Table of Contents
ToggleInflammation and hair loss are closely linked, and understanding this connection is crucial for addressing hair thinning. At Kopelman Hair, we offer personalized treatments for individuals struggling with inflammation-induced hair loss, backed by over 40 years of expertise.
This article explores how inflammation can lead to hair loss, how it affects the scalp, and the most effective treatment options available.
Key Takeaways:
- Inflammation can significantly affect hair follicles and disrupt the hair growth cycle, leading to thinning and shedding.
- Early detection is vital in preventing permanent hair loss and further follicle damage.
- Effective treatments include both medical treatments and lifestyle changes such as diet, stress management, and topical treatments.
- Consult a specialist like Dr. Kopelman to develop a personalized hair loss treatment plan for inflammation-related hair loss.
Can Inflammation Cause Hair Loss?
Inflammation and hair loss are more connected than many realize. Chronic inflammation can lead to hair loss by disrupting the natural hair growth cycle, causing thinning and shedding.
When inflammation occurs in the scalp, it damages hair follicles, weakening their ability to grow hair. This inflammation can also trigger conditions like male pattern baldness or worsen other types of hair loss.
The Impact of Inflammation on Hair Follicles
Inflammation affects hair follicles by reducing their ability to grow healthy hair. Inflammatory chemicals can damage and shrink hair follicles, making them less effective at producing new hair. If the inflammation persists, it can result in scarring alopecia, which can permanently damage hair follicles and prevent hair regrowth.
Autoimmune Diseases and Their Role in Hair Loss
Certain autoimmune diseases, like alopecia areata, can trigger scalp inflammation, leading to hair loss. The immune system mistakenly attacks hair follicles, causing them to become inflamed and weakened, leading to shedding. If left untreated, autoimmune diseases can result in scarring alopecia, a condition that can lead to permanent hair loss.
Recent Studies on Inflammation and Hair Loss:
Recent research suggests that inflammation significantly disrupts the hair growth cycle. A study published in the Journal of Clinical Investigation found that inflammation in the scalp activates immune cells that target hair follicles, leading to thinning or shedding. Managing inflammation early on can help prevented hair loss and encourage healthier hair regrowth.
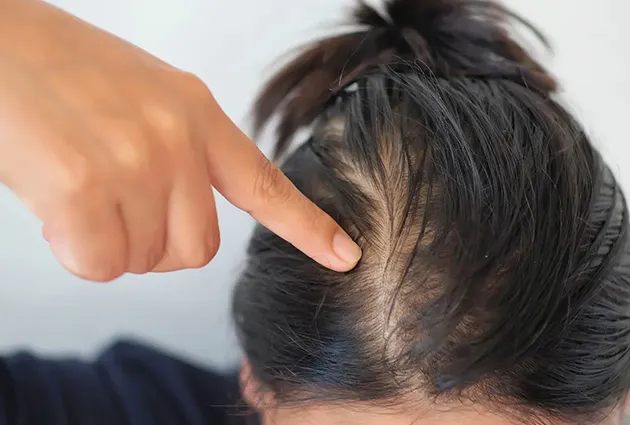
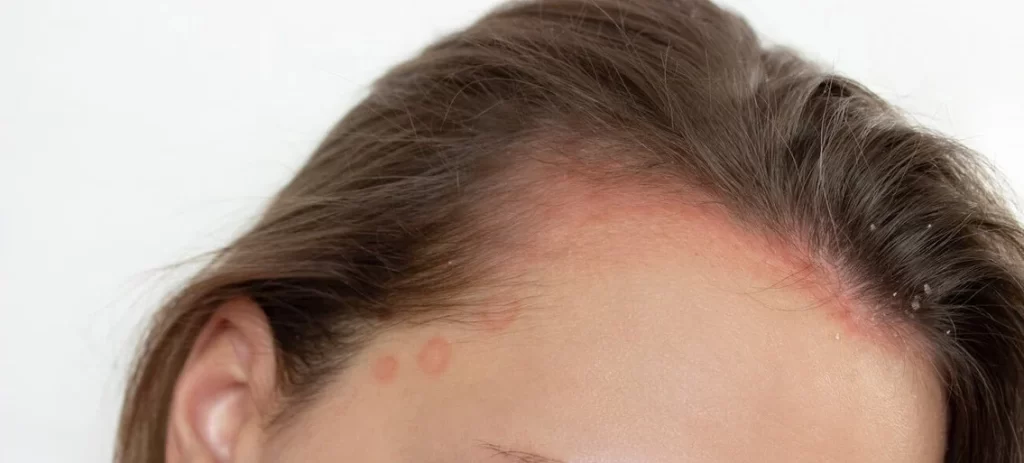
Inflammatory Hair Loss Symptoms: How to Recognize It
Recognizing the symptoms of inflammation-induced hair loss is essential for addressing the problem early. Common symptoms include gradual thinning, increased shedding, and noticeable bald patches.
