notice early changes like a wider part, slower growth, or a thinning hairline and wonder what they mean for your future. These small shifts can feel worrying, but they also give you a valuable chance to act early and protect your hair long term.
At Kopelman Hair, specialists help patients understand their genetic risk, recognize early signs, and start effective treatments to keep their hair strong and healthy. With over 40 years of experience, Dr. Ross Kopelman and his team use modern diagnostics and treatments to manage hereditary baldness with care and accuracy.
Key Takeaways
- Baldness depends on genetics, hormones, and daily habits.
- The main cause is hereditary baldness related to DHT sensitivity.
- Early signs of balding often show at the temples or crown.
- Starting treatment early can slow or stop hair loss.
- A professional diagnosis helps preserve hair and prevent future thinning.
Understanding Male Pattern Baldness
What Causes Men to Go Bald
Most men lose hair because of androgenetic alopecia, also called male pattern baldness. This genetic condition happens when hair follicles react to dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone made from testosterone. Over time, DHT makes follicles smaller, producing finer hair until growth stops.
Genes are the biggest factor, but stress, poor nutrition, and smoking can make thinning worse. Research from Vox and The Wimpole Clinic shows that men with relatives who went bald are much more likely to follow the same pattern.
How Common Is It
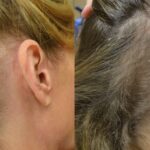
About two-thirds of men notice thinning by age 35, and around 85% have visible baldness by age 50. Hair usually starts receding at the temples before thinning appears on the crown. Catching these changes early helps prevent further loss.
The Genetics Behind Baldness
The Hereditary Component
Hereditary baldness passes through genes that control how sensitive hair follicles are to hormones. Many think baldness comes only from the mother’s side, but both parents’ genes play a role. The AR gene, found on the X chromosome, affects how follicles react to DHT.
If your close relatives went bald early, you are more likely to experience the same. Knowing your family’s history can help you prepare and take preventive steps sooner.
Predicting Risk
Online tools like the Alpecin Baldness Calculator estimate the likelihood of future baldness based on family history and current thinning. These are not medical tests, but they give a general idea of what to expect.
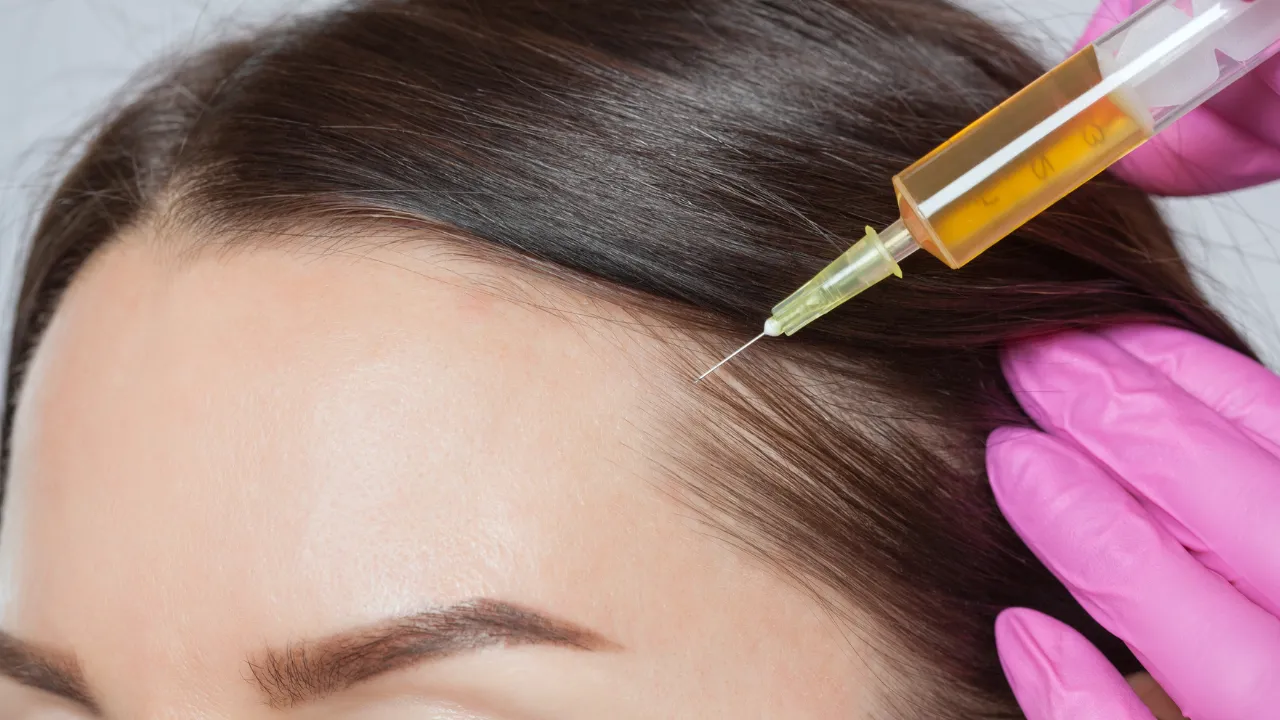
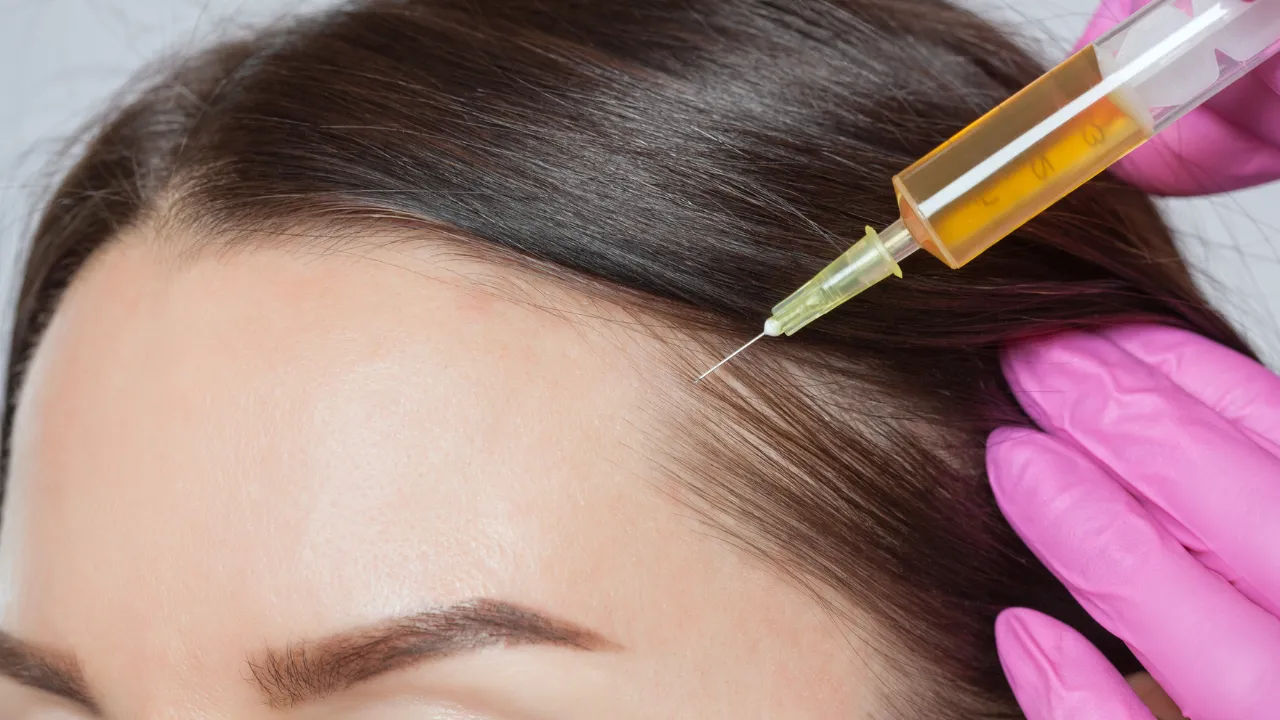
At Kopelman Hair, specialists use imaging, trichoscopy, and lab testing to detect hair miniaturization early. Spotting these changes before they’re visible helps protect existing follicles.
