Table of Contents
ToggleAt Kopelman Hair, we help patients understand the different types of alopecia and how they affect daily life. Understanding the forms of alopecia is the first step in finding causes, treatments, and rebuilding confidence.
Alopecia refers to several types of hair loss that happen in different patterns and for different reasons. The three main types are alopecia areata, androgenetic alopecia, and cicatricial alopecia. Each has its own causes, symptoms, and treatments that patients should know when seeking care.
Key Takeaways
- Alopecia includes many conditions that cause hair loss, with alopecia areata, androgenetic alopecia, and cicatricial alopecia as the main types.
- Men, women, and children can each experience different forms, so early diagnosis is crucial for proper treatment.
- Treatments range from medicines and injections to advanced hair transplant surgery by experts like Dr. Kopelman.
- Less common kinds of alopecia, such as central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia or telogen effluvium, also need medical care.
- Living with alopecia requires medical treatment and emotional support, with groups like the National Alopecia Areata Foundation (NAAF) and Alopecia UK offering guidance.
What Are the Three Main Types of Alopecia?
When people ask about the three main types of alopecia, they are looking for a straightforward answer. The most common forms are:
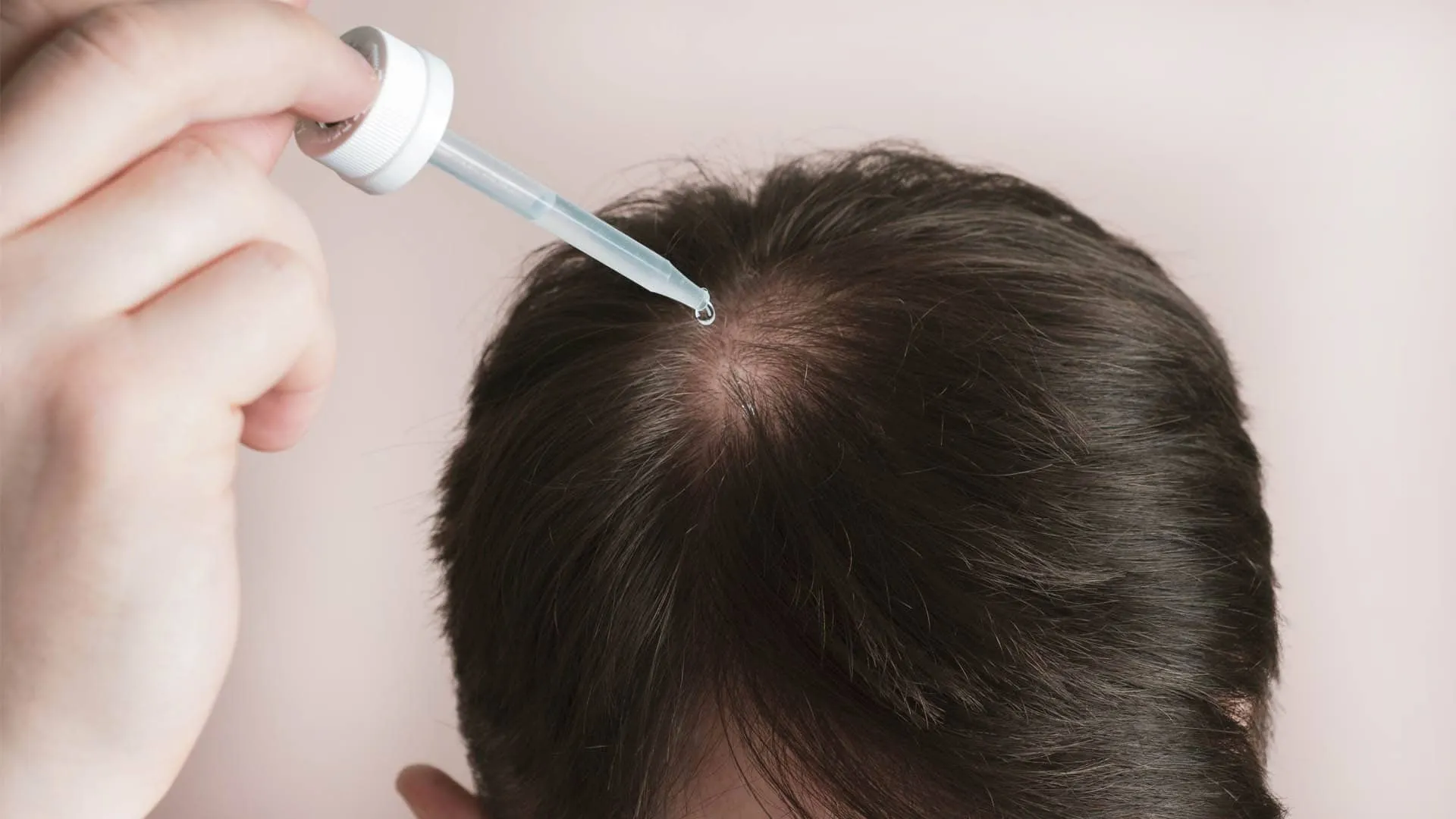
- Alopecia areata – patchy hair loss caused by an autoimmune condition.
