Table of Contents
ToggleHair loss due to hormones occurs when imbalances in estrogen, progesterone, thyroid hormones, or dihydrotestosterone DHT disrupt the hair growth cycle. This can weaken hair follicles, shorten the anagen phase, and cause excessive shedding.
At Kopelman Hair, Dr. Kopelman and his team treat hair loss from hormone problems with solutions tailored to each patient’s needs. Some cases are temporary, while conditions like female pattern hair loss or androgenic alopecia may require long-term care.
Key Takeaways
- Hormonal imbalances, such as changes in estrogen, progesterone, thyroid hormones, and dihydrotestosterone DHT can disrupt the natural hair growth cycle.
- The cycle includes the anagen phase (active growth), the resting phase, and the shedding stage when hair sheds naturally. Imbalances in sex hormone levels can interfere with these stages, weakening hair follicles.
- Some cases of hair loss due to hormones are temporary and reversible, while others, such as female pattern hair loss, androgenic alopecia, or hair loss from hormone problems, may require ongoing care.
- Effective treatments range from nutrition and lifestyle changes to advanced options like PRP therapy and hair transplantation.
What Hormones Cause Hair Loss?
Hormones regulate how hair grows and sheds. When levels are imbalanced, the follicles may shrink or stop producing strong strands. Women are often affected by changes in estrogen and progesterone during life stages such as pregnancy, postpartum, and menopause, while men are more prone to androgen-driven loss.
Women: Estrogen, progesterone, thyroid, and DHT
Changes in estrogen or progesterone can trigger sudden shedding. Thyroid dysfunction can also thin hair across the scalp. Dihydrotestosterone DHT contributes to female pattern hair loss by shortening the growth phase and weakening follicles.
Patients often ask what hormone causes hair loss in women, and these are the primary culprits. Women with PCOS face higher risks, making early diagnosis essential.
Men: Androgens, thyroid, and stress hormones
In men, a high level of dihydrotestosterone DHT is the main driver of androgenic alopecia. It gradually shrinks follicles, affecting hair density over time. Cortisol and thyroid imbalances can worsen shedding, while sex hormone fluctuations may also influence how much hair sheds daily.
Distinguishing male-pattern baldness from hair loss from hormone problems helps doctors recommend the correct treatment.

How Is Hormonal Hair Loss Diagnosed?
Doctors start with a scalp examination and medical history review. Blood tests are used to measure thyroid, reproductive, and sex hormone levels to confirm the cause. In rare cases, a scalp biopsy is performed to exclude other conditions.
Diagnosis shows whether the issue is temporary or progressive. For example, postpartum shedding often improves on its own, while conditions like thyroid disease or androgenic alopecia need medical treatment. Early evaluation improves the chances of regrowth.
Signs of Hormonal Hair Loss
Hormonal hair loss may cause gradual thinning or sudden shedding. Recognizing the signs early allows for timely care.
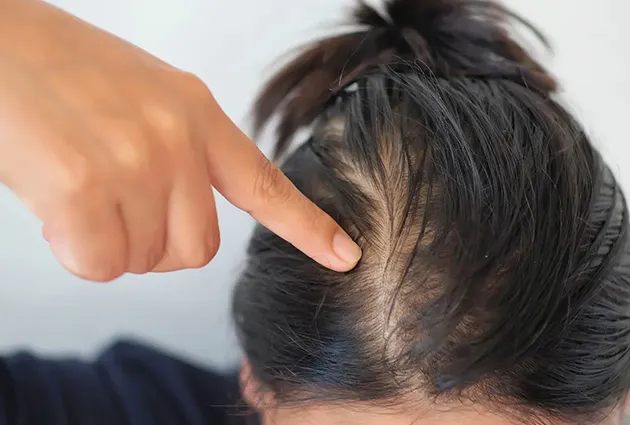
Thinning hair from hormones
Women often notice thinning along the crown or part line. In men, loss typically begins at the temples or vertex. Unlike patchy conditions, thinning hair from hormones is usually diffuse.
