Table of Contents
ToggleAt Kopelman Hair, we understand that many patients are unsure about the different types of hair loss. The question of telogen effluvium vs alopecia is common, and the answer is key to proper care. Dr. Kopelman and our team use over 40 years of experience to guide every patient.
In simple terms, telogen effluvium is temporary hair shedding after stress, illness, or hormone changes. Alopecia, including androgenetic alopecia, is usually long-term and continues without treatment. To better understand these conditions, you can also review our guide on hair loss basics.
Key Takeaways
- Telogen effluvium is short-term shedding triggered by stress, illness, or hormones. Alopecia usually causes lasting hair loss.
- Telogen effluvium happens suddenly and improves in months. Alopecia, such as female pattern hair loss, develops slowly and does not stop on its own.
- Both conditions can overlap. Treatment ranges from supportive care to medical or surgical hair loss treatment.
- Hair loss in women often appears after childbirth or menopause. In men, genetics play a major role in loss.
- Consulting a specialist like Dr. Kopelman provides clear answers, support, and long-term results.
What Is Telogen Effluvium?
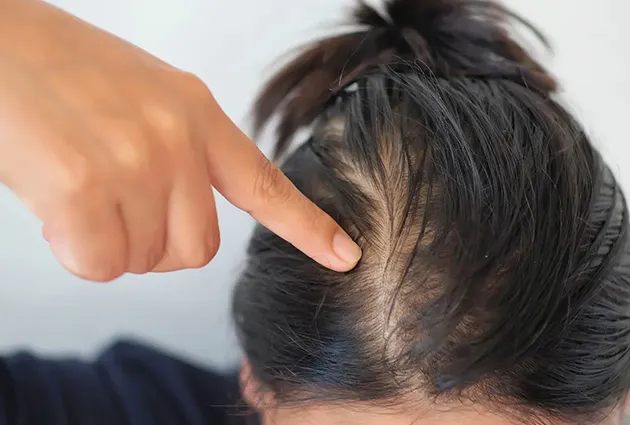
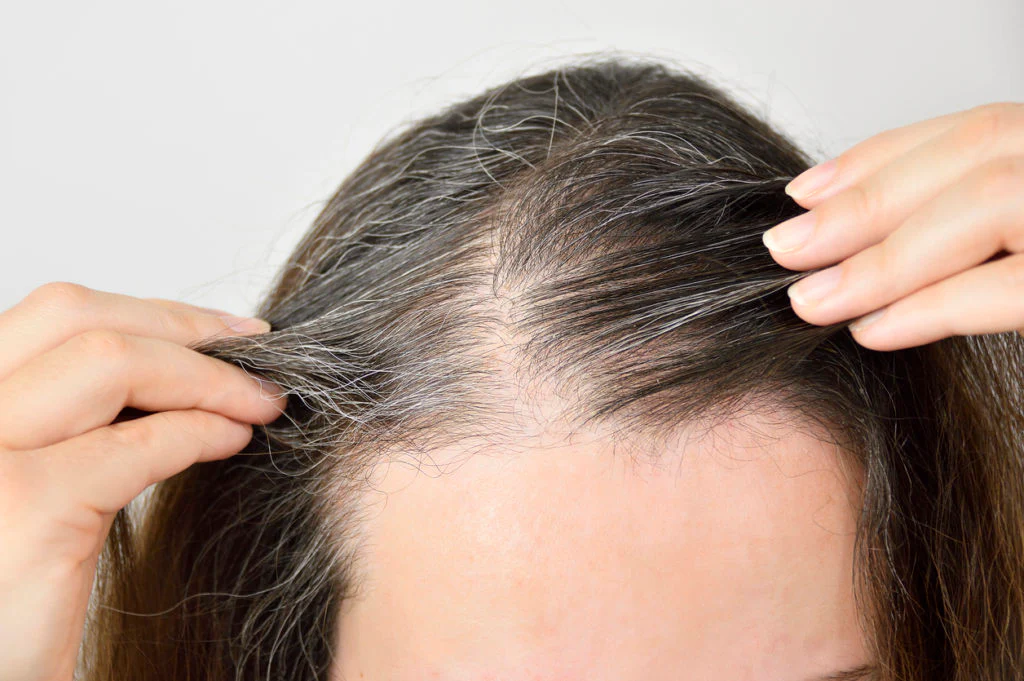
Telogen effluvium is a short-term form of hair shedding. It happens when many follicles enter the resting phase of the hair growth cycle, called the telogen phase. Shedding often starts a few months after a major trigger. Patients notice a sudden drop in hair density.
