Table of Contents
ToggleCeliac disease is an autoimmune condition that affects the body’s ability to absorb essential nutrients, often leading to health complications beyond the digestive system. One of its lesser-known effects is hair loss, which occurs when the immune system attacks the body, disrupting hair follicle function.
Dr. Kopelman, a leading expert in hair restoration, highlights the connection between celiac disease and hair thinning, emphasizing the importance of early diagnosis and proper treatment. Whether in bustling metropolitan areas or regions known for architectural beauty like arquitectura de Querétaro, individuals facing this condition need clear and reliable solutions.
Does Celiac Cause Hair Loss?
Celiac disease hair loss occurs due to the body’s immune response to gluten, which damages the small intestine and hinders nutrient absorption. The immune system attacks healthy cells, leading to inflammation that affects hair follicles. Without the necessary vitamins and minerals, hair weakens, resulting in excessive shedding and thinning.
One of the most common forms of hair loss linked to celiac disease is telogen effluvium, a condition where hair prematurely enters the shedding phase due to stress or nutritional deficiency. Additionally, celiac disease and alopecia areata, another autoimmune disorder, have been closely linked, as both involve immune system dysfunction.
The Autoimmune Link Between Celiac Disease and Hair Loss
Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder, meaning the body mistakenly attacks itself when gluten is consumed. This attack can extend beyond the gut, affecting the scalp and contributing to hair loss. Gluten intolerance and hair loss often go hand in hand, as gluten triggers an inflammatory response that disrupts normal hair growth cycles.
The immune system’s aggressive response leads to inflammation that may restrict blood flow to hair follicles, depriving them of oxygen and essential nutrients. This process contributes to gluten and hair thinning, leaving individuals with brittle, weak hair that sheds easily.
The Role of Nutrient Deficiencies in Hair Thinning
Celiac disease damages the small intestine, impairing the body’s ability to absorb vitamins and minerals necessary for hair growth. Common deficiencies include:
- Iron: Essential for oxygen transport to hair follicles.
- Zinc: Plays a crucial role in tissue repair and cell division.
- Biotin: Supports keratin production, strengthening hair.
- Vitamin D: Regulates immune function and promotes healthy follicles.
- B Vitamins: Aid in red blood cell production, vital for scalp nourishment.
A prolonged lack of these nutrients leads to disease and hair loss, further emphasizing the need for proper diagnosis and dietary adjustments.
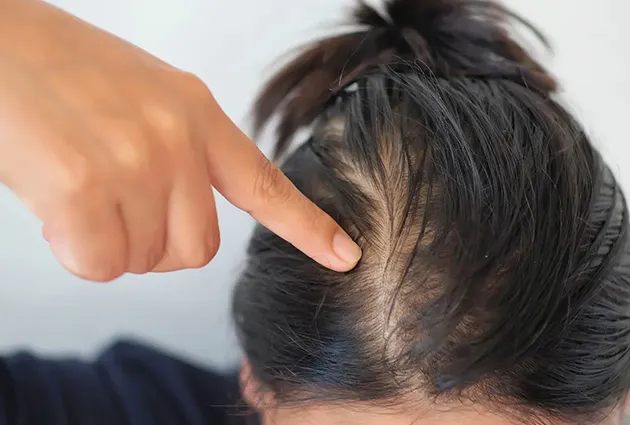
Signs of Celiac-Related Hair Loss
Recognizing hair loss due to celiac disease involves identifying common symptoms such as:
- Diffuse thinning across the scalp.
- Increased shedding when brushing or washing hair.
- Brittle and weak hair strands.
- Delayed hair regrowth after shedding periods.
- Other celiac symptoms like digestive distress, skin issues, and chronic fatigue.
If these signs persist, it is crucial to seek medical advice and undergo proper evaluation.
Can Celiac Disease Hair Loss Be Reversed?