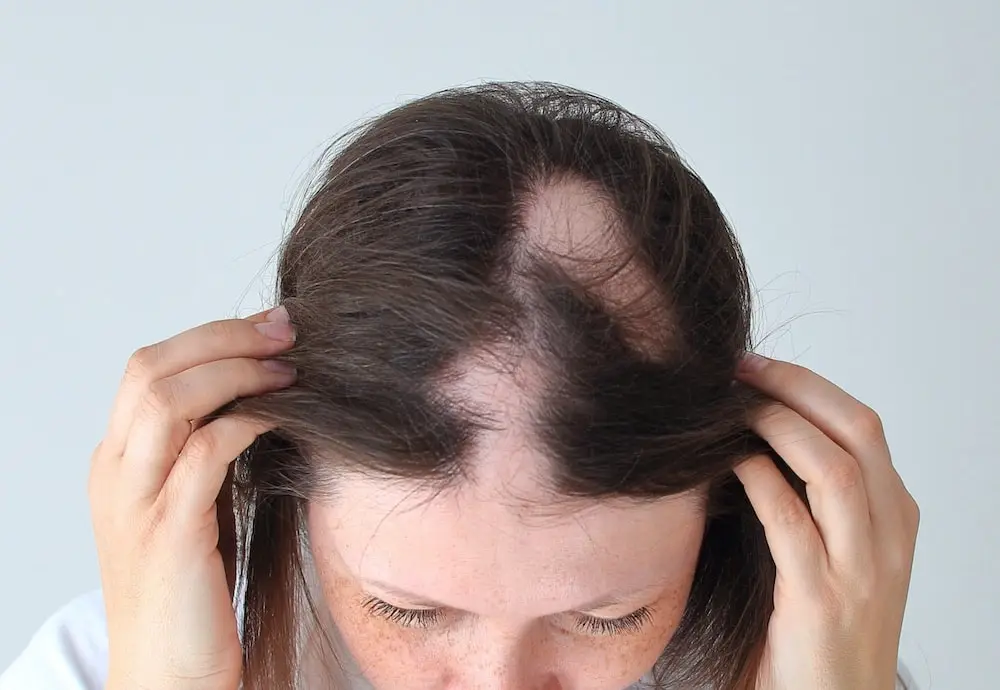
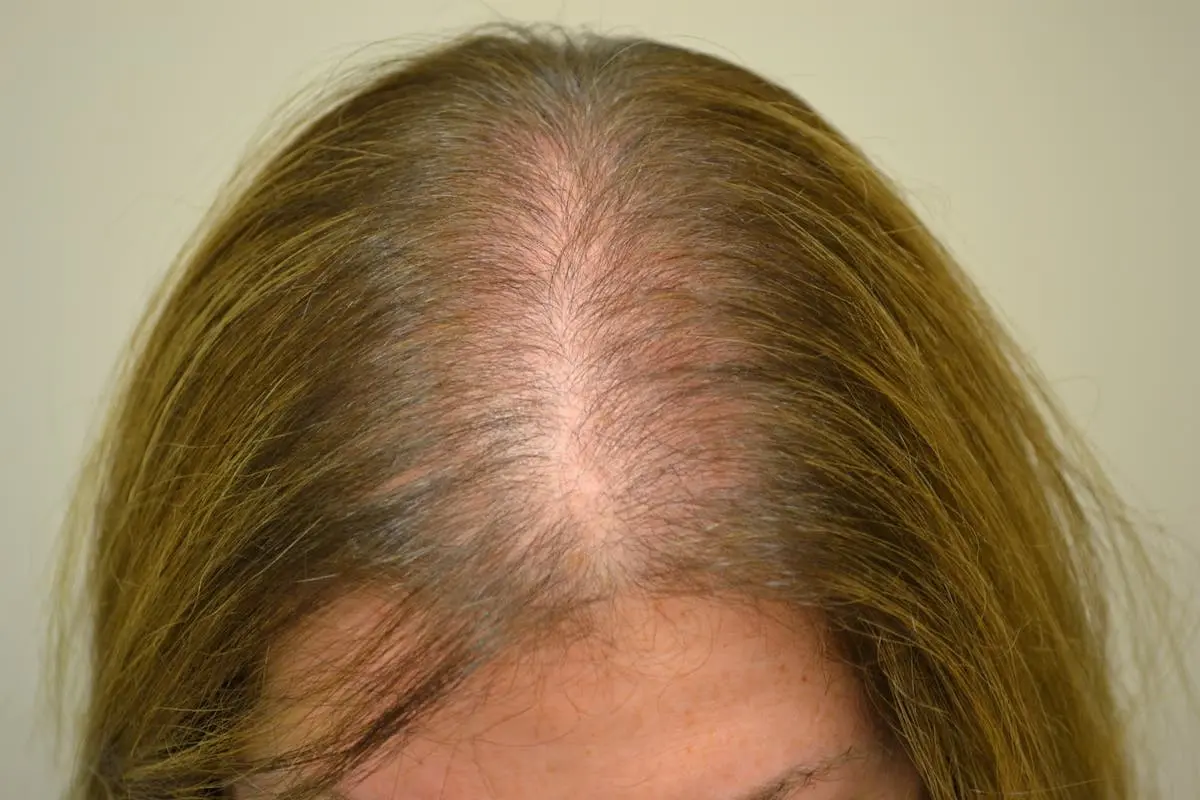
- Androgenetic alopecia – slow hair thinning, often called male or female pattern hair loss.