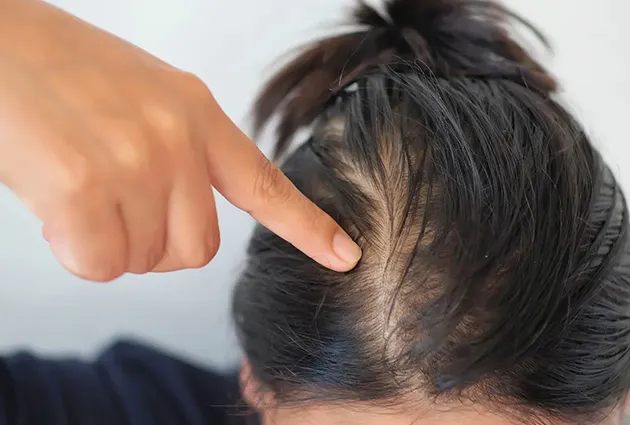
Early Signs of Balding
What to Watch For
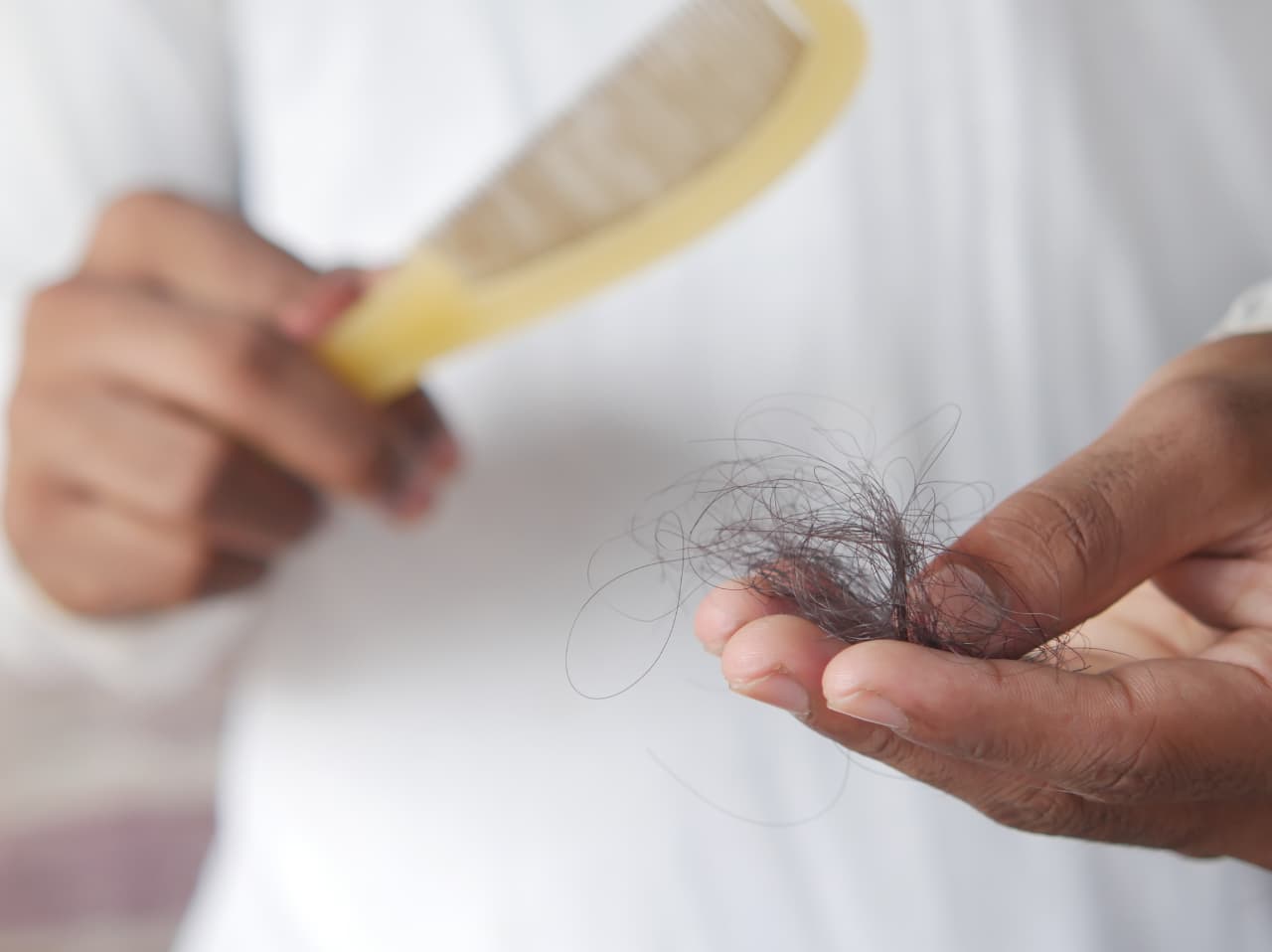
Early signs of balding are often subtle. You may see a receding hairline or notice more shedding while showering or brushing. The hairline can start forming an “M” shape, and thinning usually appears on the crown or temples.
Other warning signs include:
- Extra hair on pillows or in drains
- A wider part line
- Less volume or density
- Slower regrowth after cutting
Once follicles shrink too much, regrowth becomes difficult. Paying attention early allows for effective treatment.
The Role of DHT
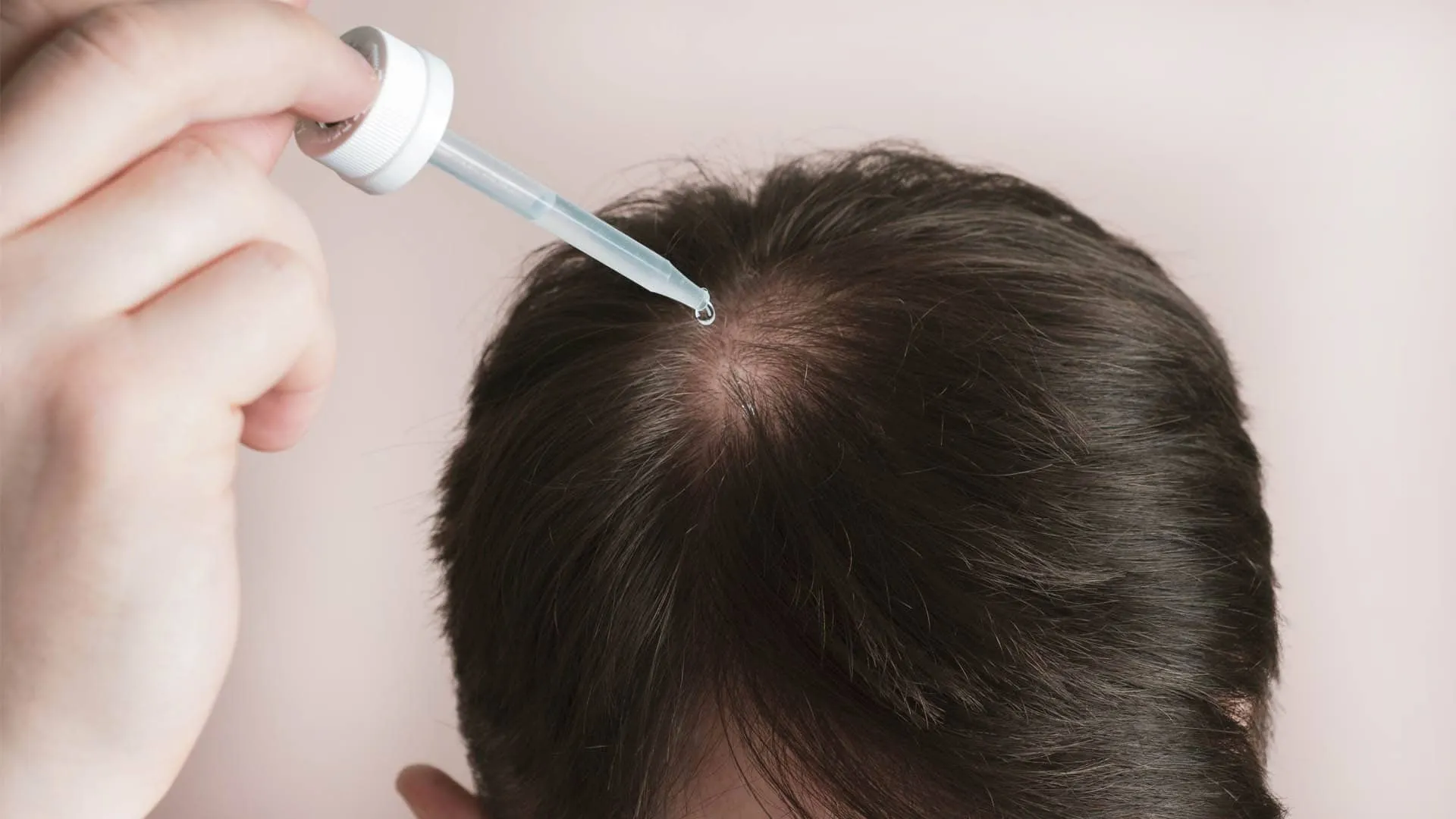
Hair receding often begins when DHT attaches to follicles, shortening the growth phase. Over time, the strands become finer and stop growing. Medications that lower or block DHT, such as Finasteride or topical solutions, can help slow this process.
Can You Tell If You’ll Go Bald?
Family History as a Predictor