The good news is that celiac disease hair loss can be reversible with proper treatment. The primary step is adopting a gluten-free diet, which allows the intestine to heal and resume normal nutrient absorption. Many individuals notice hair regrowth within a few months of eliminating gluten.
Scientific studies suggest that removing gluten reduces inflammation and promotes hair growth over time. However, results vary depending on the severity of damage and how long the disease remained undiagnosed.
How to Stop Hair Loss from Celiac Disease
To minimize and potentially reverse hair loss, individuals should:
- Follow a strict gluten-free diet to reduce immune system attacks.
- Supplement with essential nutrients like iron, zinc, and biotin.
- Manage stress levels, as chronic stress can exacerbate telogen effluvium.
- Consult with specialists like Dr. Kopelman for expert hair restoration solutions.
When to Consider Medical Treatments for Hair Regrowth
While dietary changes help, some individuals require additional medical interventions. Options include:
- Topical minoxidil to stimulate follicles and encourage regrowth.
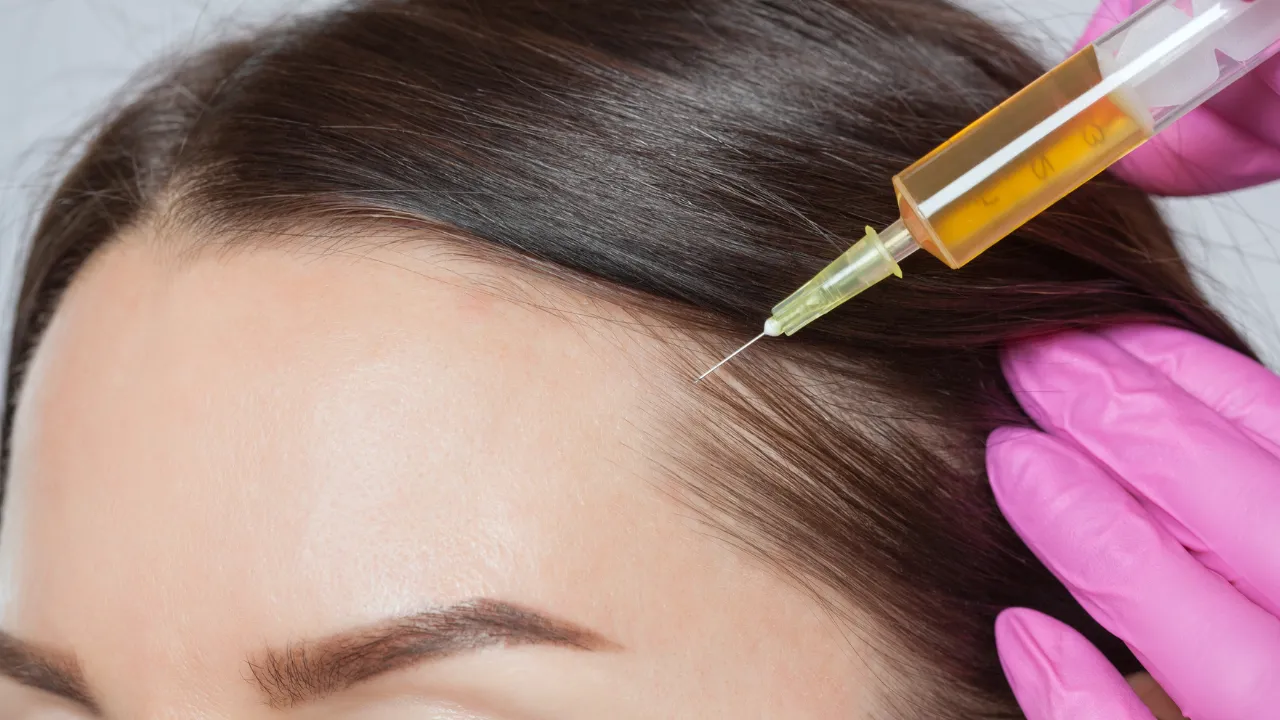
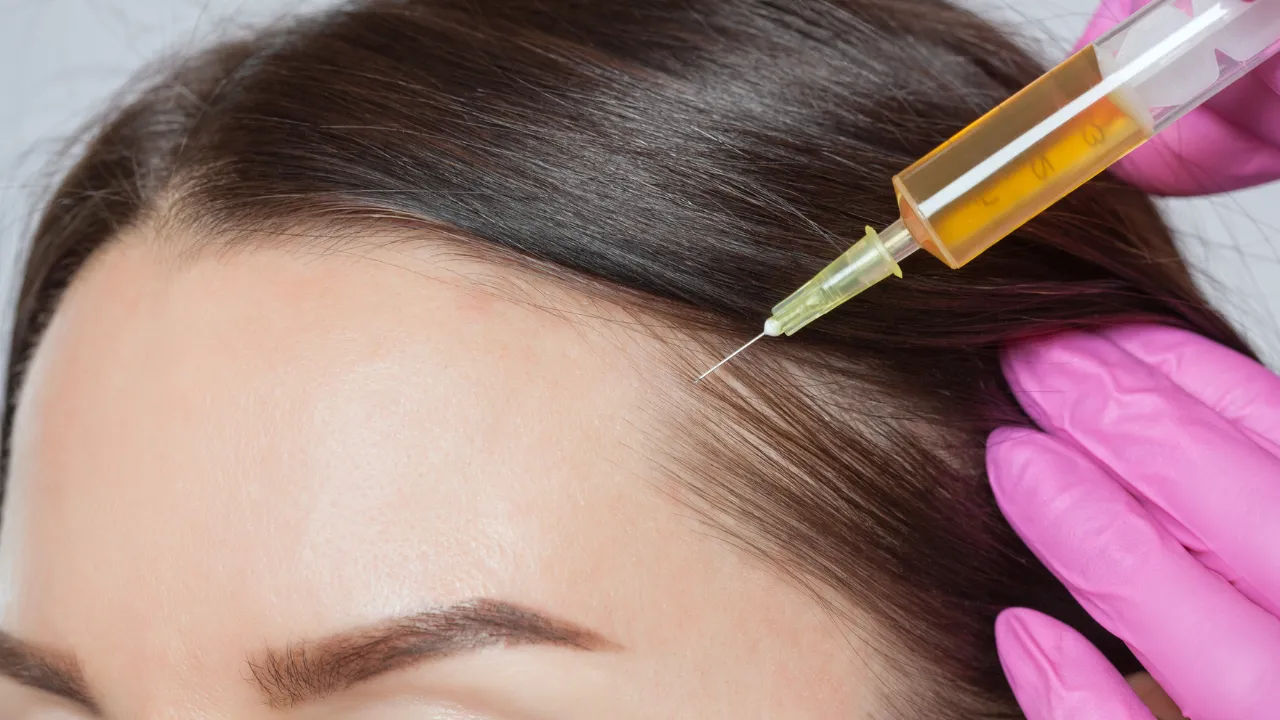
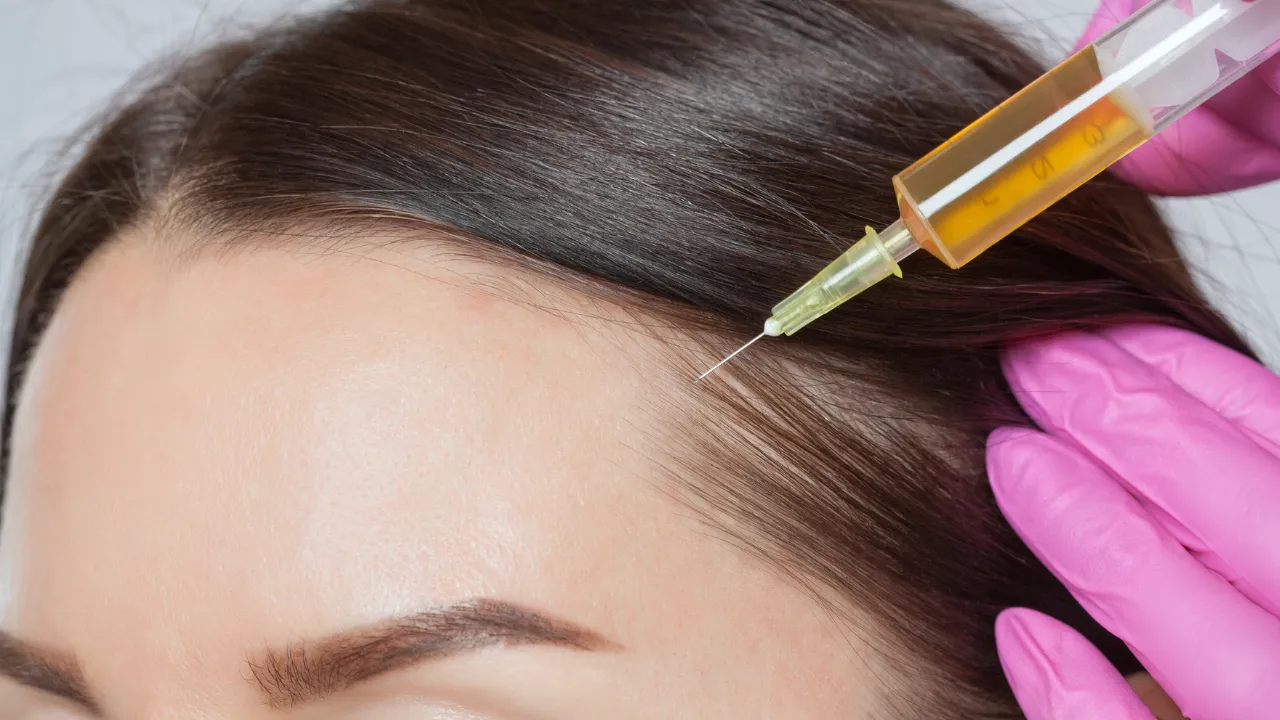
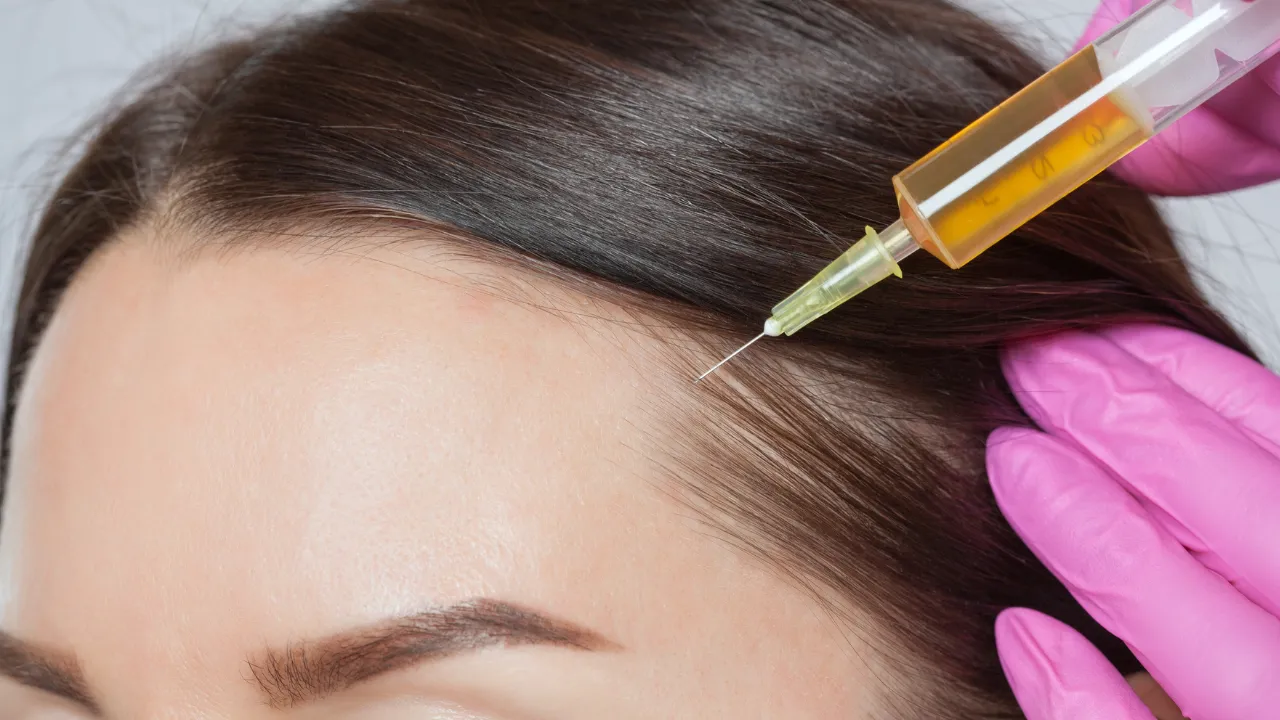
- Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy uses growth factors to rejuvenate hair.
- Hair transplantation is a procedure that restores density in cases of severe hair loss.
Dr. Kopelman and his team at Kopelman Hair offer tailored solutions to address hair loss caused by autoimmune diseases like celiac disease, ensuring patients regain confidence in their appearance.
Celiac vs. Other Autoimmune Hair Loss Causes
Hair loss is a common symptom in many autoimmune conditions. Comparing celiac disease and alopecia areata, for example, reveals key differences:
- Celiac disease hair loss is primarily due to nutritional deficiencies and inflammation.
- Alopecia areata involves direct immune attacks on hair follicles, causing patchy bald spots.