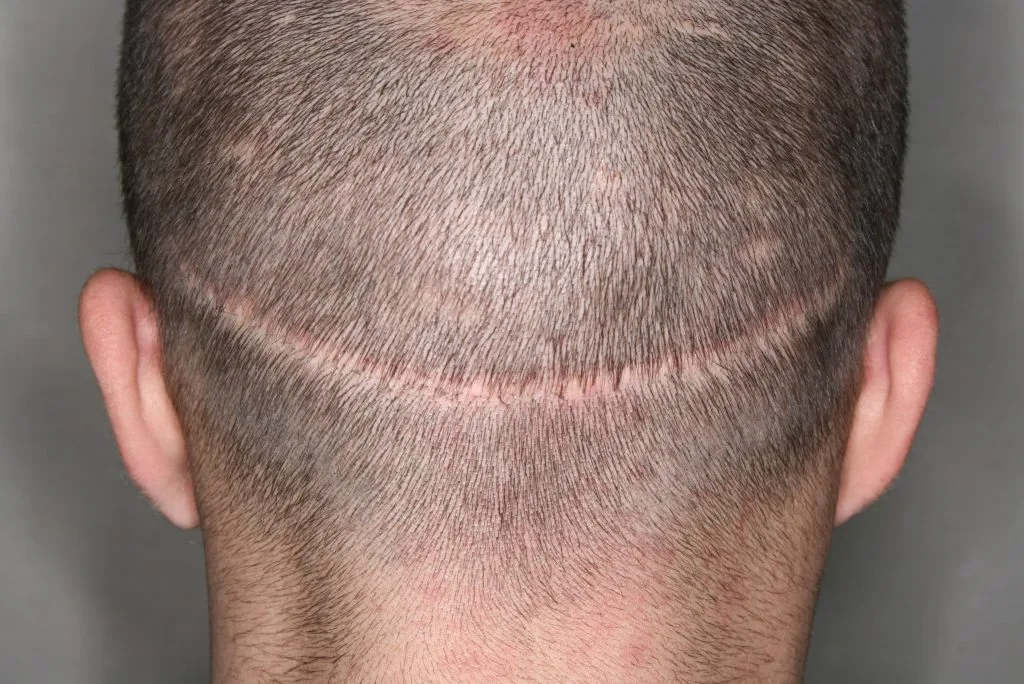
- Cicatricial alopecia – scarring hair loss that destroys hair follicles and leads to permanent hair loss.
These types are the main categories, but many variations exist. Knowing the difference helps patients recognize symptoms and seek help from a specialist, such as Dr. Kopelman.
Causes and Types of Alopecia
Hair loss happens for many reasons, from genes to immune problems. Understanding both causes and the types of alopecia helps patients choose the right treatment. You can learn more about the main alopecia causes in this detailed guide.
Types of Alopecia Areata
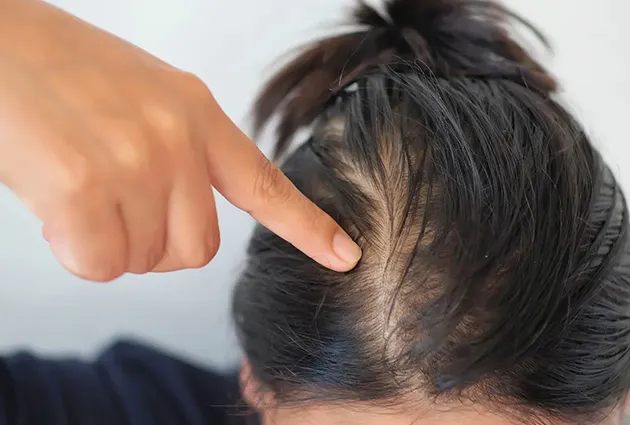
Alopecia areata develops when the immune system attacks hair follicles. It may appear as small bald spots. In severe cases, it can become alopecia totalis (complete hair loss on the scalp) or universalis (all body hair). Stress and family history can also play a role.
