Table of Contents
ToggleHair loss can be distressing, especially when the hair is forcefully removed. If you’ve ever had hair pulled out from the root, you may wonder whether it will grow back or if permanent damage has occurred.
At Kopelman Hair, we treat hair loss at every stage, combining decades of experience with trusted medical insight to help patients understand and recover.
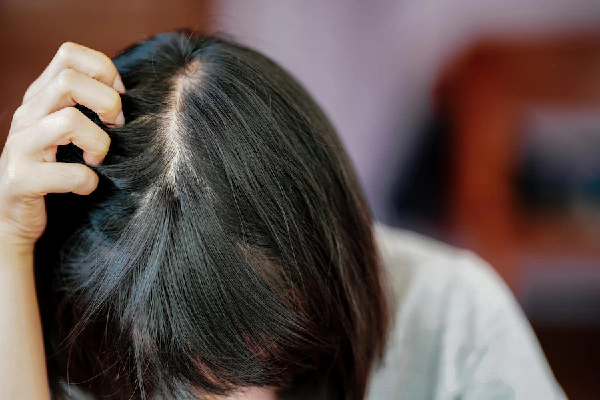
The hair you see above the skin is the shaft, while the living part sits inside the follicle beneath the skin. The bulb is at the base of the follicle and contains cells that produce the hair shaft. Surrounding the follicle are structures, including the root sheath, that supply blood and nutrients.
Understanding these parts makes it easier to know what happens when hair is pulled from the root.
Key Takeaways
- Hair can regrow after being pulled from the root if the follicle remains intact, with signs including no scarring and a healthy bulb.
- Regrowth often occurs within two to three months, but repeated pulling or certain conditions can cause permanent follicle damage.
- The hair bulb is part of the strand, not the follicle, so its presence does not mean the follicle is gone.
- Prevention and scalp care, such as avoiding tight hairstyles and using gentle products, help protect follicle health.
- Behavioral conditions like trichotillomania require both hair loss treatment and mental health support for lasting improvement.
Can Hair Grow Back After Being Pulled from the Root?
Yes — in most cases, hair will grow back after being pulled from the root if the follicle is not permanently damaged.
Will It Grow Back? Signs and Recovery Factors
In most cases, hair can grow back after being pulled from the root. Regrowth depends on whether the follicle is intact and undamaged. Hair grows from follicles beneath the skin. If these structures are unharmed, they can produce new strands of hair within weeks.
Signs that support regrowth include:
- No visible scarring
- Mild or no inflammation
- A small white bulb at the end of the pulled hair
Repeated pulling or trauma can inflame or scar the follicle, reducing the chance of regrowth.
Regrowth Timeline and Expectations
Regrowth follows the hair growth cycle:
- Anagen phase: Active growth stage when the follicle produces new hair.
- Telogen phase: Resting stage when hair is shed and replaced, also known as the resting phase.
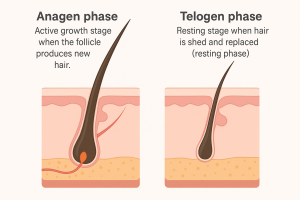
New growth often appears in 2 to 3 months. The rate varies with age, health, and types of hair. At Kopelman Hair, we guide patients through realistic expectations and monitor recovery when pulling a hair follicle out is frequent.
Research shows that healthy follicles can re-enter growth within weeks if not scarred. Studies on traction alopecia confirm that repeated trauma is the main cause of irreversible damage.
Does Pulling the Bulb Mean Permanent Loss?
The bulb is part of the hair strand and naturally comes out when the hair completes its cycle. Permanent loss occurs if the follicle beneath the skin is scarred or destroyed, often after repeated trauma, certain conditions, or when scar tissue develops in a balding area.
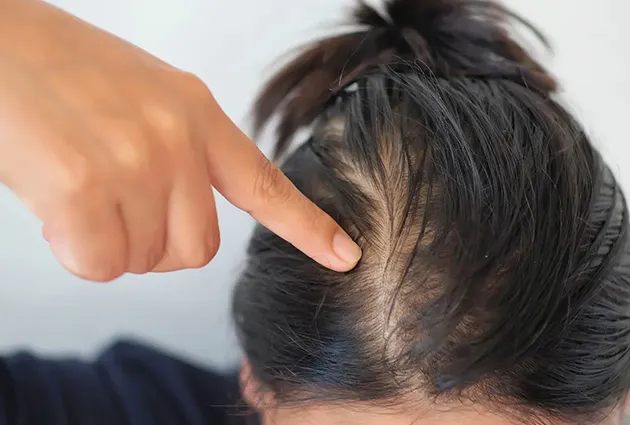
What Hair Pulled from the Root Looks Like
Identifying the Hair Bulb
When hair is pulled from the root, you might see a soft, white bulb at the end. This club-shaped structure anchors the strand within the follicle. The bulb is part of the hair shaft, not the follicle.
