Table of Contents
ToggleAt Kopelman Hair, we help women navigate autoimmune hair loss with advanced treatments and personalized care. Dr. Kopelman leads our team, combining decades of experience and modern techniques to restore hair health. Understanding this condition is the first step toward real solutions.
Key Takeaways
- Autoimmune hair loss in women occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks hair follicles, with conditions such as alopecia areata, lupus, and lichen planopilaris being common causes.
- Symptoms can include patchy or diffuse hair loss, scalp discomfort, and changes in skin or nails, highlighting the need for timely medical evaluation.
- Women with autoimmune disorders face a higher risk of hair loss; however, treatment options, including medications, procedures, and lifestyle changes, can help improve hair regrowth and overall quality of life.
- Treatments may involve corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, or surgical solutions, though they carry potential side effects and require professional guidance.
- Dr. Kopelman emphasizes early diagnosis, personalized care, and supportive strategies to manage hair loss effectively and protect patients’ confidence and well-being.
About Dr. Kopelman and His Expertise
Dr. Kopelman is a board-certified hair restoration surgeon with over 40 years of experience treating autoimmune hair loss in women. His approach blends science, compassion, and advanced technology. Women trust him for personalized care tailored to individual needs. His goal is to improve both medical outcomes and quality of life for his patients.
Understanding Autoimmune Hair Loss
What It Is and Why It Happens
Autoimmune hair loss in women occurs when immune cells mistakenly attack the hair follicles, resulting in thinning or bald spots. Conditions like alopecia areata often trigger this reaction, though other autoimmune disorders such as lupus and lichen planopilaris can also contribute.
Dr. Kopelman explains that T-cells interrupt hair growth, leading to shedding or patchy loss. Knowing this helps women see why treatments aim to reduce inflammation and protect hair follicles.
Illnesses and Autoimmune Conditions Linked to Hair Loss
Several autoimmune diseases can cause hair loss, including:
- Alopecia Areata: Patchy bald spots.
- Alopecia Totalis: Total loss of scalp hair.
- Alopecia Universalis: Loss of scalp and body hair.
- Lupus: Can cause widespread thinning.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: May indirectly lead to hair loss.
- Atopic Dermatitis: A skin disease that also affects the skin and hair.
- Lichen Planopilaris: An inflammatory condition that damages hair follicles and may cause scarring.
Different types of alopecia areata, such as totalis and universalis, demonstrate the varied nature of autoimmune hair loss. Dr. Kopelman notes that women with autoimmune diseases often have a higher risk of hair loss and recommends discussing hair health during medical visits.
Causes and Risk Factors in Women
Hormonal, Genetic, and Environmental Triggers
Autoimmune hair loss is often associated with hormonal fluctuations, genetic predisposition, and stress. Conditions like menopause, thyroid disease, or family history increase risk. Environmental stressors may also play a role. Identifying triggers helps women work with Dr. Kopelman to plan effective prevention and treatment strategies.
Recognizing Symptoms
Common Symptoms in Women
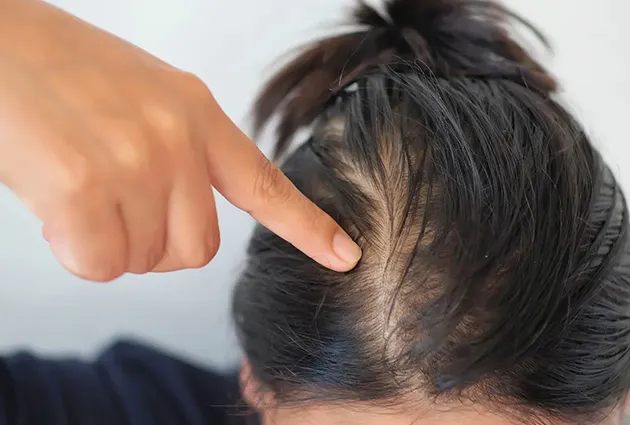
Women may see more hair in brushes, patchy bald spots, or diffuse thinning. Scalp redness, itching, or tenderness can signal inflammation. Dr. Kopelman advises seeing a doctor if hair loss seems sudden or severe. Monitoring these symptoms helps track progress toward hair regrowth.
Patchy vs. Diffuse Hair Loss
Patchy loss creates bald spots, a common symptom of alopecia areata. Diffuse loss spreads thinning across the scalp. Dr. Kopelman uses exams and medical history to distinguish between them and guide treatment options. Early identification increases the chance of successful hair regrowth.