Hair fall from hormonal imbalance vs other causes
Excess shedding may appear as clumps on pillows, brushes, or drains. This type of hair loss affects the entire scalp rather than isolated patches. If hair sheds more than usual over several weeks, it often indicates a hormonal trigger.
Types of Hair Loss Linked to Hormones
- Telogen effluvium – excessive shedding after stress or pregnancy, when hairs prematurely enter the resting phase.
- Anagen effluvium – loss during the anagen phase caused by medications or hormone disruption.
- Androgenetic alopecia – pattern loss linked to dihydrotestosterone DHT in both men and women.
- Female pattern hair loss – thinning along the crown and part, influenced by hormonal shifts.
Will Hormonal Hair Loss Grow Back?
The outcome depends on which hormones are involved and how long they have been affecting hair follicles.
Temporary vs permanent loss and reversibility
Loss caused by postpartum changes or thyroid imbalance usually improves once hormone levels normalize. In contrast, DHT-driven conditions like androgenic alopecia or female pattern hair loss may progress without treatment.
Factors affecting regrowth
Genetics, age, and lifestyle influence recovery. Early treatment, stress management, and proper nutrition improve results.
Normal Hair Loss Benchmarks
It is normal if a person loses 50–100 hairs per day during the shedding cycle. Persistent excess beyond this range suggests an imbalance that requires evaluation.
Patients often wonder if regrowth is possible. Understanding the growth phase, resting phase, and shedding cycle explains why treatment is necessary for long-term results.
Hormonal Hair Loss Treatments
Effective treatment requires targeting the underlying hormone imbalance. Options range from natural methods to advanced procedures.
How do you stop hormonal hair loss?
Stopping hair loss requires testing and correcting the source, whether it is thyroid dysfunction, cortisol imbalance, or high dihydrotestosterone DHT. With proper care, hair grows stronger over time.
How to stop hormonal hair loss naturally