Seeing the bulb doesn’t mean permanent damage. It often shows that the hair was in the telogen phase and not ripped from the growing anagen phase.
Root Pulling vs Shedding: Key Differences
Shedding:
- Happens daily as part of the hair cycle
- Hair falls out naturally
- Bulb may be present, but no pain or inflammation
Root pulling:
- Caused by force
- May cause redness or sensitivity
- Can damage follicles if frequent
Myths About Hair Pulled from the Root
Is Follicle Damage Permanent?
What Happens When the Hair Bulb Is Pulled Out
When the bulb is pulled, the follicle may be disturbed. In single instances, the follicle usually heals. Repeated pulling can degrade the structure.
This may lead to:
- Shorter regrowth cycles
- Finer, weaker hair
- Delayed or stalled regrowth
Risks of Repeated Hair Follicle Pulling
Frequent pulling can cause scarring, permanently destroying follicle function. This is known as traction alopecia and is common with tight hairstyles or trichotillomania.
Early signs include thinning patches, reduced density, and tenderness. At Kopelman Hair, Dr. Kopelman evaluates patients with chronic hair-pulling to prevent further loss.
When Hair Follicles Stop Producing Hair
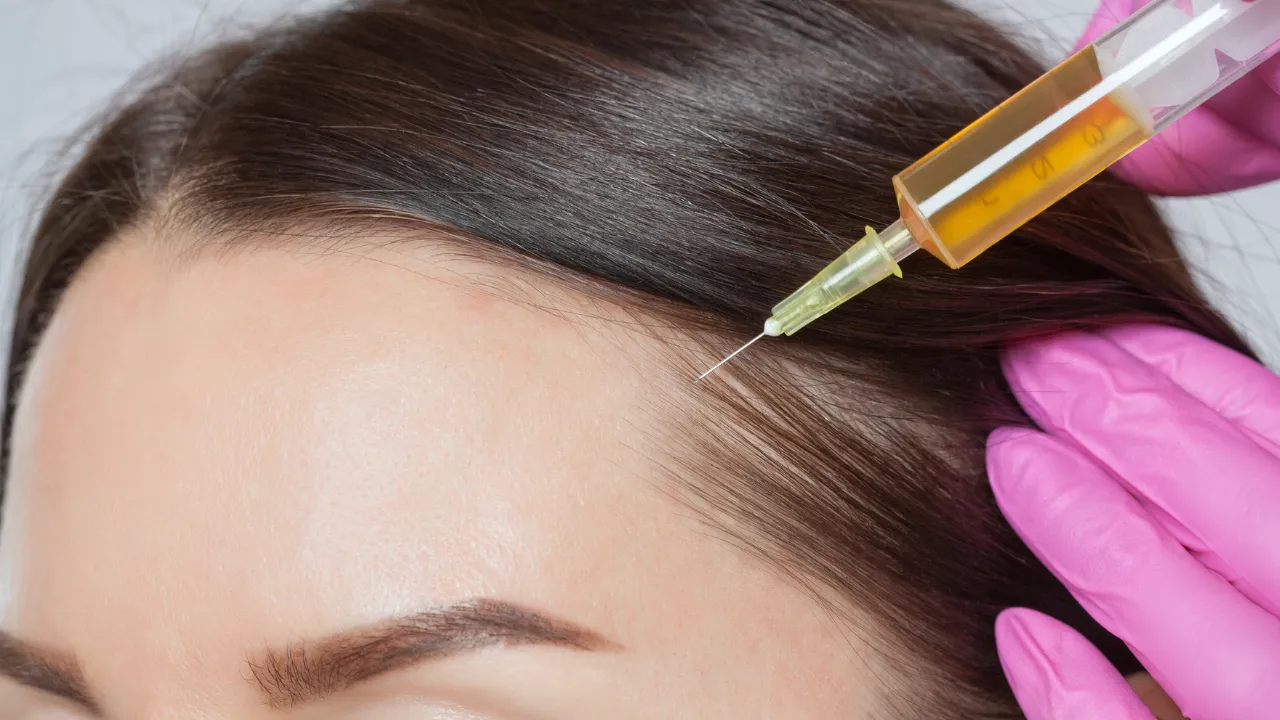
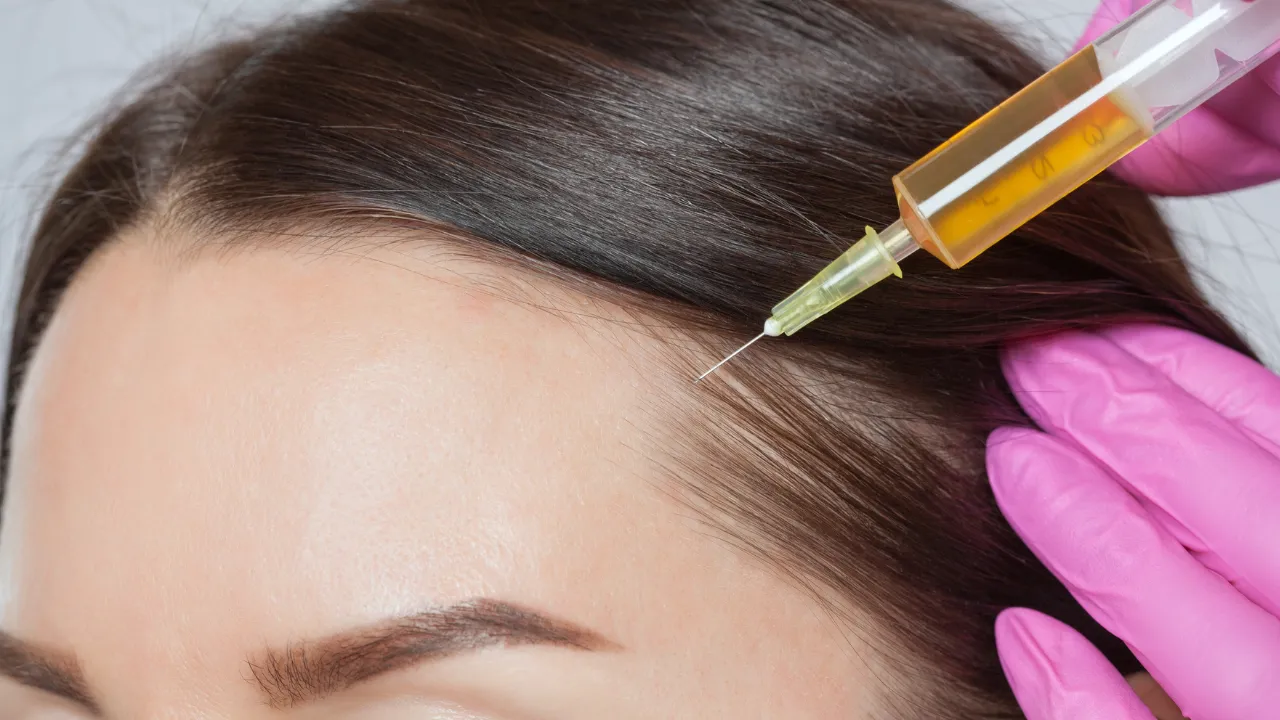
Once a follicle scars, hair stops growing in that area. Topical treatments or supplements will not restore growth when scar tissue forms. Hair transplantation may be needed to restore density.
If areas where hair was pulled do not regrow after several months, consult a specialist.
Common Conditions That Affect Hair Regrowth After Root Pulling
Conditions that can make regrowth harder include:
- Folliculitis
- Alopecia areata
- Psoriasis or seborrheic dermatitis
If you notice itching, flaking, or redness with hair loss, a dermatologist can diagnose and treat the cause.
How to Treat and Prevent Damage
Treatment Options After Pulling Hair by the Root
If hair was pulled recently, focus on calming the area and supporting regrowth.
Consider:
- Cool compress
- Avoiding tight hairstyles
- Using topical minoxidil under supervision
If hair bulb-pulling events are frequent, consult a hair loss expert to reduce side effects like irritation or uneven regrowth.
