Table of Contents
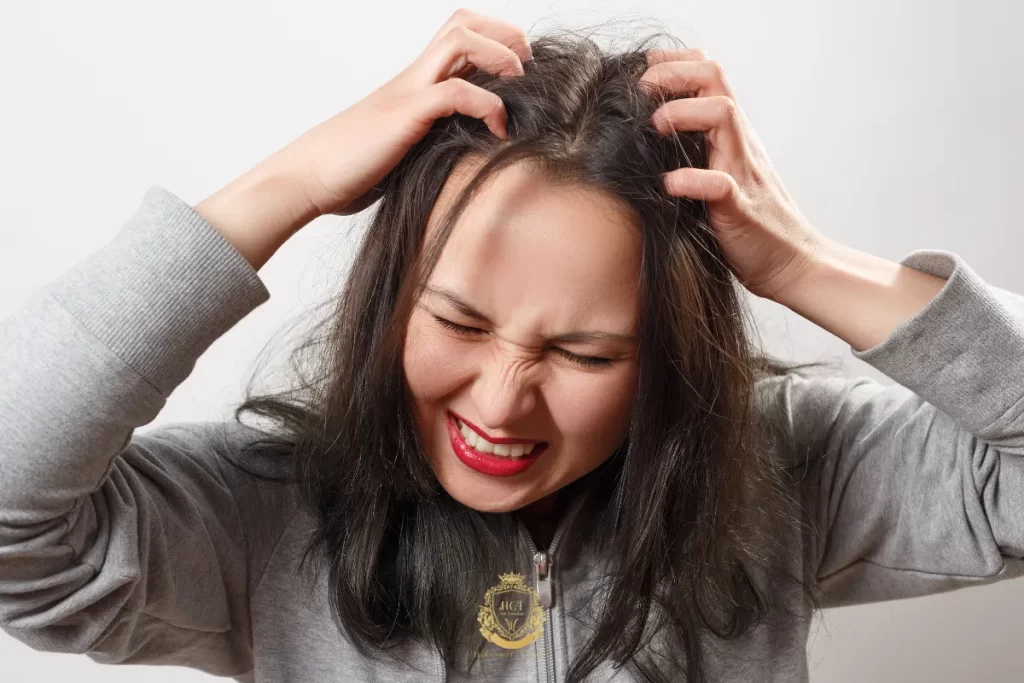
ToggleA burning sensation on the scalp can feel confusing and frustrating—especially when it appears without a rash or visible irritation.
At Kopelman Hair, we frequently encounter patients with burning scalp syndrome and thyroid symptoms, many of whom are unaware of the link between thyroid disorders and scalp sensitivity. This article explains that link and guides you through causes, diagnosis, and treatment options from leading experts in hair and scalp health.
Key Takeaways
- Thyroid imbalances, including hypothyroidism and autoimmune disorders, can cause burning sensations on the scalp and contribute to hair loss.
- Burning scalp syndrome related to thyroid issues often results from nerve sensitivity and hormonal disruptions that affect the scalp’s function.
- Diagnosis typically involves thyroid blood tests, scalp evaluations, and a review of symptoms to determine the underlying cause accurately.
- Treatment focuses on regulating thyroid levels, relieving nerve-related scalp discomfort, and restoring hair health through personalized care.
- Dr. Joel Kopelman provides expert evaluation and targeted solutions for patients experiencing burning scalp and thyroid-related hair concerns.
Can Thyroid Cause Burning Scalp or Hair Loss?
Yes, thyroid disorders can affect the scalp. Both hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism disrupt hormone levels that regulate nerve function, skin sensitivity, and hair growth. This imbalance can trigger unusual sensations like burning or tingling in the scalp—often without visible signs.
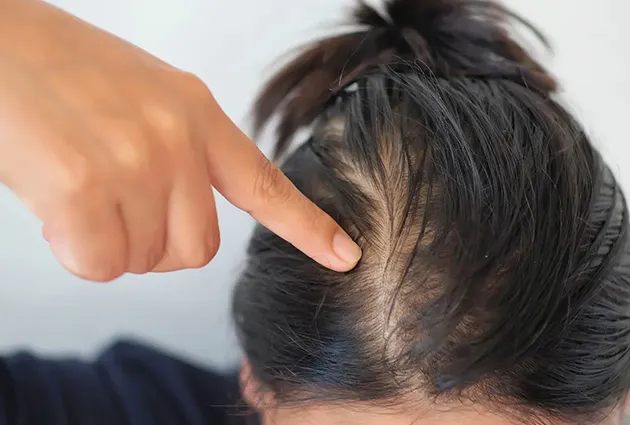
Thyroid dysfunction also affects hair follicles. You may notice your hair becoming thin, brittle, or falling out in patches. This connection explains why burning scalp and thyroid symptoms often appear together.