If your father, grandfather, or uncles went bald, you may share the same tendency. Hereditary baldness usually follows a pattern starting at the temples and crown.
But not everyone with a genetic risk loses all their hair. Hormones, scalp condition, and lifestyle choices can change how fast or how much you lose.
Diagnostic Methods
Modern diagnostics make predicting baldness more accurate. Doctors often use:
Trichoscopy – magnified imaging to see shrinking follicles.
Scalp mapping – measures the number of active and resting follicles.
Blood tests – check hormones and nutrients linked to hair growth.
These tools reveal whether thinning is genetic or caused by other conditions. With the right information, treatment can be planned precisely.
Why Balding Happens at Different Ages
- Teens and Early 20s
Some men notice hair loss before age 25 because of strong sensitivity to DHT. This form of balding is rare but can progress quickly if not treated.
- 30s and 40s
This is the most common time for thinning to begin. Stress, lack of sleep, and poor diet can speed it up. Regular scalp care and early treatments make a big difference at this stage.
- After 50
By age 50, most men have visible thinning or bald spots. Consistent care can still protect remaining hair and improve its look and strength.
Can Baldness Be Prevented?
Lifestyle Factors That Influence Hair Health
You can’t change your genes, but you can protect your hair through healthy habits:
- Eat a balanced diet rich in protein, iron, zinc, and biotin.
- Quit smoking and limit alcohol use.
- Manage stress with regular exercise or relaxation techniques.
- Get enough sleep to support hormone balance.
These choices keep follicles strong and slow down the effects of hereditary baldness.
Early Medical Intervention
The sooner treatment begins, the better the results. Common options include:
- Minoxidil: Improves circulation and helps follicles grow longer.
- Finasteride: Lowers DHT levels to prevent shrinking follicles.