Scalp Care for Recovery
Basic care tips:
- Wash gently with mild shampoo
- Avoid harsh brushing
- Eat foods rich in omega-3 and biotin
When to See a Hair Specialist
Seek help if:
- No regrowth after 3 months
- Thinning or bald patches
- Habitual pulling
A specialist can examine follicles, detect scarring, and recommend treatments.
Quick self-check:
- Look for baby hairs
- Check for redness or scarring
- Monitor changes for 3 months
Daily Habits to Protect Hair Follicles
Habits that help:
- Avoid tight hairstyles
- Use a wide-tooth comb
- Keep the scalp clean
- Maintain a healthy diet
Why Do People Pull Out Their Hair?
What Is Trichotillomania?
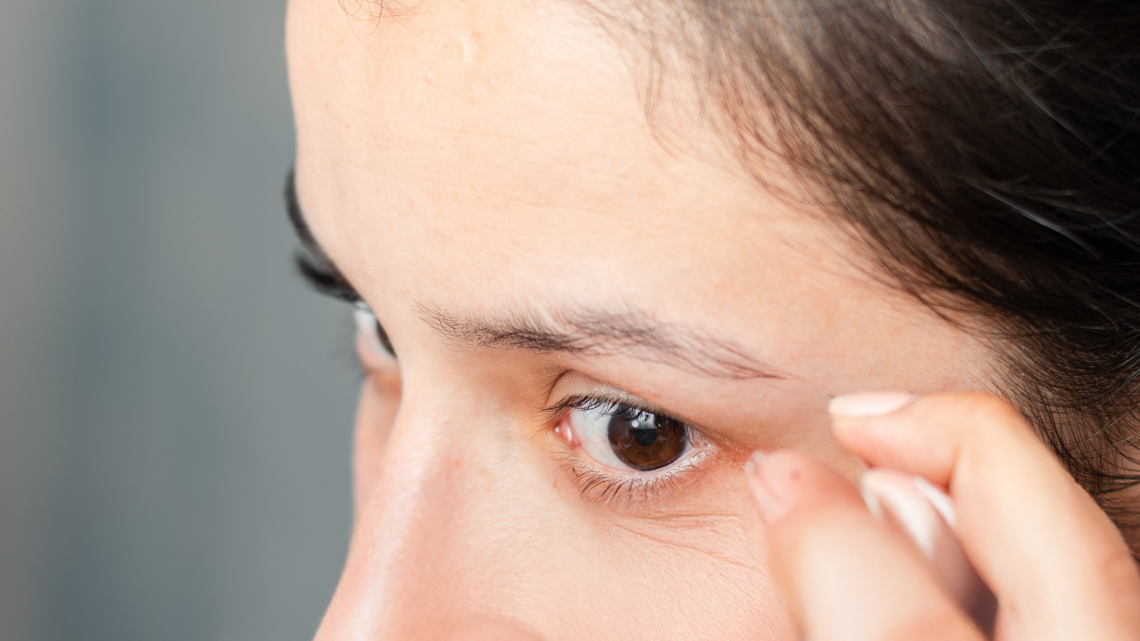
Trichotillomania is an urge to pull out hair, often linked to anxiety or stress. It can affect the scalp, eyebrows, eyelashes, and more.
In cases where eyebrow pulling leads to permanent thinning or scarring, some patients explore options like eyebrow hair restoration in NYC to rebuild natural brow density.
Common Emotional Triggers
Triggers include stress, boredom, sensory needs, and trauma. Recognizing these patterns is the first step to managing them.
Managing urges may involve habit reversal training, stress reduction, and therapy. These approaches are supported by The TLC Foundation for Body-Focused Repetitive Behaviors.
When to Seek Professional Help
If hair-pulling causes visible damage or distress, speak with a professional. At Kopelman Hair, we treat hair loss and coordinate with mental health experts when needed.
At Kopelman Hair, we understand that hair loss from pulling can be temporary or long-term. With over 40 years of experience, Dr. Kopelman and his team offer care backed by science. Dr. Kopelman is a board-certified hair restoration surgeon with expertise in surgical transplants, regenerative therapies, and scalp diagnostics.
If you are experiencing hair loss or suspect damage from pulling, schedule a consultation with Kopelman Hair today. Our team will assess your scalp health, identify the cause, and create a treatment plan tailored to your needs so you can restore your hair with confidence.