Skin and Nail Changes
Some autoimmune conditions cause nail ridges, pitting, or skin changes. Atopic dermatitis, for instance, affects the skin and can worsen hair shedding. Dr. Kopelman recommends mentioning skin or nail symptoms during consultations. This helps prevent overlooked causes of hair loss.
Treatments and Management
How to Stop or Fix Autoimmune Hair Loss
Treating autoimmune hair loss begins with identifying the underlying cause. Dr. Kopelman emphasizes the importance of medical exams and personalized care. Stress reduction, balanced nutrition, and gentle hair care also help protect hair follicles. Maintaining treatment improves chances for hair regrowth and preserves quality of life.
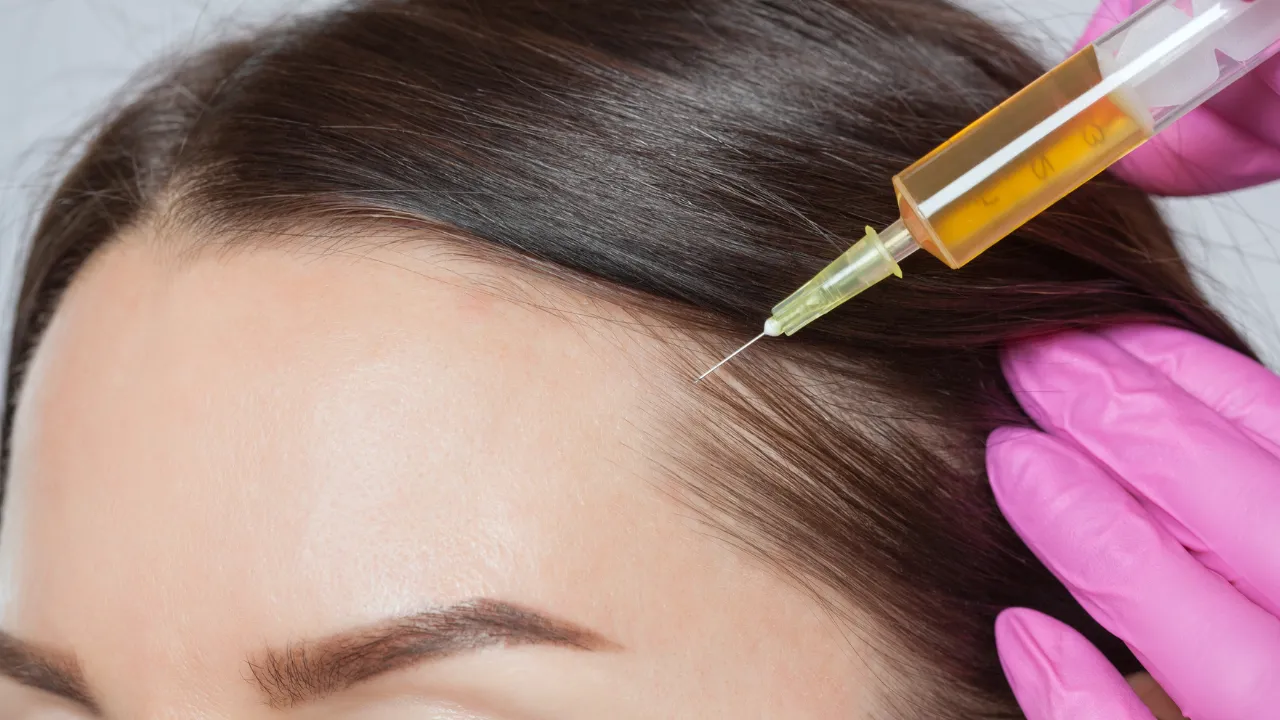
Medications and Medical Treatments
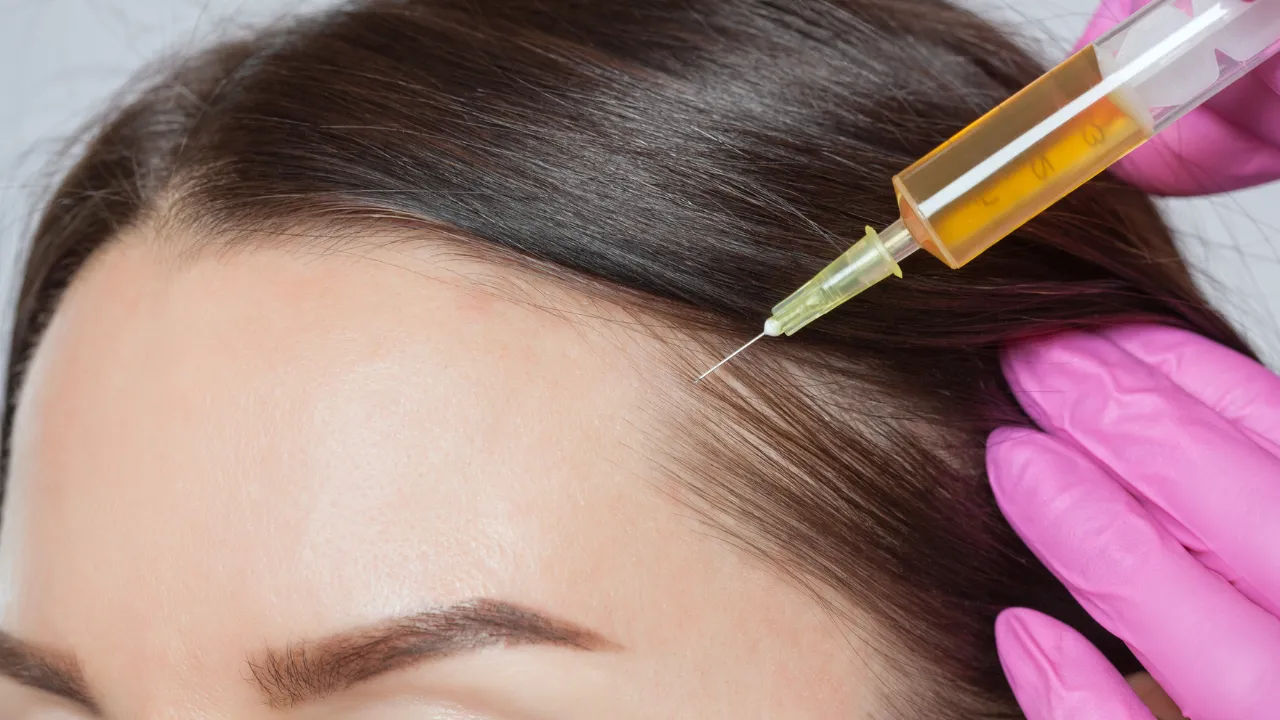