When the thyroid gland produces too little or too much hormone, it can interfere with the nerves beneath the scalp. This nerve irritation may cause pain or a burning feeling, even if the skin looks normal. People with autoimmune thyroid conditions like Hashimoto’s or Graves’ disease are more likely to report burning scalp related to thyroid activity.
If you’re experiencing this, it’s important to understand you’re not alone—and you’re not imagining it. These symptoms have a physiological basis that can be diagnosed and treated effectively.
How Different Thyroid Disorders Affect the Scalp
Not all thyroid conditions affect the scalp in the same way. Hypothyroidism (low thyroid) may slow circulation and reduce oil production, making the scalp dry and sensitive. Hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid) can increase nerve reactivity and heighten sensations like burning or itching.
Autoimmune conditions such as Graves’ disease often cause inflammation and overactivity of the thyroid, which can affect both hair and skin. These autoimmune diseases may also lead to telogen effluvium, a temporary hair shedding condition triggered by hormonal shifts or stress.
Autoimmune thyroid conditions like Hashimoto’s thyroiditis and Graves’ disease are especially linked to nerve inflammation. These conditions often trigger both hair thinning and abnormal scalp sensations. Recognizing which thyroid disease you have can help guide more precise treatment.
What Burning Scalp Syndrome Feels Like
Burning scalp syndrome isn’t always easy to describe. Some patients say it feels like sunburn. Others report tingling, itching, or a sharp heat-like sensation on the scalp. These symptoms can come and go or stay persistent for weeks.
Common sensations include:
- Scalp heat or stinging without redness
- Tingling or “pins and needles” under the skin
- Sensitivity when touching or brushing the hair
- Mild hair shedding along with pain or discomfort
In many cases, people experience these symptoms before any hair loss is visible. That’s why identifying the early signs can help prevent further complications.
This condition falls under a broader category called scalp dysesthesia burning scalp syndrome, which refers to discomfort or abnormal sensations on the scalp without a clear dermatological cause. In cases involving burning scalp and thyroid disorders, the symptoms are often linked to hormonal imbalances affecting nerve signaling.
What’s Happening Under the Skin?
Burning scalp syndrome related to thyroid changes is often linked to disrupted nerve signaling. Thyroid hormones help regulate the autonomic nervous system, which controls how nerves respond to temperature, pressure, and pain. When hormone levels are off, nerves can become hypersensitive, causing burning or tingling without visible irritation.
Reduced circulation, another thyroid-related effect, can also deprive nerves of oxygen and nutrients. This makes them more prone to firing off pain signals, especially in areas like the scalp that are already sensitive.
While the exact mechanisms behind burning scalp syndrome thyroid symptoms are not yet fully understood, research points to the role of hormone fluctuations in disrupting nerve function and skin sensitivity.
How Long Does Burning Scalp Syndrome Last?
Burning scalp symptoms can last a few days or persist for weeks, depending on the cause. When linked to thyroid disorders, the symptoms often improve once hormone levels are stabilized with treatment.
Some people experience intermittent flare-ups during periods of stress, illness, or hormone fluctuations. In autoimmune disease cases, the sensation may return unless managed with medication.
Key factors that influence duration:
- Whether thyroid levels are balanced
- Presence of chronic stress or inflammation
- Use of appropriate topical or medical treatment
- Overall health and response to medication
If symptoms last more than two weeks or worsen, a medical evaluation is recommended.
Other Causes of Scalp Burning
While thyroid issues are a common cause, they’re not the only explanation. Scalp burning can result from various conditions that affect nerves, skin, or emotional health.
Other possible causes include:
- Menopause: Hormonal shifts can cause scalp sensitivity similar to thyroid changes.