Healthy habits like a balanced diet, reduced stress, and quality sleep support hormone regulation. Natural remedies may help, but results are often limited without medical guidance.
Medical treatments: prescriptions and therapies
Doctors prescribe options such as minoxidil, finasteride, anti-androgens, or thyroid medication depending on the cause. In some cases, oral medications or corticosteroids are considered.
Nutrition, lifestyle, and supplements
Adequate protein, iron, zinc, vitamin D, and biotin strengthen follicles and improve growth. Managing stress is equally important since excess cortisol can shorten the growth phase and push more hairs into the resting phase.
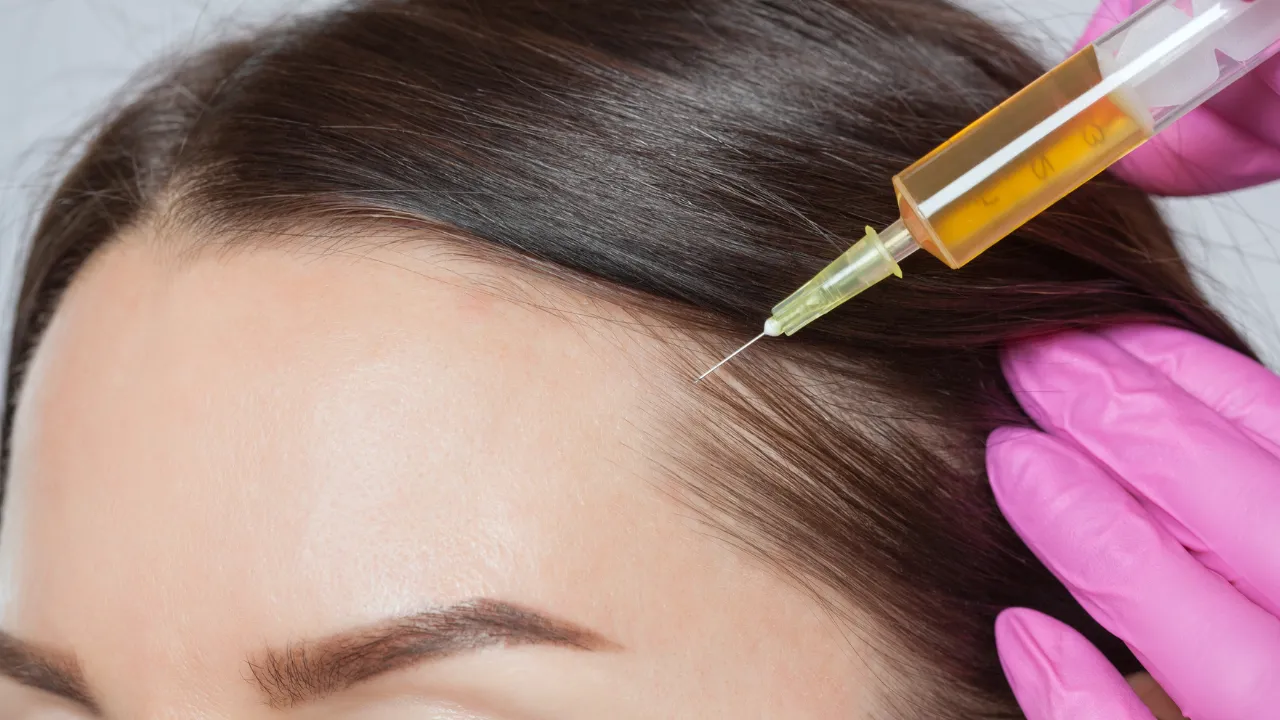
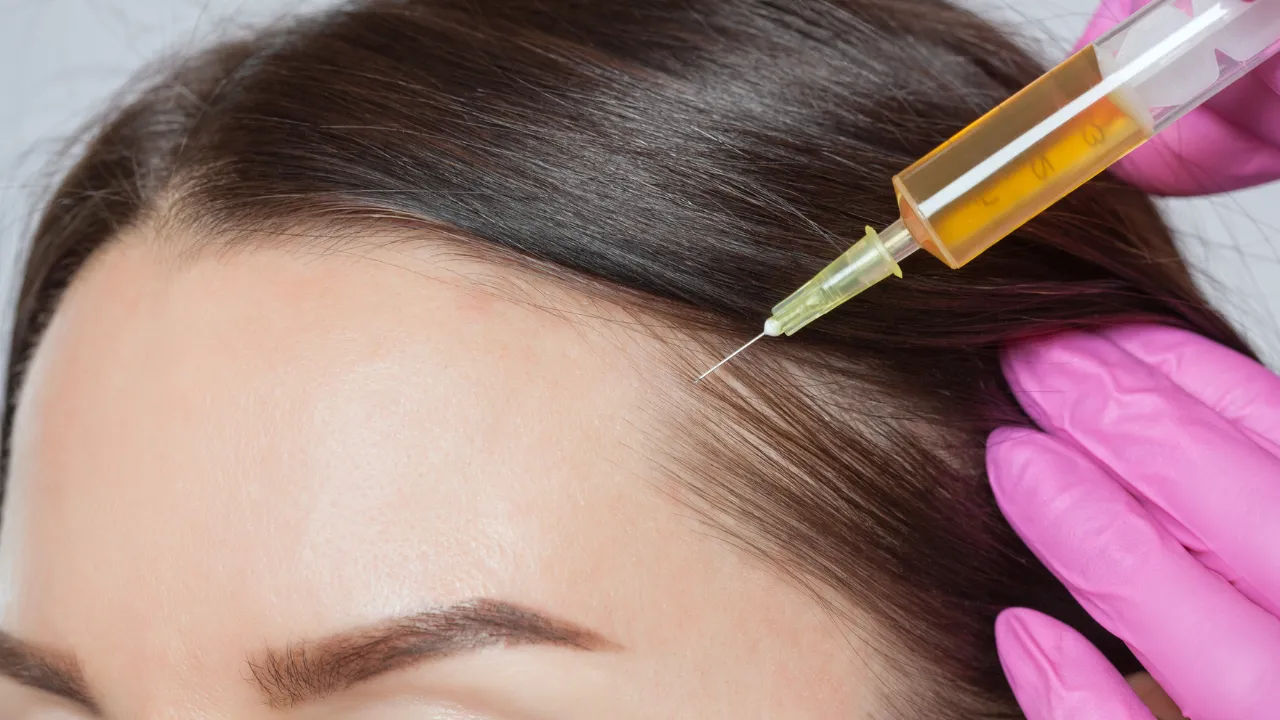
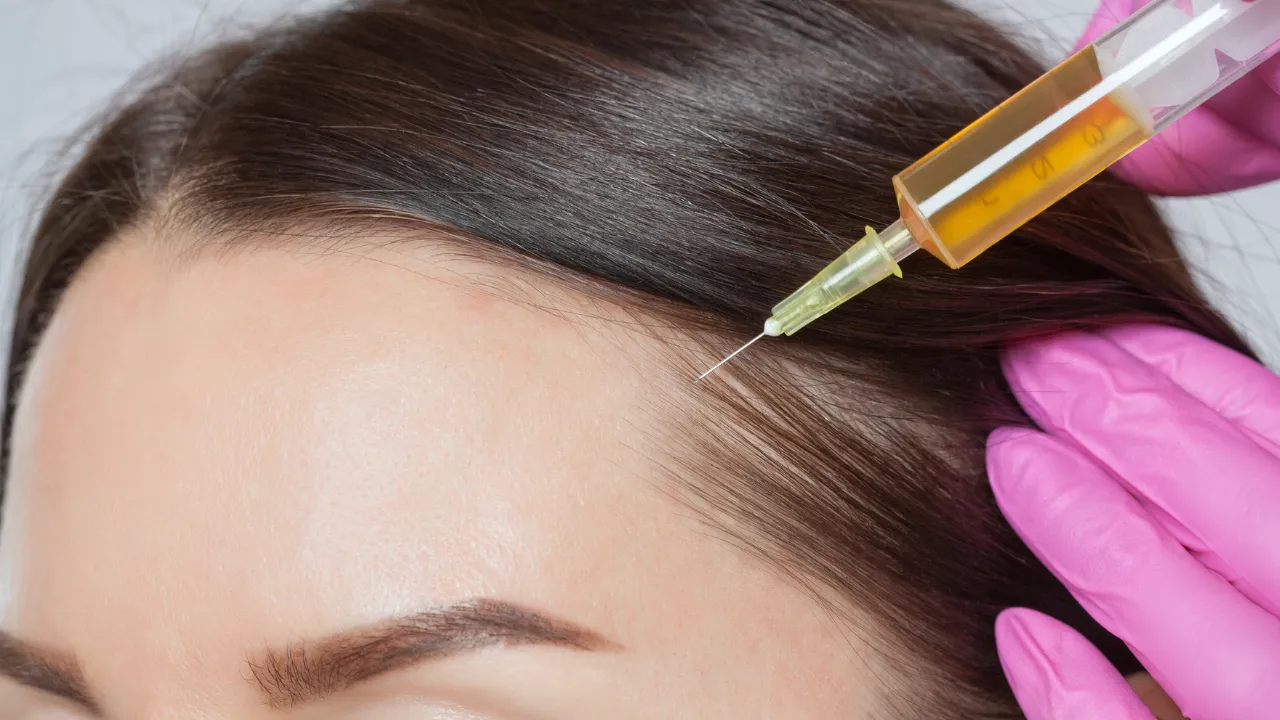
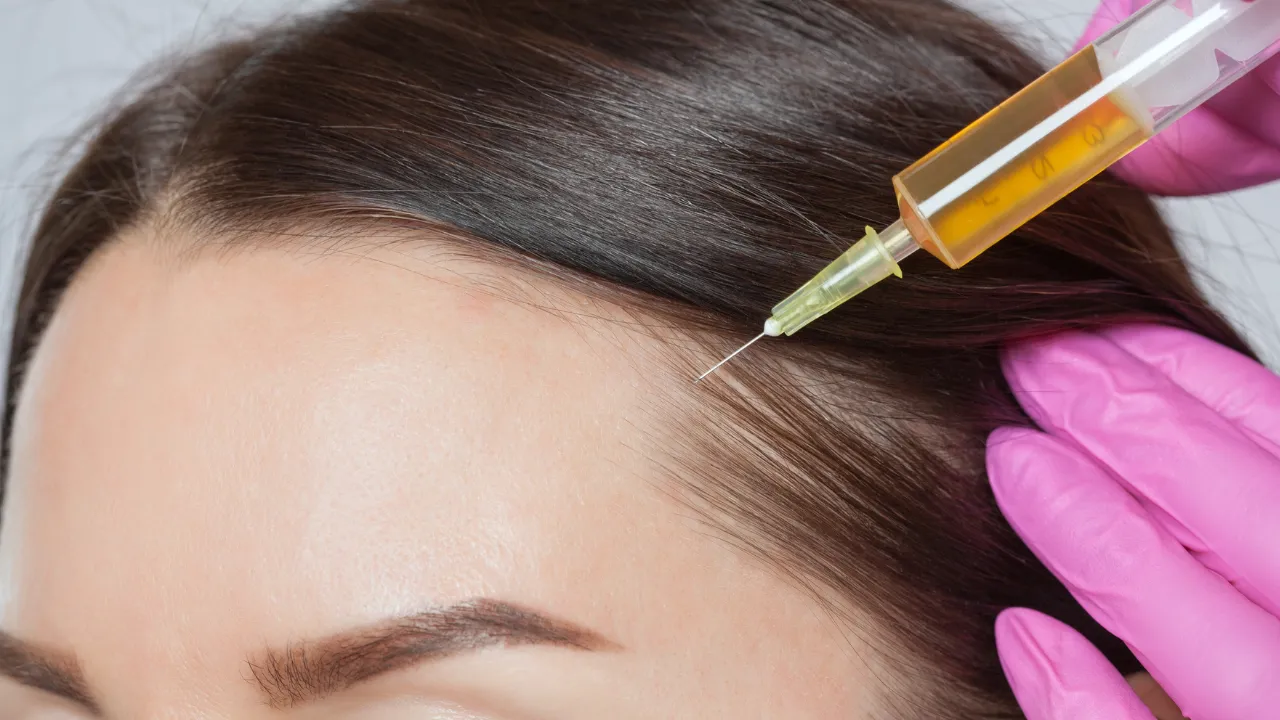
Advanced options: PRP, microneedling, transplants
PRP therapy and microneedling stimulate follicles and improve thickness. Hair transplantation, performed by experts like Dr. Kopelman, restores density when hormonal loss is long-term.
These treatments are often recommended when a hormonal imbalance continues contributing to hair loss, including both men and women.
Prevention Strategies for Hormonal Hair Loss
Prevention is not always possible, but simple lifestyle steps reduce risk. Regular medical checkups allow hormone imbalances to be detected early. Women with PCOS or men with a family history should discuss preventive strategies with a specialist.
Frequently Asked Questions on Hormonal Hair Loss
When to See a Hair Loss Specialist
Patients should see a doctor if shedding continues for more than three months, if they lose hair in patches, or if thinning progresses quickly. A specialist can identify whether hormones, genetics, or other factors are involved.
Hair loss due to hormones can be temporary or ongoing, but improvement is possible with the right care. At Kopelman Hair, patients receive expert evaluation and access to proven treatments, from medication to surgical restoration. Schedule a consultation today to take the first step toward healthier, fuller hair.