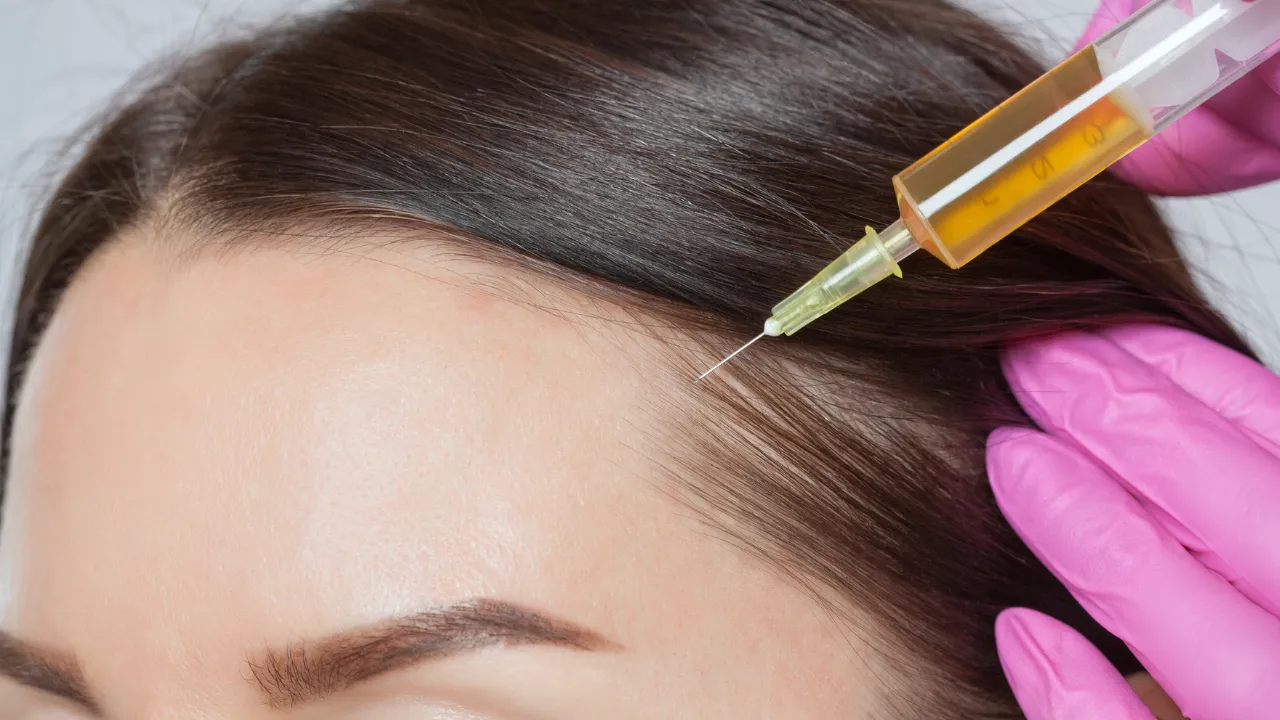
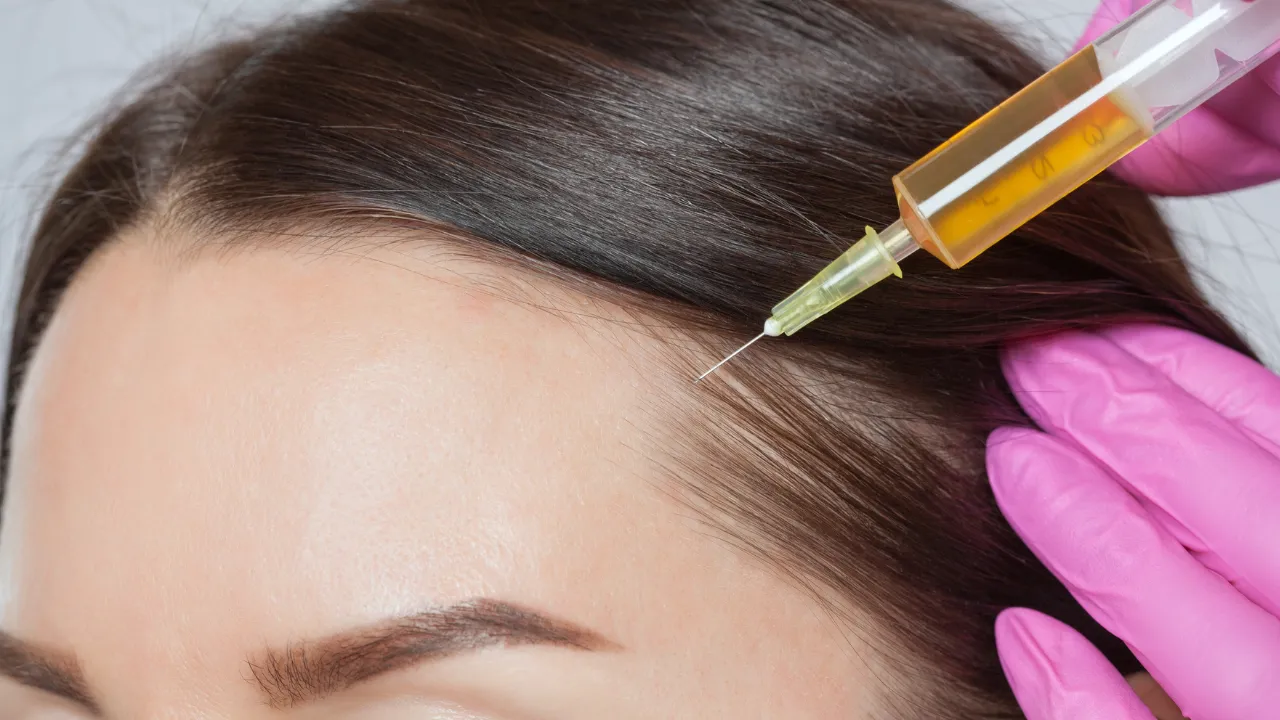
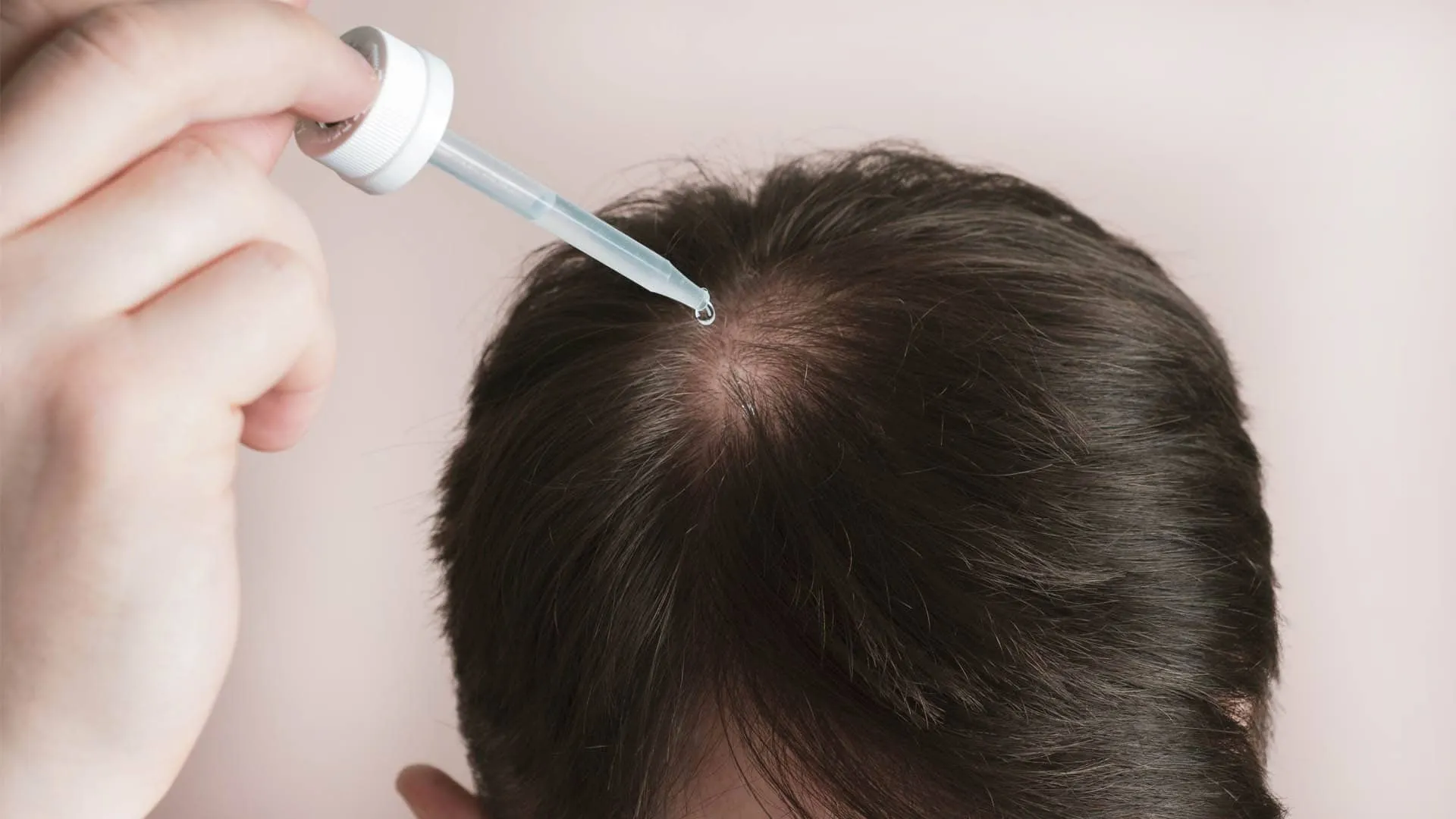
Doctors might use corticosteroid injections, oral immunosuppressants, or topical solutions like minoxidil. The FDA approves various treatments for autoimmune hair loss.
Dr. Kopelman explains that combining approaches often works best, but patients shouldn’t self-prescribe, especially when dealing with hair thinning autoimmune disease. Some treatments carry side effects, so women should discuss risks and benefits with a specialist.
Hair Restoration Procedures
Women experiencing ongoing hair loss may consider surgical options or treatments like scalp micropigmentation. At Kopelman Hair, Dr. Kopelman employs precise techniques to achieve natural-looking results.