- Stress and anxiety: Chronic stress affects nerve function and circulation, sometimes triggering scalp burning.
- Scalp infections: Fungal or bacterial infections can cause inflammation and burning sensations.
- Contact dermatitis: Reactions to hair products or dyes may cause scalp irritation and burning.
- Scalp dysesthesia: A condition where nerve endings misfire, creating sensations like burning without skin changes.
- Diffuse hair loss: Often associated with underlying hormonal changes or nutritional deficiencies.
Understanding the root cause is essential. A burning scalp related to thyroid imbalance will require different care than one caused by dermatitis or anxiety.
Diagnosing the Cause of Burning Scalp
Getting the right diagnosis means identifying what’s happening beneath the surface. If you’re experiencing persistent scalp burning, a thorough medical evaluation is necessary to rule out underlying conditions.
Diagnosis typically includes:
- Thyroid panel blood test: Measures levels of TSH, T3, and T4 hormones.
- Scalp examination: Checks for inflammation, skin conditions, or visible irritation.
- Hair loss assessment: Reviews patterns of shedding to identify possible thyroid-related loss.
- Neurological evaluation: Rules out nerve damage or dysfunction.
At Kopelman Hair, Dr. Joel Kopelman takes a comprehensive approach. He combines medical testing with detailed patient history to determine whether your symptoms are due to a thyroid disorder, dermatological issue, or nervous system imbalance.
Dr. Kopelman’s experience with complex scalp conditions ensures that no symptom is dismissed and that every treatment is rooted in a clear diagnosis.
One patient at Kopelman Hair, a woman in her early 40s with undiagnosed hypothyroidism, came in complaining of a constant burning scalp and increased shedding. After a full thyroid panel and scalp evaluation, Dr. Kopelman identified hormone imbalance as the primary cause. Following treatment and close monitoring, her symptoms decreased significantly within weeks, and hair regrowth began shortly after.
When to Seek Medical Help
Temporary issues can cause burning sensations on the scalp, but persistent discomfort should not be ignored. If symptoms last longer than 7–10 days, worsen, or begin affecting your sleep or mood, it’s time to consult a specialist.
You should also see a doctor if:
- You’re already being treated for a thyroid condition
- Symptoms began after starting thyroid medication
- You notice hair loss or visible scalp changes
- Over-the-counter treatments are not helping
Early diagnosis helps prevent long-term scalp nerve sensitivity and supports better hair recovery.
Treatment Options for Burning Scalp and Hair Loss
Once the underlying cause is confirmed, treatment becomes more effective and personalized. In cases of burning scalp syndrome with thyroid symptoms, managing thyroid hormone levels is key.
Here are common treatment strategies:
1. Hormone Regulation
- Patients with hypothyroidism may need synthetic thyroid hormones (like levothyroxine).
- Those with hyperthyroidism might require medication to reduce hormone production.
2. Scalp Symptom Relief
- Topical corticosteroids: Reduce inflammation or burning sensation.
- Lidocaine creams: Numb localized areas of scalp discomfort.
- Antihistamines: Help in cases with allergic components.
3. Stress Management
- Relaxation techniques, cognitive behavioral therapy, or light exercise may ease nerve sensitivity caused by stress.