Types of Alopecia Hair Loss
Not all alopecia is linked to the immune system. Androgenetic alopecia alopecia areata telogen effluvium are examples of different causes. Androgenetic alopecia is linked to hormones and genes. Traction alopecia comes from repeated pulling of the hair. These forms of alopecia include conditions that develop slowly but can impact quality of life.
Additional Types of Alopecia
Some less common types are important to know. They may not affect as many people, but they matter for a correct diagnosis.
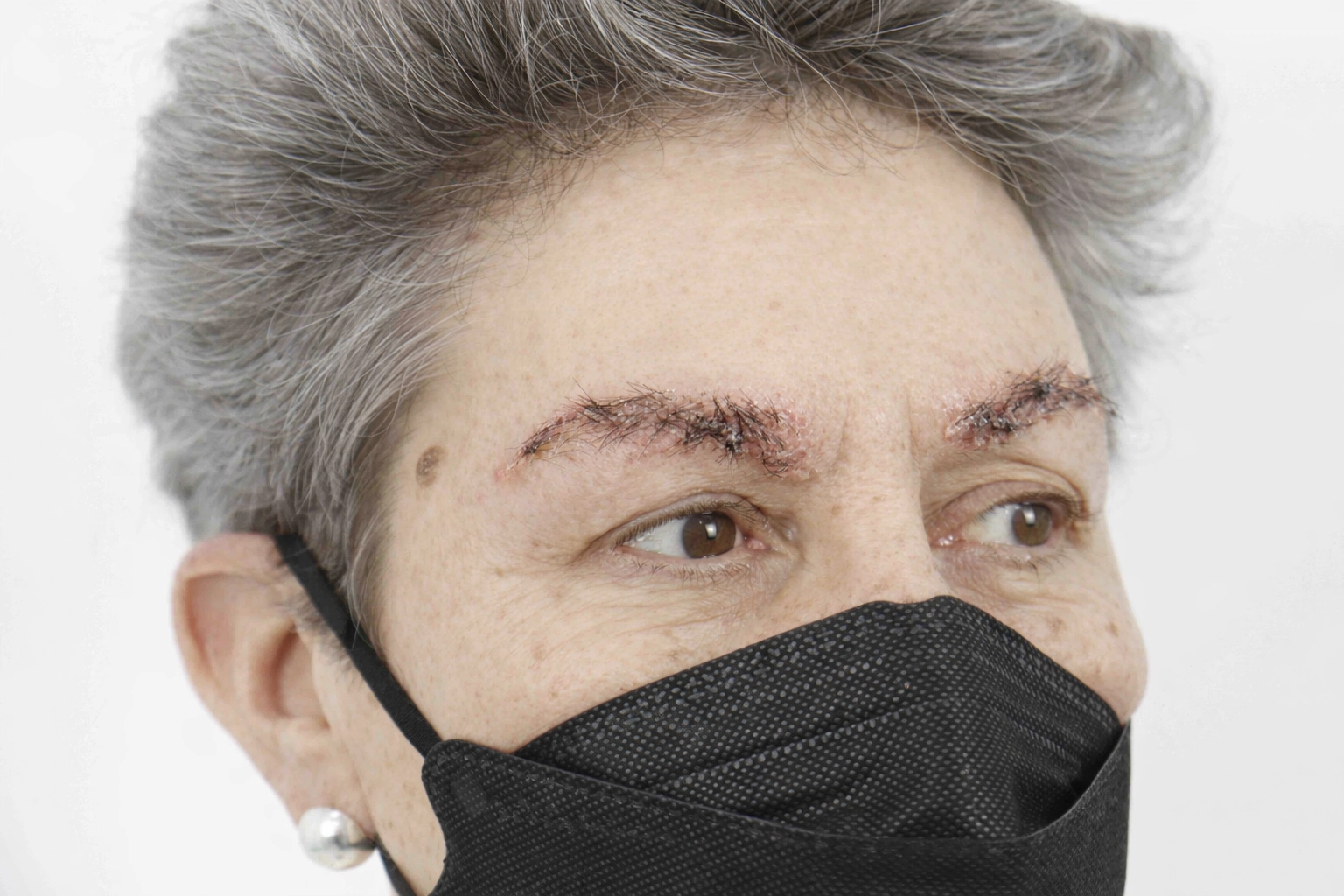
- Frontal fibrosing alopecia – scarring alopecia that pushes back the hairline, often in older women.
