Table of Contents
ToggleAt Kopelman Hair, we often hear patients ask about the difference between hair thinning vs balding. Understanding this distinction is key to choosing the right solution. With over 40 years of experience, our team focuses on diagnosing each case accurately to guide you toward effective treatment.
Key Takeaways
- Hair thinning and balding are distinct—thinning reduces density, while balding causes defined, often permanent patches.
- The hair growth cycle and follicle health play a critical role in both conditions.
- Stress, styling, hormones, and family history are common triggers of different types of hair loss.
- Treatment ranges from lifestyle changes and medication to surgical solutions like hair transplants.
Key Differences Between Hair Thinning and Balding
Thinning hair often results from environmental or lifestyle factors. You may still have full coverage, but strands are finer or fewer. Balding leads to permanent gaps, especially along the temples or crown.
Balding vs Thinning: Patterns and Signs
Balding typically follows a genetic pattern, starting at specific spots. Thinning appears more evenly. The difference between balding and thinning lies in visibility and permanency.
Hair Thinning but Not Falling Out
Thinner-looking hair without shedding often signals early-stage changes in the hair growth cycle. It’s not always a sign of balding, especially when follicles are still active.
Difference Between Thin Hair and Balding
Having naturally fine hair differs from balding. Thinning refers to a change in density, while balding is a form of permanent hair loss.
Both involve the hair follicle, but balding typically means the follicle has shrunk or stopped producing hair.
How Lifestyle Affects Hair Loss
Every day habits significantly influence whether you retain or lose hair. Poor hair care, diet, or stress can cause thinning.
Common causes of hair loss include:
- Overuse of heat tools
- Tight hairstyles (traction alopecia)
- Smoking and sleep deprivation
- Chronic stress
When hair falls excessively, these habits are often a contributing factor.
Medical Causes of Thinning and Balding
Some types of hair loss are triggered by underlying conditions, not just age or genetics.
Key causes:
- Androgenetic alopecia (most common)
- Telogen effluvium (post-illness shedding)
- Thyroid or hormonal imbalance
- Autoimmune issues (e.g., alopecia areata)
- Nutritional deficiencies
- Certain medications
In some cases, a drug’s side effects can include temporary or permanent hair loss. A medical review helps clarify the cause.
Whether the issue is thinning or balding, Dr. Kopelman conducts a detailed review to recommend the right solution.
Hair Thinning vs Hair Loss
Understanding the distinction between hair thinning vs hair loss helps guide proper treatment. Hair thinning may involve changes in volume or texture, while hair loss includes visible patches or severe shedding.
Thinning often reverses with improved hair care and nutrition. Hair loss from genetic or medical conditions may need more targeted intervention.
Normal Hair Shedding or a Problem?
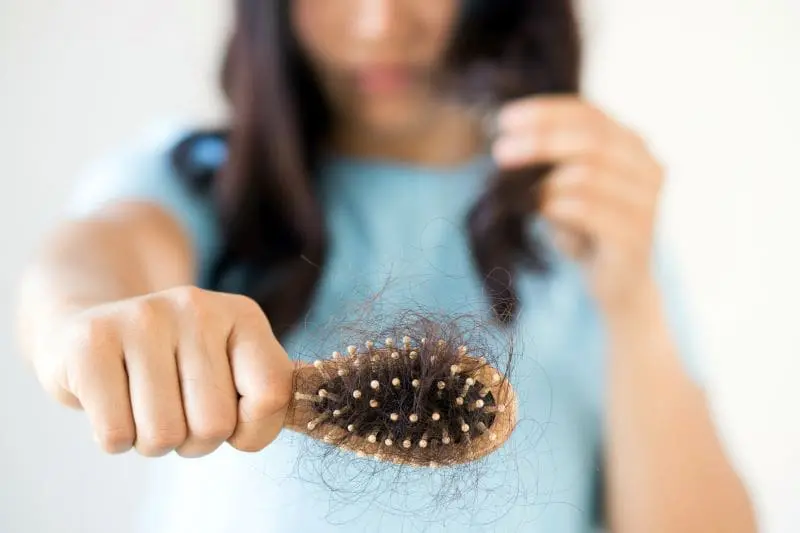
Shedding 50–100 strands per day is normal. Beyond that, you may be facing a deeper issue.