Patient scenarios
Many women experience shedding after childbirth. Others lose more hair after illness or surgery. These cases demonstrate that telogen effluvium is a temporary condition associated with a clear triggering event.
Causes and triggers
The common cause of hair loss in telogen effluvium includes fever, childbirth, rapid weight loss, poor diet, or medicine use. Stressful events may push more follicles into entering the telogen stage at once. For a deeper look at other triggers, see our article on what causes hair loss.
How many hairs fall in telogen effluvium?
The normal number of hairs lost daily is 50 to 100. In telogen effluvium, people may lose 300 or more. This is easily visible on pillows or in the shower.
How long does hair loss last?
Shedding often lasts three to six months. Hair usually grows back once the trigger is gone.
What Is Androgenetic Alopecia?
Androgenetic alopecia, also known as pattern hair loss, is a chronic condition. Unlike telogen effluvium, it does not stop naturally.
Causes and risk factors
This condition happens when the hair follicle is sensitive to androgens. Family history is the biggest risk factor.
Symptoms and progression
Men often see receding hairlines or crown loss. Women notice female pattern hair loss as thinning along the part line.
Diagnosis methods
Doctors check the scalp, family history, and sometimes order a blood test. They often find miniaturized follicles in androgenetic alopecia.
Key Differences Between Telogen Effluvium and Alopecia
People often ask about androgenetic alopecia vs telogen effluvium. The two can look alike but are very different.
How to tell the difference?
Telogen effluvium starts suddenly and causes diffuse shedding. Alopecia develops slowly in a clear pattern.
Onset, duration, and pattern
Telogen effluvium improves in months. Androgenetic alopecia gets worse over time and needs treatment.
Telogen effluvium vs androgenetic alopecia treatment
Telogen effluvium often improves on its own with basic care. Alopecia may need minoxidil, oral medicine, or surgery.
In short, telogen effluvium is sudden and temporary. Alopecia is gradual and long-lasting.
Telogen Effluvium vs Specific Types of Alopecia
Can telogen effluvium look like alopecia areata?
Yes, but the patterns differ. Alopecia areata creates patchy bald spots. Telogen effluvium causes even thinning.
Telogen effluvium vs alopecia areata symptoms
Alopecia areata shows defined spots. Telogen effluvium is more diffuse.
Telogen effluvium vs alopecia totalis
Alopecia totalis results in complete scalp loss. Telogen effluvium never goes this far.
Androgenetic Alopecia and Telogen Effluvium: Overlap and Coexistence
Shared symptoms and confusion
Both can cause thinning, which confuses patients. Telogen effluvium may also expose hidden androgenetic alopecia.
When both occur together
Some patients have both conditions. Doctors must determine which part is temporary and which is permanent.
Telogen Effluvium vs Alopecia in Women and Men
Female-specific patterns and treatment
Hair loss in women often starts during pregnancy or menopause. Postpartum shedding improves in months, while menopause can expose genetic alopecia. You can also read about related concerns like a receding hairline in women
Male-specific patterns and treatment
Men often notice receding hairlines and thinning of the crown. Stress can add telogen effluvium on top of genetic loss.
Telogen Effluvium vs Alopecia Pictures
What pictures can show
Photos can help spot diffuse shedding versus pattern loss. Doctors use them to track changes. For more examples, see our gallery of pictures of telogen effluvium.