4. Hair Restoration Treatments
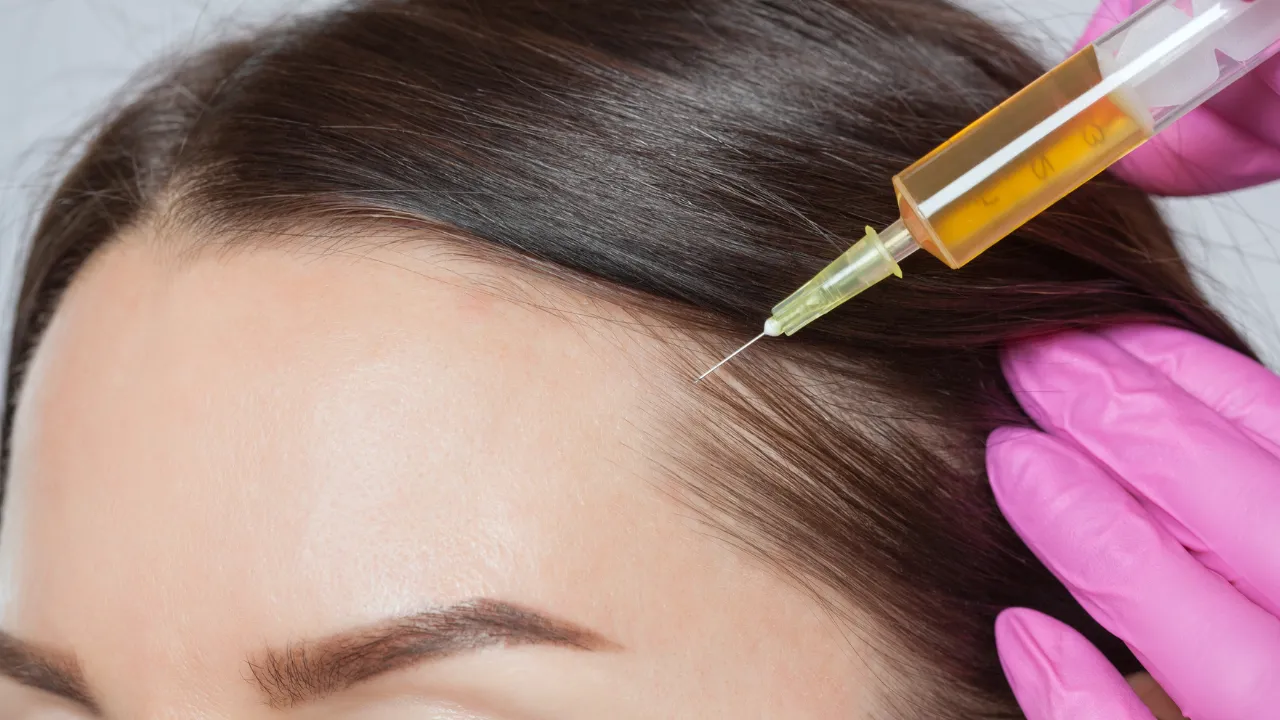
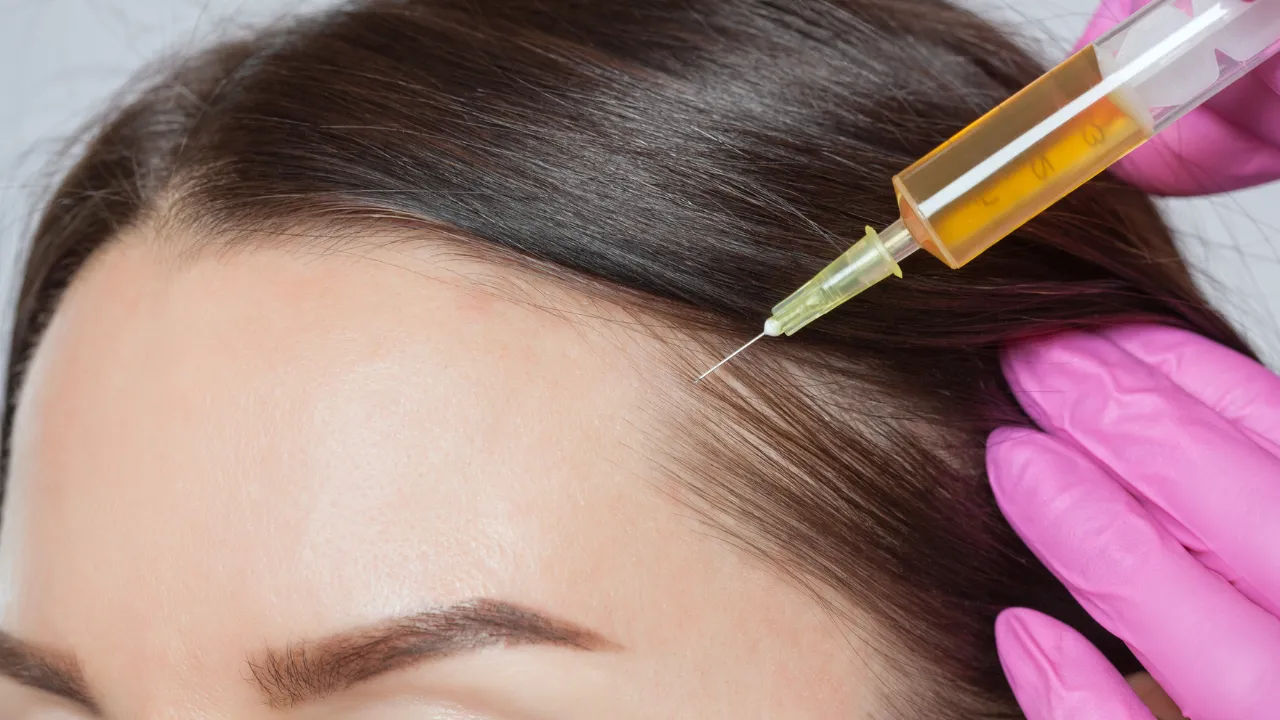
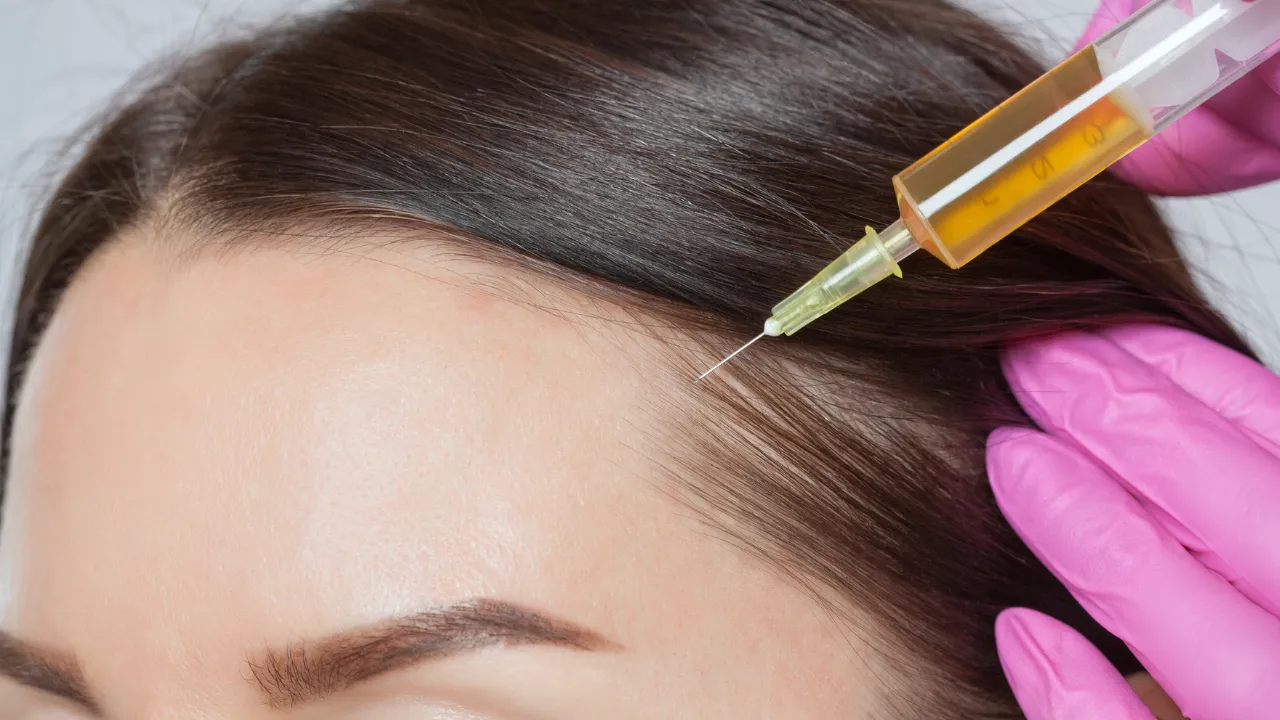
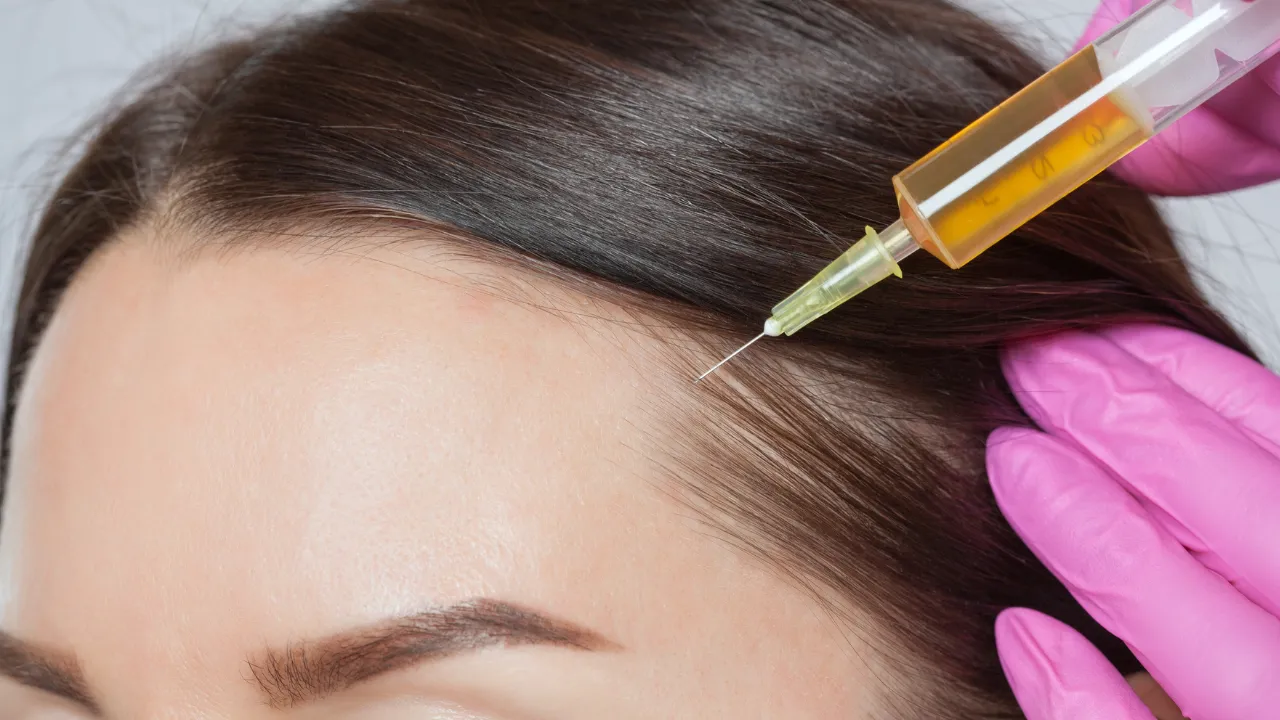
- In cases where hair loss has begun, Dr. Kopelman may recommend platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy or low-level laser therapy to support regrowth and reduce inflammation.
- For more advanced hair loss, hair transplant surgery may be considered after stabilizing thyroid function.
5. At-Home Care Tips
- Avoid irritating shampoos or hair products.
- Use gentle brushes and avoid excessive heat styling.
- Keep a symptom journal to track flare-ups and possible triggers.
What to Expect From Treatment