Shedding vs Permanent Loss
If your shedding lasts longer than a few months or leads to visible scalp, it may be time to seek help. Balding is usually permanent without treatment, while thinning can often be reversed.
Does Thinning Always Mean Balding?
Not necessarily. Many reversible factors cause thinning. Balding usually progresses unless addressed early.
Monitoring the amount of hairs you shed daily can help you detect changes early and take action.
Am I Balding or Just Thinning?
Clarity comes from tracking symptoms and changes over time.
Signs You Might Be Balding
- A receding hairline
- Bald spots or scalp visibility
- Thinner ponytail
- More hair in your brush or shower
If you’re noticing multiple signs, a consultation with Dr. Kopelman can help clarify the condition.
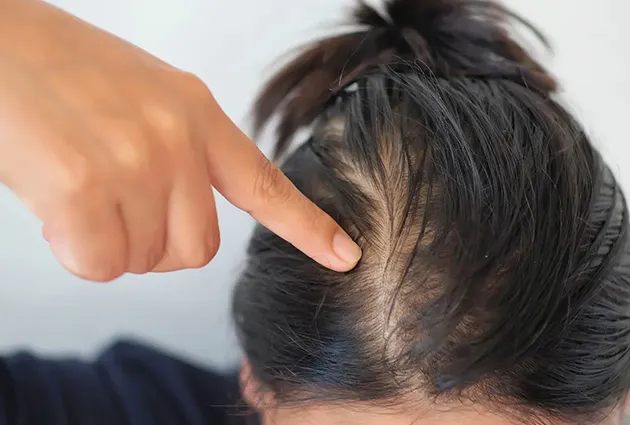
My Hair Is So Thin I Can See My Scalp
Scalp visibility doesn’t always mean balding. Fine hair naturally reveals more skin. But if it’s a new or worsening condition, seek evaluation.
Gender Differences in Hair Loss
Male Hair Thinning vs Balding
Men often lose hair in a defined pattern. Early signs include a receding line or thinning crown. Left untreated, thinning may become permanent.
Hair Thinning vs Balding in Females
Women usually see diffuse thinning rather than patches. Causes often involve iron levels, hormones, or post-partum changes.
How to Prevent Further Hair Loss
You can slow or prevent progression by adopting proactive habits.
Ways to help:
- Be gentle with your hair—avoid pulling or over-brushing
- Treat any underlying medical issues
- Improve nutrition and hydration
- Reduce daily stressors
- Consult a specialist early
These steps won’t cure all types, but they reduce long-term damage and promote hair growth.
Managing Anxiety About Hair Loss
Hair changes affect confidence. It’s normal to feel overwhelmed, especially if the cause isn’t obvious.
Dr. Kopelman’s team provides support and clear next steps to help patients regain control and peace of mind.
Can Thinning Hair Grow Back?
Regrowth Is Often Possible
When follicles are still active, treatments can restore density. Early care improves outcomes.
Key Influences
- Duration of the thinning
- Type and cause
- Age and scalp health
- Response to therapy
Dr. Kopelman customizes each plan to match your condition and goals.
Treatment Options
We offer solutions tailored to your specific type of hair loss, scalp condition, and long-term needs.