- Telogen effluvium – sudden shedding after stress, illness, or hormone changes. Patients can view real-life examples in these pictures of telogen effluvium for better understanding.
- Anagen effluvium – fast hair loss from chemotherapy or toxins.
- Ophiasis pattern alopecia areata – hair loss in a band around the scalp edges.
- Central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia – starts at the crown and often affects women of African descent.
Other scarring conditions, such as lichen planopilaris and discoid lupus erythematosus, also cause lasting damage. These scarring types of alopecia include cases where the follicle is destroyed and hair does not grow back.
Other Forms of Alopecia
Other forms include cicatricial alopecia, which scars the scalp, and telogen effluvium, where stress or illness pushes hair into the shedding stage. Each needs a correct diagnosis for safe care.
Medical Guidelines and References
The American Academy of Dermatology divides alopecia into scarring and non-scarring types. The Mayo Clinic and the NHS also note that alopecia areata, androgenetic alopecia, and cicatricial alopecia are the main categories.
Kopelman Hair adheres to these medical guidelines to ensure that treatments are safe and effective.
Alopecia in Women, Men, and Children
Hair loss looks different across groups. Men, women, and children can each have unique patterns and causes.
Types of Alopecia in Women
Women often notice hair thinning across the scalp instead of bald spots. Female pattern hair loss is the most common type, showing as a wider part line. Hormones, pregnancy, or thyroid issues can also trigger hair loss in women.
Types of Alopecia in Men
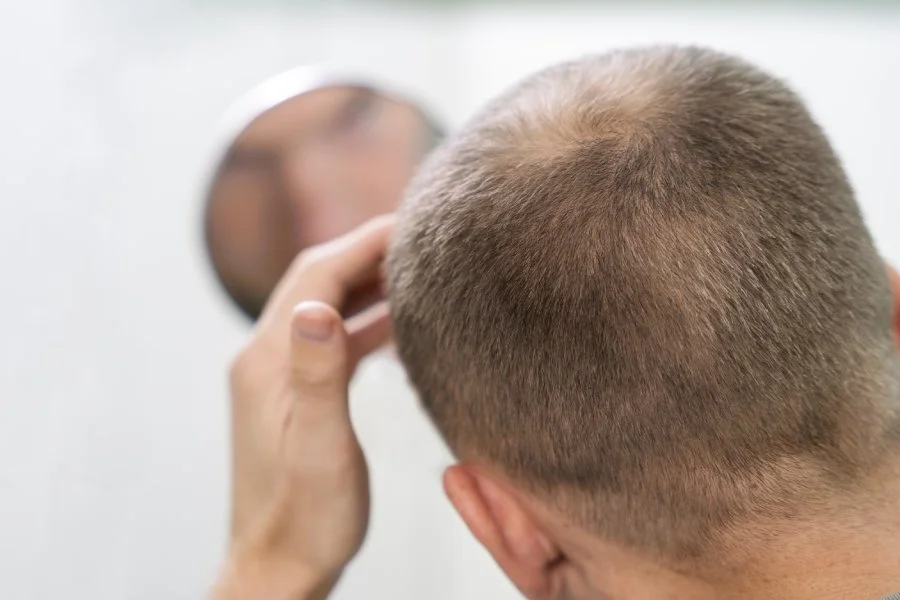
Men often have androgenetic alopecia, also called male pattern baldness. It begins with a receding hairline or thinning crown. Genes play a strong role, and without treatment, hair loss often continues over time.
Types of Alopecia in Children
Children can develop alopecia areata, which causes sudden bald patches. Infections like tinea capitis may also cause hair loss. Prompt treatment is crucial for protecting health and maintaining confidence in young patients.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Spotting signs early helps treatment. Common symptoms include:
- Gradual or sudden hair thinning
- Patchy bald areas
- Extra shedding when brushing or washing
- Itchy or irritated scalp
Doctors diagnose by examining the scalp, reviewing health history, and sometimes using blood tests or biopsies. At Kopelman Hair, only trained physicians perform these steps for accurate results.
When to Seek Medical Advice
Patients should see a doctor if hair loss is sudden, patchy, or painful. Early help improves outcomes.
Useful first steps include writing down shedding patterns, noting stress or lifestyle changes, and avoiding new chemical treatments before diagnosis. These steps help doctors find the cause faster.
Treatment Options for Alopecia
Treatment depends on the type and how advanced it is. Each patient benefits from a plan tailored to their specific condition.