Most patients start to feel relief from scalp burning within 2 to 4 weeks of adjusting their thyroid medication. Symptom improvement may be faster when paired with topical treatments or nerve-calming therapies.
Hair regrowth, if affected, typically follows within 2 to 3 months once thyroid levels are balanced. Results can vary depending on the severity and duration of the condition. Many patients report not only symptom relief but also increased hair density as their scalp health improves.
Can Thyroid Medications Trigger Scalp Burning?
In rare cases, people beginning thyroid hormone replacement therapy—such as levothyroxine—may temporarily experience burning or tingling sensations. This may be due to the body adjusting to new hormone levels or increased sensitivity in nerve endings.
These symptoms usually resolve as hormone levels stabilize. However, if burning persists after starting thyroid medication, you should consult your doctor to ensure dosage and absorption are appropriate.
Other types of hair loss, like alopecia areata, androgenetic alopecia, and scarring alopecia, may also be confused with thyroid-related issues. Proper diagnosis will help determine whether thyroid disease, immune conditions, or unrelated scalp disorders are the true cause.
Your Next Step
If you’re experiencing persistent scalp burning, hair shedding, or suspect a thyroid-related issue, don’t wait. Schedule a consultation with Dr. Joel Kopelman to receive a personalized diagnosis and treatment plan tailored to your needs. Your scalp health and hair recovery start with expert care.