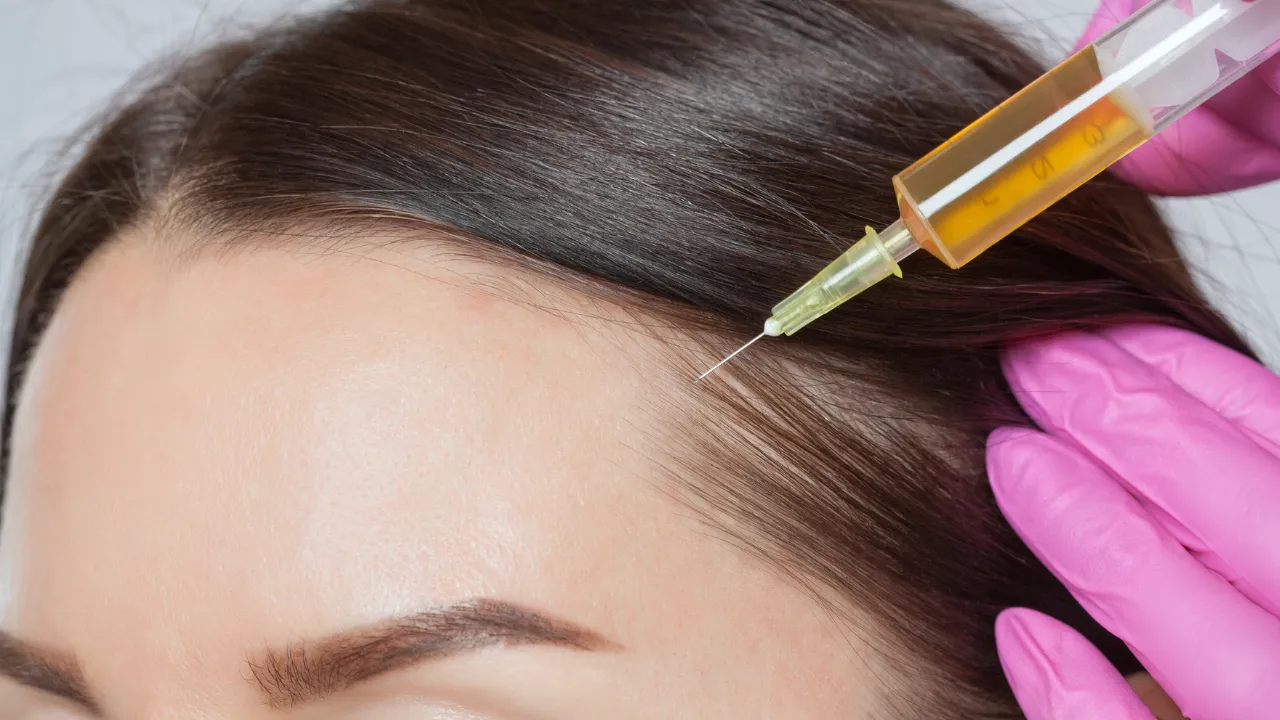
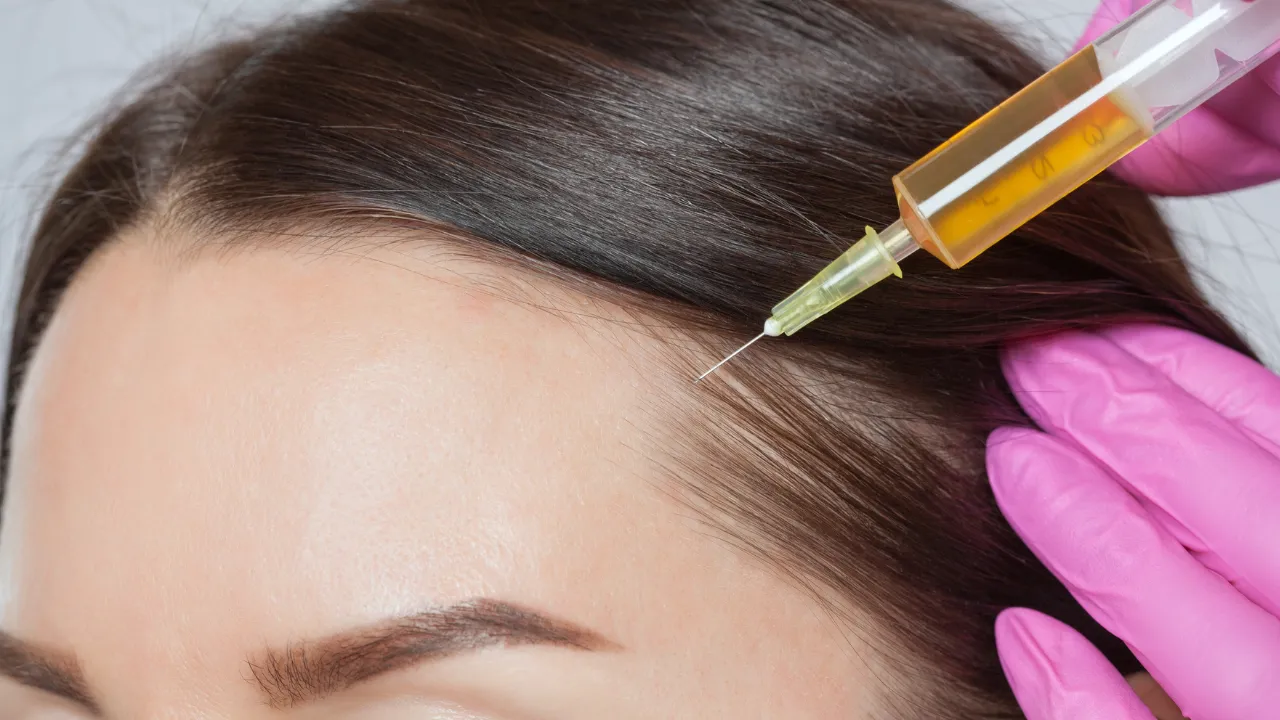
- PRP Therapy: Uses your blood’s growth factors to stimulate new hair.
- Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT): Improves scalp circulation and strengthens follicles.
Combining these treatments can improve results and maintain long-term growth.
Hair Transplantation for Genetic Baldness
Modern Techniques
Hair transplantation restores density by moving healthy follicles from the back or sides of the scalp to thinning areas. Modern Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) techniques create natural results without visible scars.
Most patients recover quickly and notice new growth within three to six months.
Who Is a Candidate
The best candidates have steady hair loss and enough donor hair. A full evaluation helps determine suitability and design a personalized plan for optimal results.
Emotional and Psychological Impact
Hair loss can affect how men feel about themselves. Many connect hair with youth and confidence, so losing it can be frustrating.
Education and support make the process easier. Today’s treatments let men keep a natural look and feel comfortable at any stage.
At Kopelman Hair, patients receive not only treatment but also guidance and long-term care to help them feel confident and supported.
When to See a Specialist
Schedule an appointment if you notice:
- Quick or excessive thinning
- A receding hairline before age 25
- Patchy loss or irritation
- Family history of early baldness
The earlier you act, the better your results. Delaying treatment can lead to permanent follicle loss.
Long-Term Outlook
Baldness develops slowly, but consistent treatment helps control it. Starting care early keeps follicles active longer. Many men maintain a fuller head of hair well into later life with the right routine.
Follow-up visits ensure your treatment continues to work. Combining medical solutions with healthy habits offers the best protection against long-term thinning.
Final Advice
Genetics may influence whether you go bald, but you still have control. Knowing your risk, spotting early signs, and getting treatment early can help you keep your hair longer.
Kopelman Hair combines advanced technology, medical care, and surgical expertise to deliver natural, lasting results. Whether you notice minor thinning or clear hereditary baldness, timely evaluation and personalized care can protect your appearance and confidence for years to come.