Medications
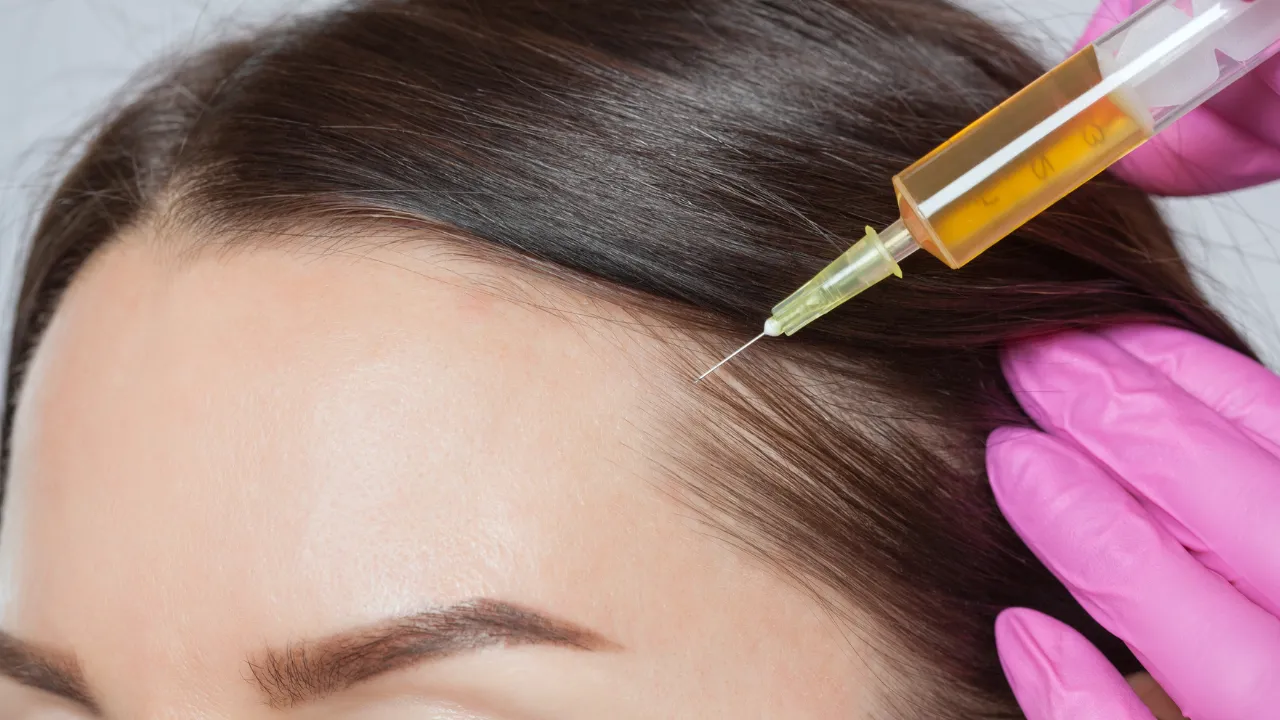
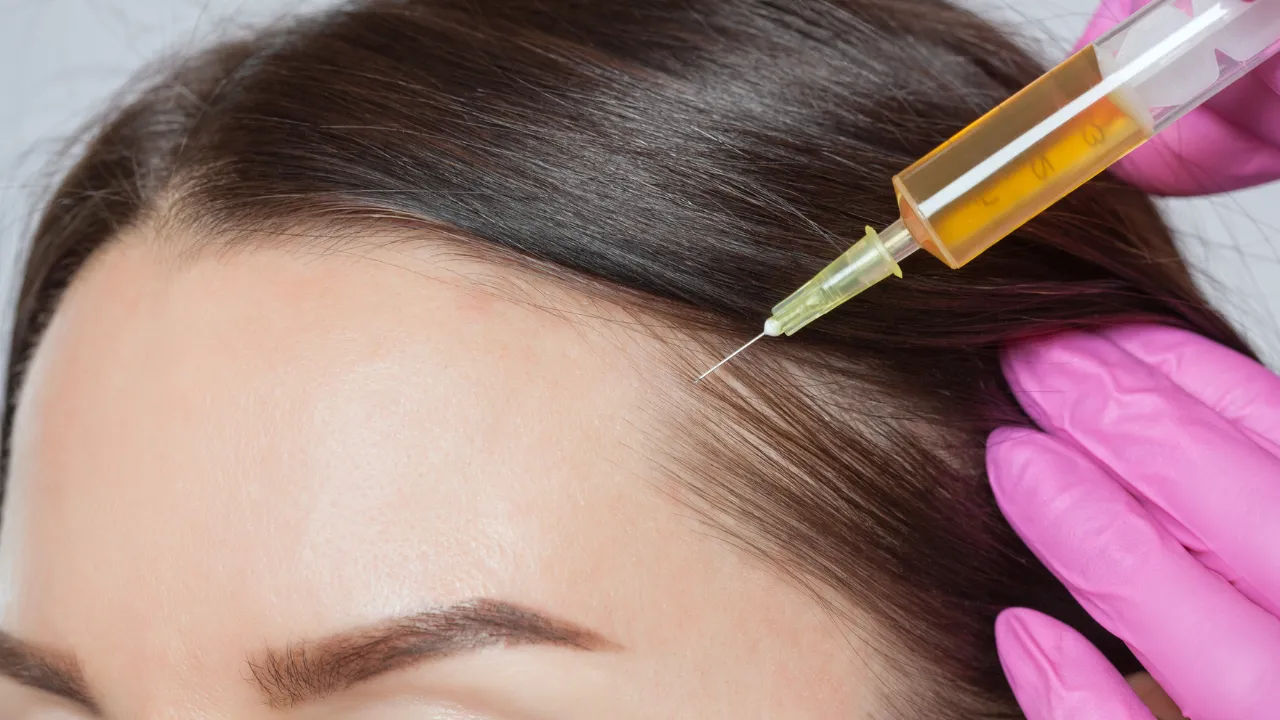
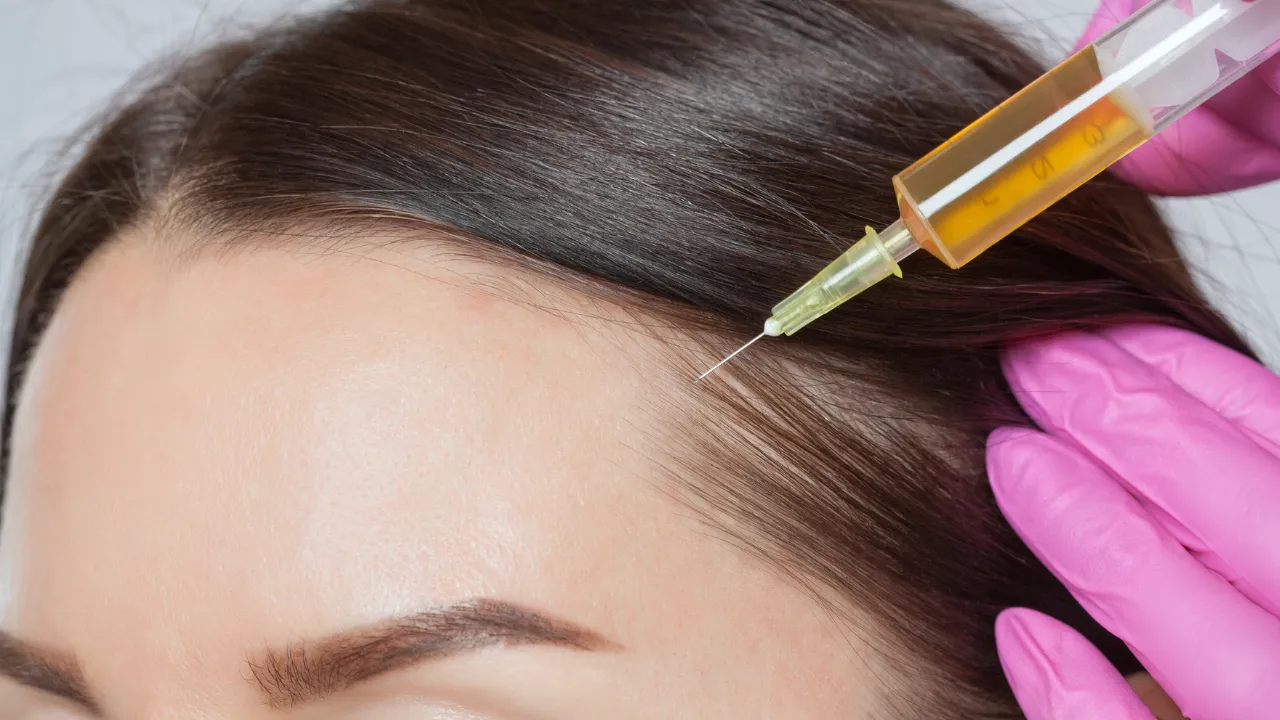
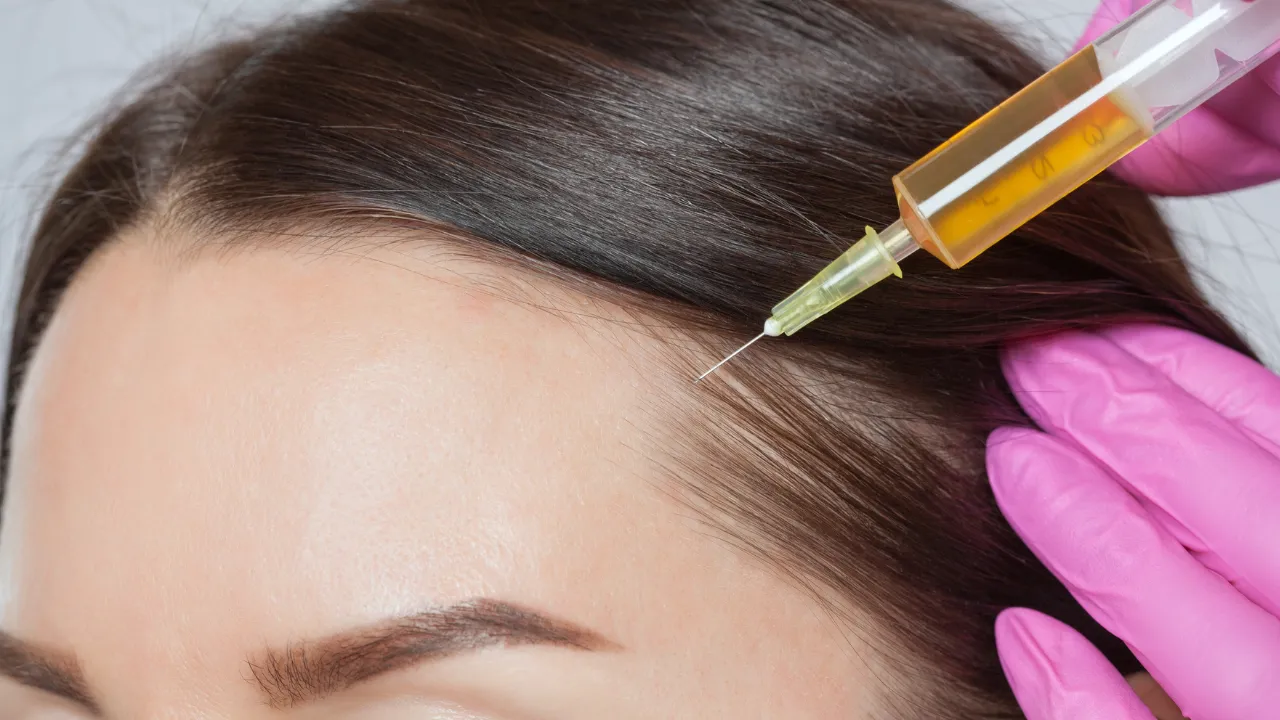
Minoxidil and finasteride are commonly used for androgenetic alopecia. Steroid injections may help with alopecia areata by calming the immune attack. Doctors decide which options are safe for each patient.
Hair Transplant Solutions
For stable hair loss, transplants can be a lasting solution. Dr. Kopelman has over 40 years of experience in advanced hair restoration. His methods provide natural results that restore confidence.
Lifestyle and Support Care
Good nutrition, stress control, and avoiding tight styles help protect hair. Counseling and support groups can also help with the emotional effects.
Treatments by Alopecia Type
- Alopecia areata – steroid injections or immune therapy.
- Androgenetic alopecia – medicines or hair transplants.
- Cicatricial alopecia – drugs to reduce inflammation.
