Table of Contents
ToggleAt Kopelman Hair, we often meet patients who ask about the link between testosterone and hair loss. The connection is real, but it is more complex than most people think. Testosterone influences hair growth through its conversion into dihydrotestosterone (DHT), which can weaken follicles in certain individuals.
It also affects facial hair development, and many wonder does testosterone affect beard growth? a related process governed by the same hormones.
If you are experiencing hair changes, understanding the role of hormones is key. Dr. Kopelman and our team explain the science, address myths, and guide patients toward effective treatments tailored to their specific needs.
Key Takeaways
- Testosterone itself does not directly cause hair loss, but its byproduct DHT can shrink follicles and lead to male pattern hair loss in genetically sensitive individuals.
- Both men and women can experience hair loss from hormone changes, though female cases may also involve conditions like PCOS or menopause that alter hormone balance and body hair growth.
- Low testosterone can cause thinning hair, but in some cases, hair loss from low hormone levels may be reversible with proper medical treatment.
- Preventive steps such as DHT blockers, balanced nutrition, stress reduction, and early recognition of warning signs help slow progression and stimulate hair growth.
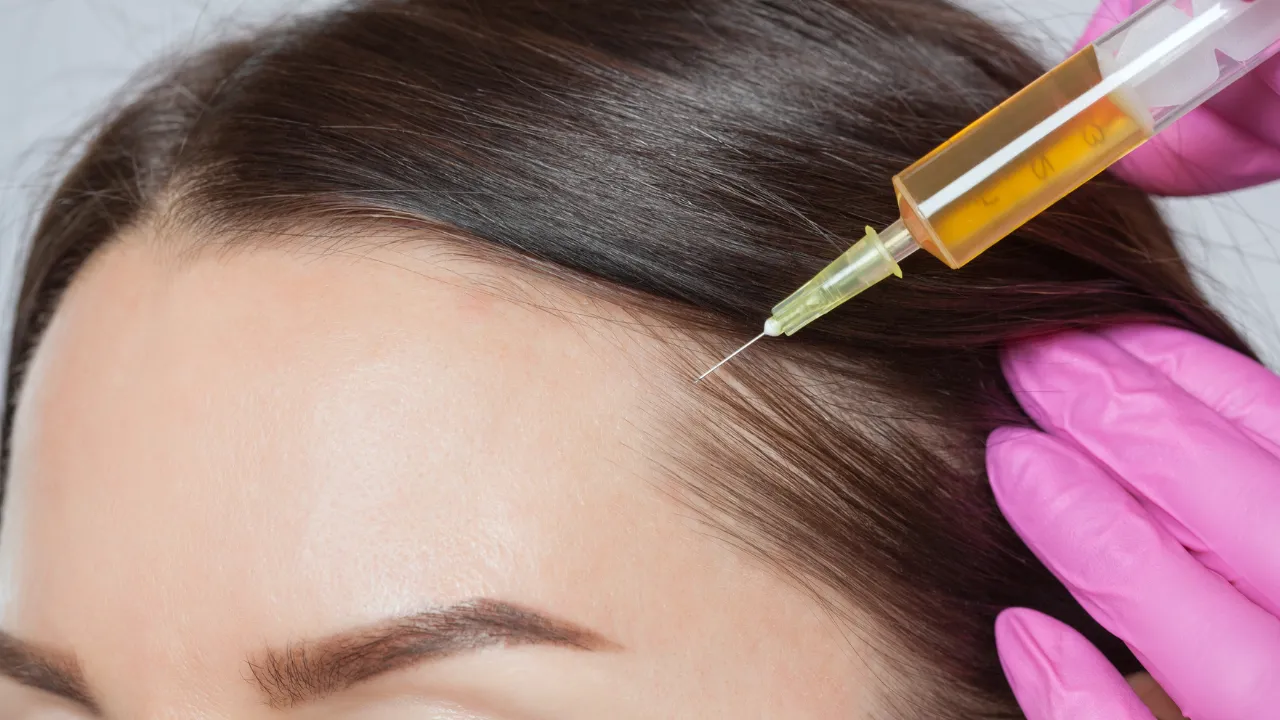
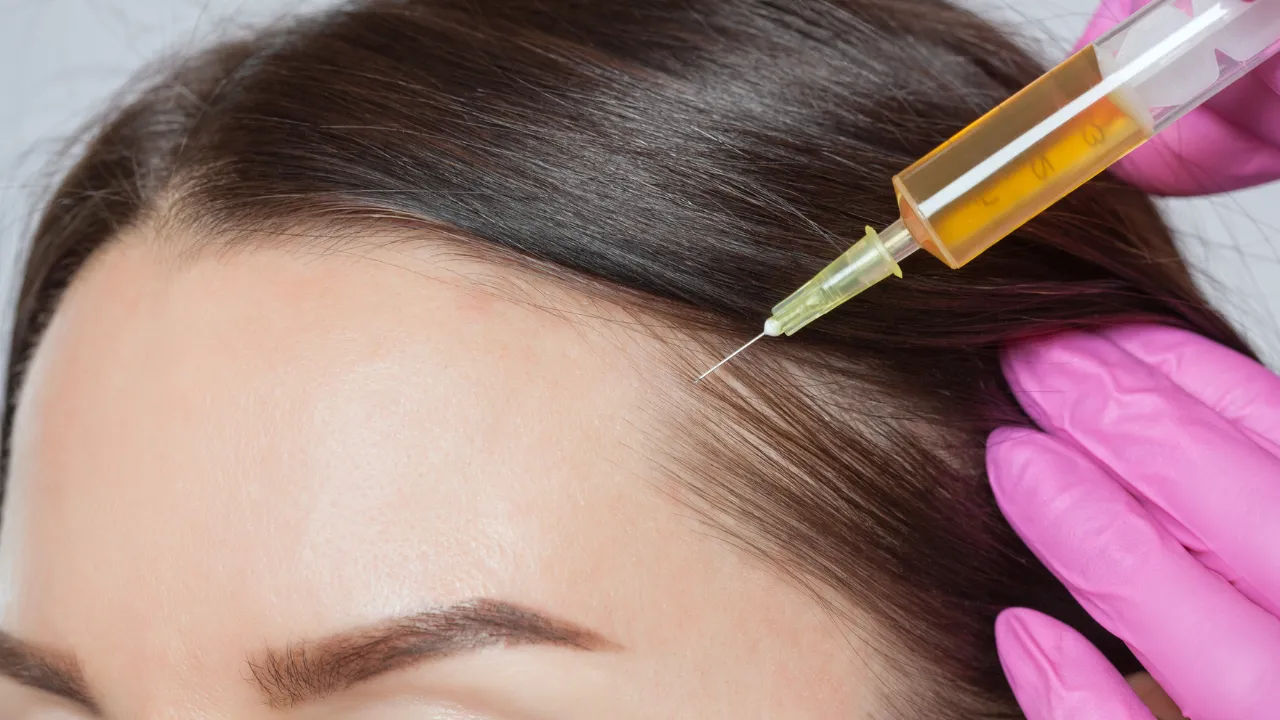
- Effective treatment options include medications like finasteride and minoxidil, PRP therapy, and, in advanced cases, hair transplantation performed by specialists such as Dr. Kopelman.
Testosterone and Hair Loss in Men and Women
Testosterone and Hair Loss in Males (Male Baldness from Testosterone)
In men, testosterone converts into DHT, which attaches to hair follicles. For those genetically sensitive, this leads to male baldness from testosterone and eventually male pattern hair loss. The hair thins over time, creating a receding hairline or crown loss.
Not every man with higher testosterone develops baldness. Genetics, scalp sensitivity, and overall health all play a role. Two men with the same level of testosterone can experience hair loss in very different ways.
Male pattern baldness is the most recognized form of androgenetic alopecia. It follows a predictable path, starting at the temples or crown, and worsens over time if untreated.
Testosterone and Hair Loss in Females and Hair Growth in Females
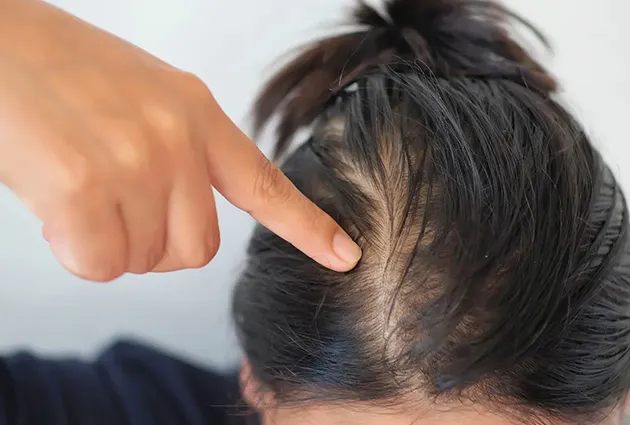
Women produce less testosterone, but it still impacts their hair. High levels can cause thinning on the crown, often seen with PCOS. Low levels may also reduce density, especially after menopause.