Non-Surgical Treatments
- Minoxidil or finasteride
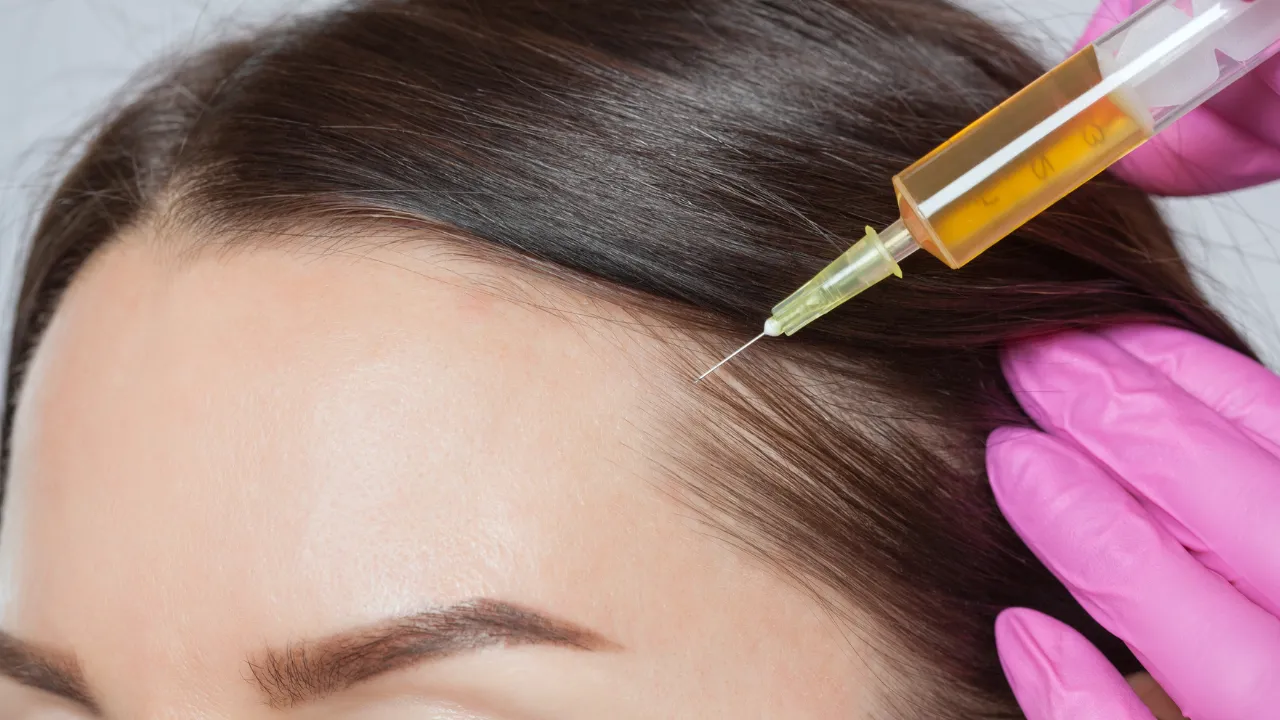
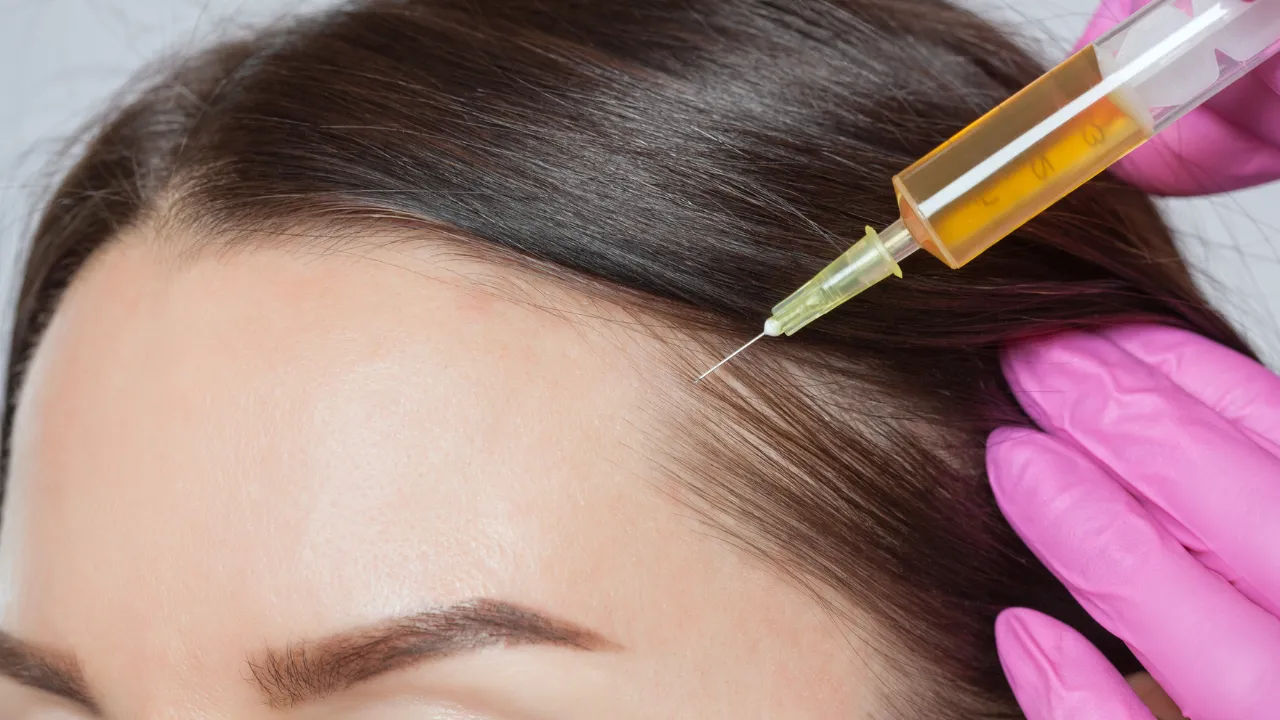
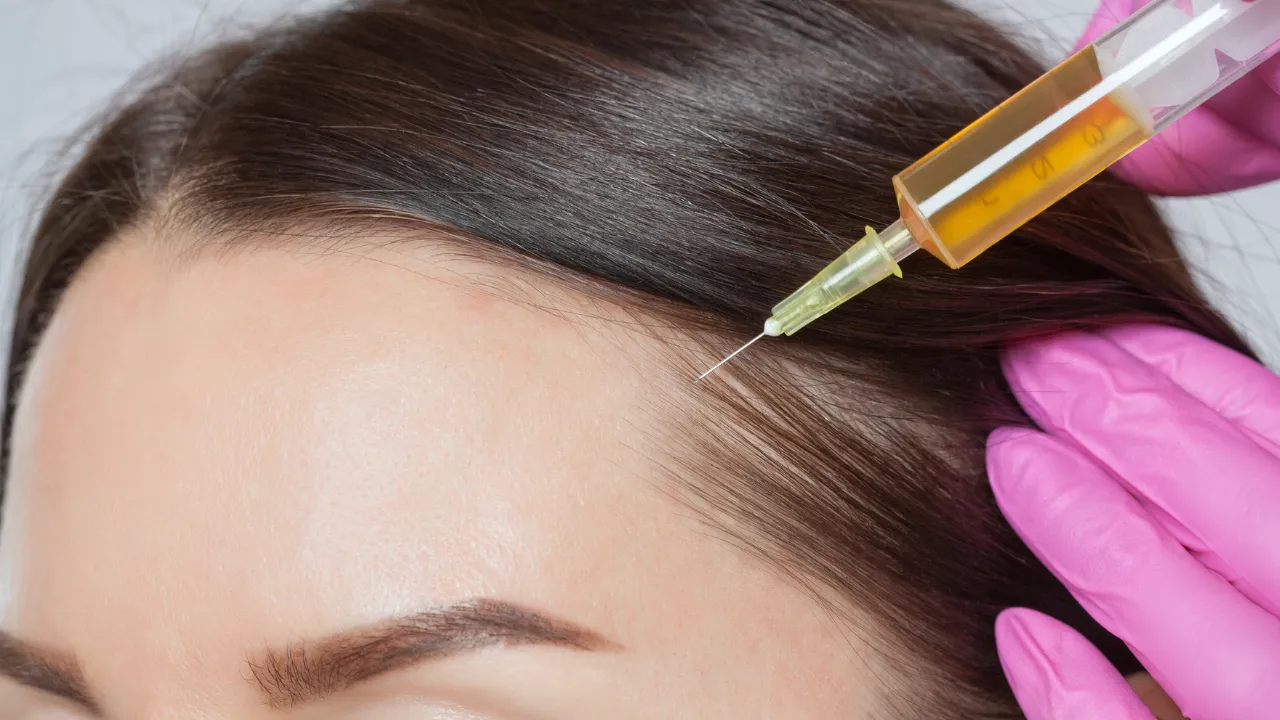
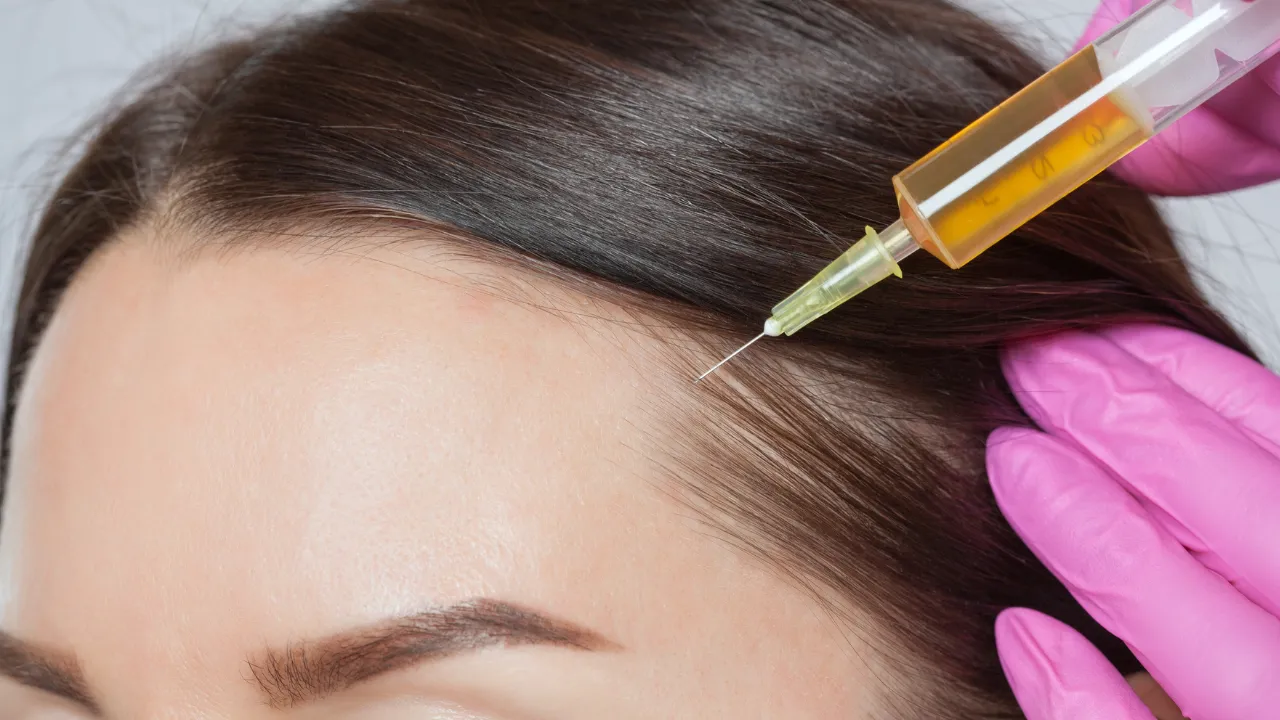
- PRP injections
- Laser stimulation
- Microneedling
- Supplements
Surgical Solutions
When nonsurgical efforts fail, transplant may be ideal. Dr. Kopelman uses FUE to restore natural density with minimal downtime.
Hair Thinning vs Balding: Quick Comparison
Ready to take the next step? Schedule a consultation with Dr. Kopelman today to receive a personalized evaluation and expert guidance tailored to your hair restoration needs.