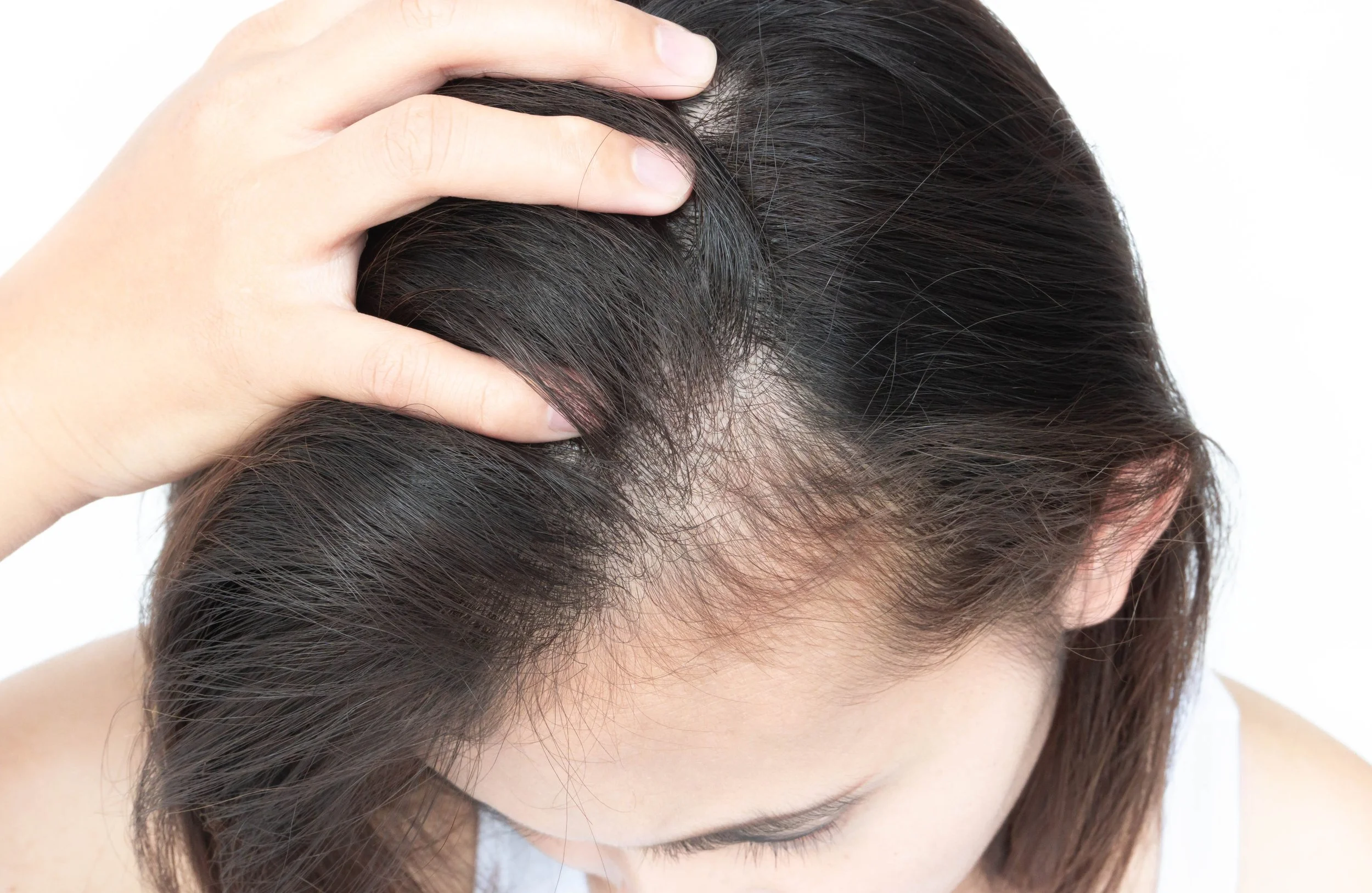

When photos help diagnosis
At-home photos help patients watch progress. Doctors compare images to confirm if both telogen effluvium and androgenetic alopecia are present.
Emotional and Psychological Impact
Hair loss affects more than looks. Many people feel stress, worry, or low confidence. Sudden shedding can feel scary, while ongoing alopecia can feel discouraging.
Dr. Kopelman reminds patients that both conditions can be managed. Talking with family, joining groups, or getting counseling can reduce anxiety while treatment starts.
Telogen Effluvium or Hair Loss?
How can I tell if my shedding is telogen effluvium or alopecia?
Sudden, diffuse hair shedding is more often telogen effluvium. Slow, patterned thinning points to alopecia. A doctor visit gives clear answers.