Some women improve with balanced hormone therapy that helps stimulate hair growth. In women, this condition is often referred to as female pattern hair loss, which typically presents as diffuse thinning rather than complete bald spots.
PCOS and menopause strongly affect testosterone levels in women. PCOS can increase androgens, causing thinning of the scalp while also increasing facial and body hair. During menopause, falling estrogen and relative changes in testosterone may trigger gradual shedding.
Does Testosterone Cause Hair Loss?
Testosterone and Loss of Hair Explained
Testosterone itself does not directly cause shedding. The issue lies in its byproduct, DHT, which gradually shrinks follicles. The process of testosterone to DHT conversion is what drives miniaturization in genetically sensitive individuals.
The sensitivity of follicles to DHT is inherited. That is why testosterone and loss of hair vary among individuals. A man with strong genetic resistance can keep his hair even with high hormone levels.
High Testosterone and Baldness vs Low Testosterone and Hair Loss
High testosterone and baldness are linked mainly through DHT conversion. Sensitivity to DHT determines the outcome. Very low testosterone may also trigger thinning.
Is Hair Loss from Low Testosterone Reversible?
Hair loss associated with low testosterone levels may improve when hormone levels are corrected. Results depend on genetics, age, and scalp condition.
Hormonal Treatments and Hair Loss Side Effects
Testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) can accelerate shedding in those predisposed. Misuse of anabolic form of testosterone often worsens loss. Doctors may adjust therapy or add a treatment option such as DHT blockers to protect follicles.
Testosterone and Hair Loss Correlation (Role of DHT)
DHT shortens the growth phase of hair, leading to miniaturization. This correlation explains why some experience hair loss despite normal hormone levels.
Testosterone and Alopecia
Testosterone and alopecia are connected mainly in androgenetic cases. Autoimmune alopecia, however, has different causes and needs other treatments.
Scientific Evidence on Testosterone and Hair Follicles
Research published in Nature confirms that androgens regulate stem cell activity in hair follicles. DHT binds more strongly to receptors than testosterone, explaining why blocking it is a proven therapeutic approach.
Can Hair Grow Back While Taking Testosterone?
Will My Hair Grow Back If I Take Testosterone?
Regrowth is possible if follicles remain active. Patients on testosterone therapy who experience hair loss can still benefit from treatments such as finasteride or minoxidil.
How to Prevent Hair Loss While Taking Testosterone
To protect hair during therapy:
- Consider DHT blockers when recommended.
- Maintain a balanced diet rich in protein and vitamins.
- Reduce stress, which worsens shedding.
- Have regular specialist check-ups.
Lifestyle Factors That Influence Testosterone and Hair Health
Stress, poor diet, and lack of sleep all affect testosterone balance and hair health. Patients who adopt healthy routines often experience hair loss at a slower pace.
Early Signs of Testosterone-Related Hair Loss
Recognizing symptoms early improves outcomes. Key signs include:
- Thinning at the crown or temples.
- A widening part in women.
- Slower regrowth after normal shedding.