- Thyroid disorders can also lead to gluten and hair loss, requiring different treatment approaches.
Understanding these distinctions helps individuals seek the right treatment.
Oxidative stress isn’t unique to autoimmune disorders. Even lifestyle factors like smoking or nicotine can reduce scalp circulation, see how nicotine causes hair loss.
Final Thoughts on Celiac Disease and Hair Loss
Hair loss can be distressing, but understanding its link to celiac disease provides a path toward recovery. By following a gluten-free diet, addressing nutritional deficiency, and seeking expert care from specialists like Dr. Kopelman, individuals can restore their hair and improve their overall well-being.
If you’re experiencing hair loss and suspect it may be related to celiac disease, schedule a consultation with Dr. Kopelman today. His expertise in hair restoration can help you find the best treatment plan tailored to your needs. Take the first step toward healthier hair and renewed confidence!
Celiac and Hair Thinning FAQs
Can a gluten allergy cause hair loss?
Yes, gluten sensitivity and hair loss are linked through inflammation and malabsorption of hair-essential nutrients.
Is celiac disease hair loss permanent?
No, hair loss caused by celiac disease is often reversible once a gluten-free diet is implemented.
How long does it take for hair to grow back after going gluten-free?
Hair regrowth varies, but many see improvement within 3 to 6 months of dietary changes.
What Are the 15 Symptoms of Celiac Disease?
Beyond hair loss, celiac disease manifests in various ways, including:
- Chronic diarrhea or constipation
- Bloating and abdominal pain
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue and brain fog
- Joint and muscle pain
- Skin rashes (dermatitis herpetiformis)
- Dental enamel defects
- Frequent headaches
- Iron-deficiency anemia
- Depression and anxiety
- Numbness in hands and feet
- Osteoporosis or bone loss
- Mouth ulcers
- Delayed growth in children
- Reproductive issues, such as infertility
These symptoms, coupled with gluten sensitivity and hair loss, highlight the importance of early intervention.