Treatment and Management Options
Medical treatments
Doctors may suggest minoxidil or oral medicine for alopecia. Telogen effluvium often improves without long-term drugs.
Lifestyle and supportive care
Healthy eating, stress control, and gentle styling all help. Fixing vitamin or mineral gaps is also key.
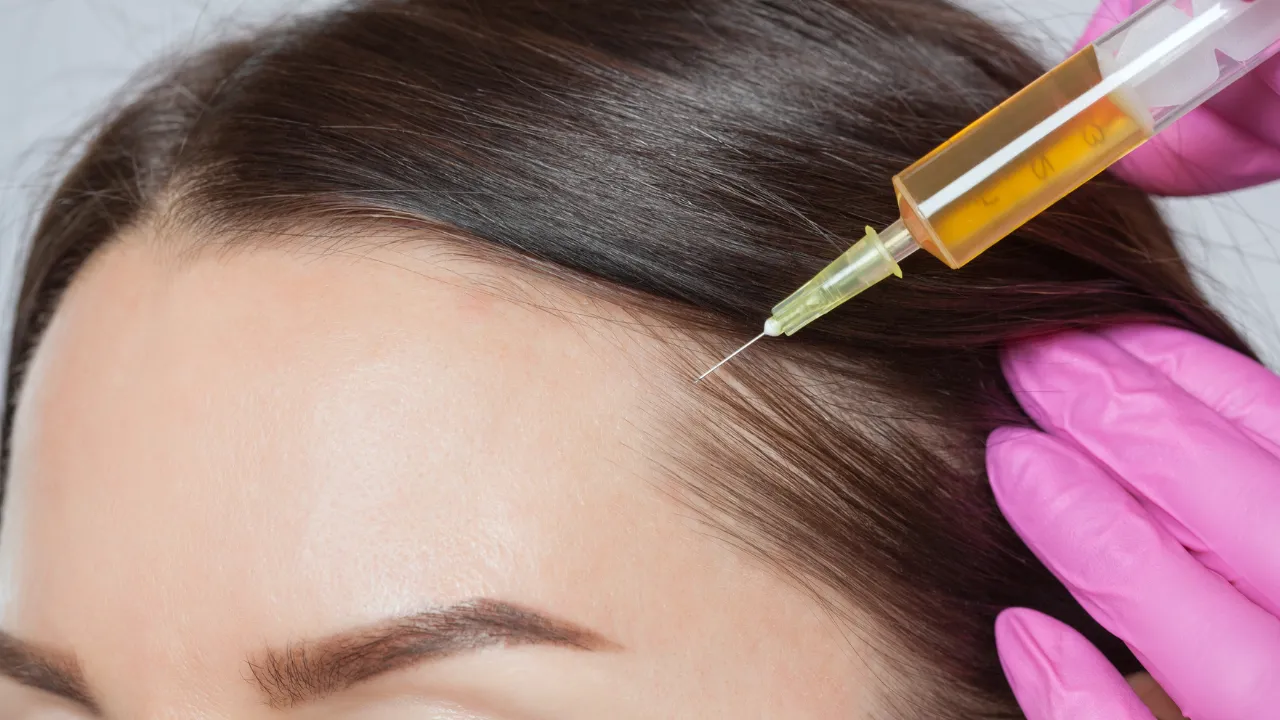
Advanced hair restoration
For permanent loss, surgery is an option. At Kopelman Hair, Dr. Kopelman utilizes advanced transplant methods to achieve natural-looking results.
In short, telogen effluvium improves with time. Alopecia usually needs treatment to stop progression.
Prevention and Early Intervention
Early steps can lower risk for both conditions:
- Eat a balanced diet.
- Manage stress with exercise or rest.
- Avoid harsh styling or tight hairstyles.
- Visit a doctor when shedding increases.
Patients with a family history should see a specialist often. This helps catch androgenetic alopecia early.
When to Seek Professional Help
If shedding is heavy, lasts long, or causes distress, seek help. Dr. Kopelman and his team check if it is telogen effluvium, androgenetic alopecia, or both. Early diagnosis leads to better results.
To get clear answers and explore personalized treatment options, schedule a consultation with Kopelman Hair today.