These treatments match each condition and give patients the best chance of success.
Living with Different Kinds of Alopecia
Managing alopecia is more than just treatment. Many patients use wigs, concealers, or scalp micropigmentation. Emotional care is also crucial, as hair loss can significantly impact confidence and social interactions. By treating both the medical and emotional sides, outcomes improve.
Support and Resources for Patients
Patients often benefit from extra support. Groups and resources help people share experiences and find advice.
Trusted organizations such as the National Alopecia Areata Foundation (NAAF) and Alopecia UK offer guides, forums, and local support networks. These resources help with daily challenges and emotional health.
Highlight:
- Support groups can help alleviate feelings of isolation.
- Guides help patients understand treatment choices.
- Forums and helplines provide practical tips.
FAQs About Types of Alopecia
Is alopecia permanent?
Not always. Some forms, like telogen effluvium or mild alopecia areata, may improve over time.
Others, such as cicatricial alopecia or cases linked to discoid lupus erythematosus, cause permanent hair loss because they scar the scalp and destroy follicles.
Doctors can confirm if hair may grow back after an exam and, when needed, tests like blood work or a biopsy.
Can alopecia be cured?
There is no single cure for all alopecia. Some conditions can be controlled with medicine, lifestyle changes, or surgery.
Treatment plans depend on the type and severity of hair loss and the patient’s goals.
Advances in care, including work at Kopelman Hair, give many patients long-term hope and meaningful improvement.
Ready to Take the Next Step?
If you are noticing hair loss and want expert guidance, schedule a consultation with Kopelman Hair today. Dr. Kopelman and his team provide personalized treatments to help restore your hair and confidence.