Women should discuss their goals and risks before making a decision. Knowing all options helps women choose the best plan for achieving a high quality of life and appearance.
Lifestyle and Coping Strategies
Women can avoid heat styling, harsh chemicals, and tight hairstyles. Balanced nutrition supports hair health, particularly in terms of iron and vitamin D. Dr. Kopelman recommends seeking emotional support, as hair loss can significantly impact confidence. Positive lifestyle changes improve mental health and overall quality of life.
Treatments often take months for results. Dr. Kopelman urges patience and realistic expectations for regrowth. Staying committed to a plan increases the chances of hair regrowth and stability.
Treatment Options for Autoimmune Hair Loss
Women have several treatment options, including medications, lifestyle changes, and procedures. Dr. Kopelman advises discussing all choices with a specialist for the best outcome. Exploring these options can help reduce hair loss and improve quality of life.
When to See a Doctor
Doctors use exams, scalp biopsies, and blood tests to diagnose autoimmune hair loss. Dr. Kopelman says that early care improves the chances of regrowth. Women should seek medical help if hair loss persists or is accompanied by other health symptoms. Timely treatment minimizes permanent hair loss and protects the overall quality of life.
If you’re experiencing autoimmune hair loss or want personalized guidance, schedule an appointment with Dr. Kopelman at Kopelman Hair to explore tailored solutions and start your journey toward hair regrowth and restored confidence.