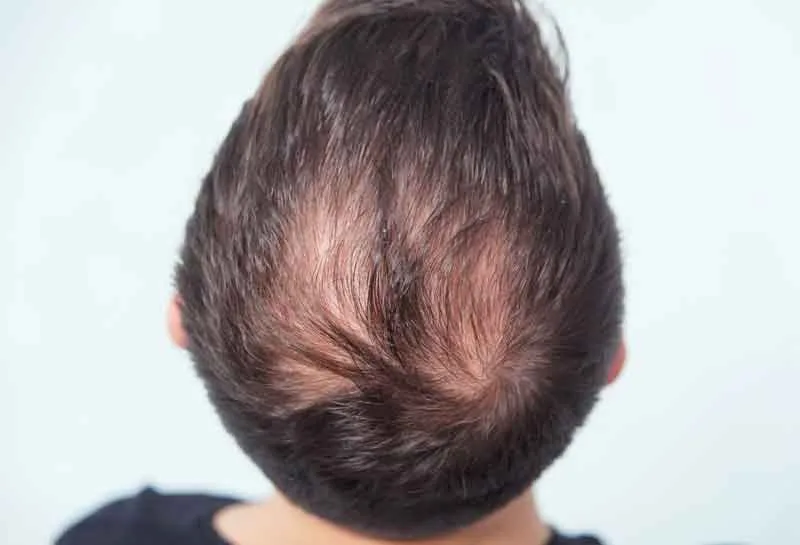
Consulting a hair restoration specialist when these appear allows timely intervention.
Treatments for Testosterone-Related Hair Loss
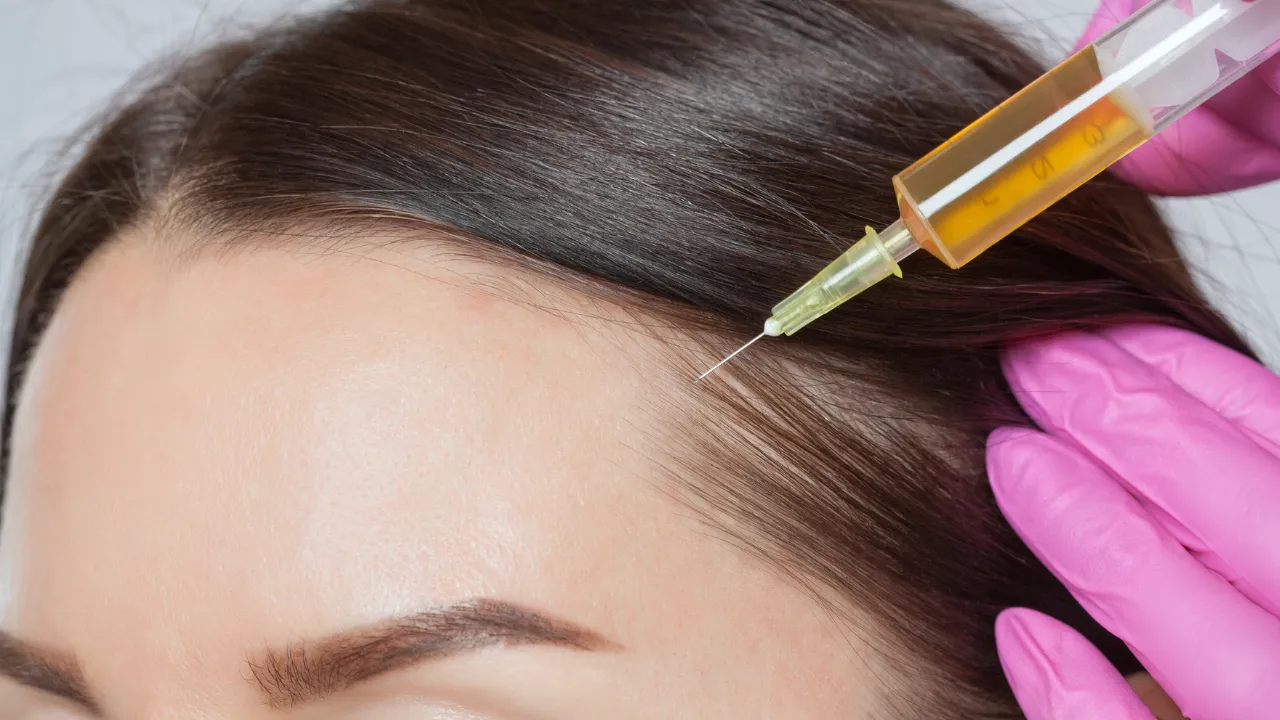
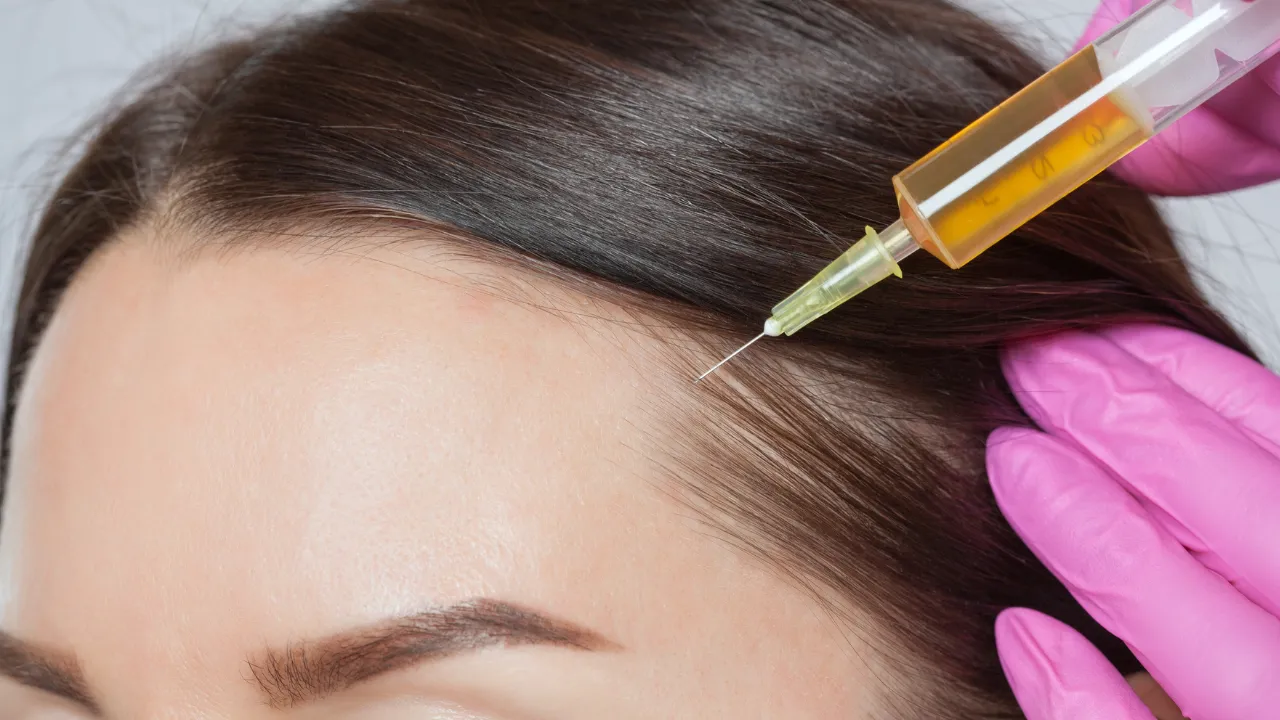
Medical Options (Finasteride, Minoxidil, PRP)
Finasteride lowers DHT, slowing male pattern baldness. Minoxidil stimulates follicles, and PRP uses a patient’s own blood to strengthen growth. Advanced cases may require surgical transplantation by experts such as Dr. Kopelman.
Lifestyle and Dietary Changes
Healthy habits improve scalp health, even if they cannot fully stop androgenetic alopecia. Patients should:
- Eat foods rich in zinc, biotin, and omega-3s.
- Exercise regularly.
- Get enough sleep.
Lifestyle and Nutrition Factors in Hair Health
High sugar diets, poor protein intake, and excess alcohol worsen follicle health. Balanced meals and hydration support long-term scalp health and improve results of other treatments.
When to See a Hair Restoration Specialist
If you experience hair loss despite preventive steps, consulting a specialist is the next step. At Kopelman Hair, we evaluate hormone levels, genetic factors, and scalp health before recommending care.
Dr. Kopelman’s 40+ years of experience in hair restoration ensure patients receive advanced options and proven solutions tailored to their needs.
FAQs on Testosterone and Hair Loss
-
Does testosterone cause hair loss?
Not directly – DHT, a byproduct of testosterone, is responsible.
-
Is hair loss from testosterone permanent?
Not always. If follicles remain active, treatments can restore growth.
-
How can I prevent hair loss on testosterone therapy?
Regular monitoring, medical treatments, and lifestyle changes help reduce risks.
If you are starting to notice hair thinning or want expert guidance on managing testosterone and hair loss, schedule a consultation with Kopelman Hair today. Our team, led by Dr. Kopelman, will evaluate your needs and create a personalized plan to help you protect and restore your hair with proven solutions.