Inflammation can also cause scalp discomfort, redness, or swelling. If left untreated, this can contribute to scarring alopecia and permanent hair loss.
Early Signs of Inflammation-Induced Hair Loss
Thinning at the crown or temples, with a noticeable decrease in hair density, is often an early sign of inflammation-related hair loss. Prompt treatment is necessary to prevent hair loss from becoming permanent.
Frequently Asked Questions about Inflammation and Hair Loss
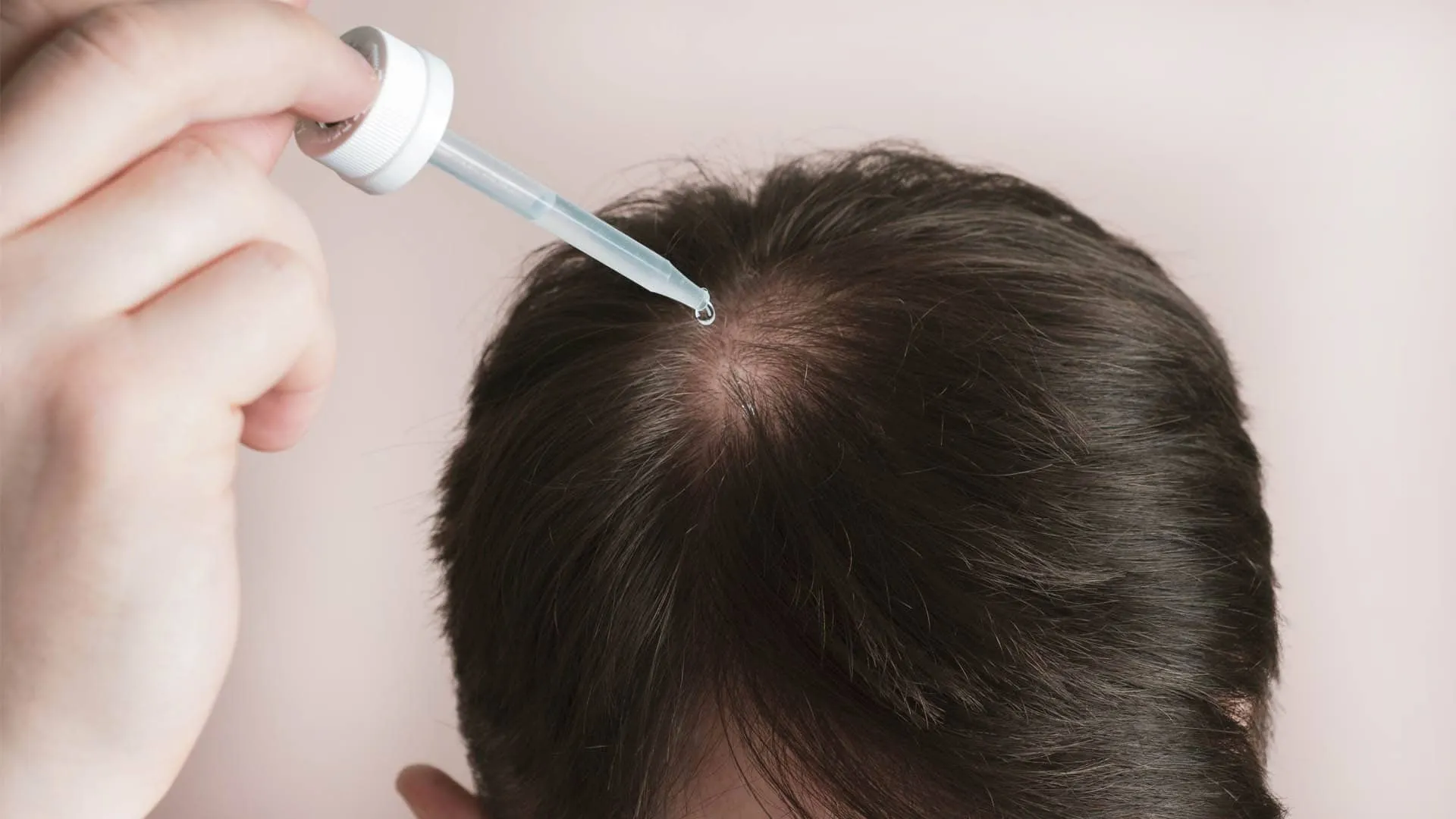
Effective Treatments for Inflammation-Related Hair Loss
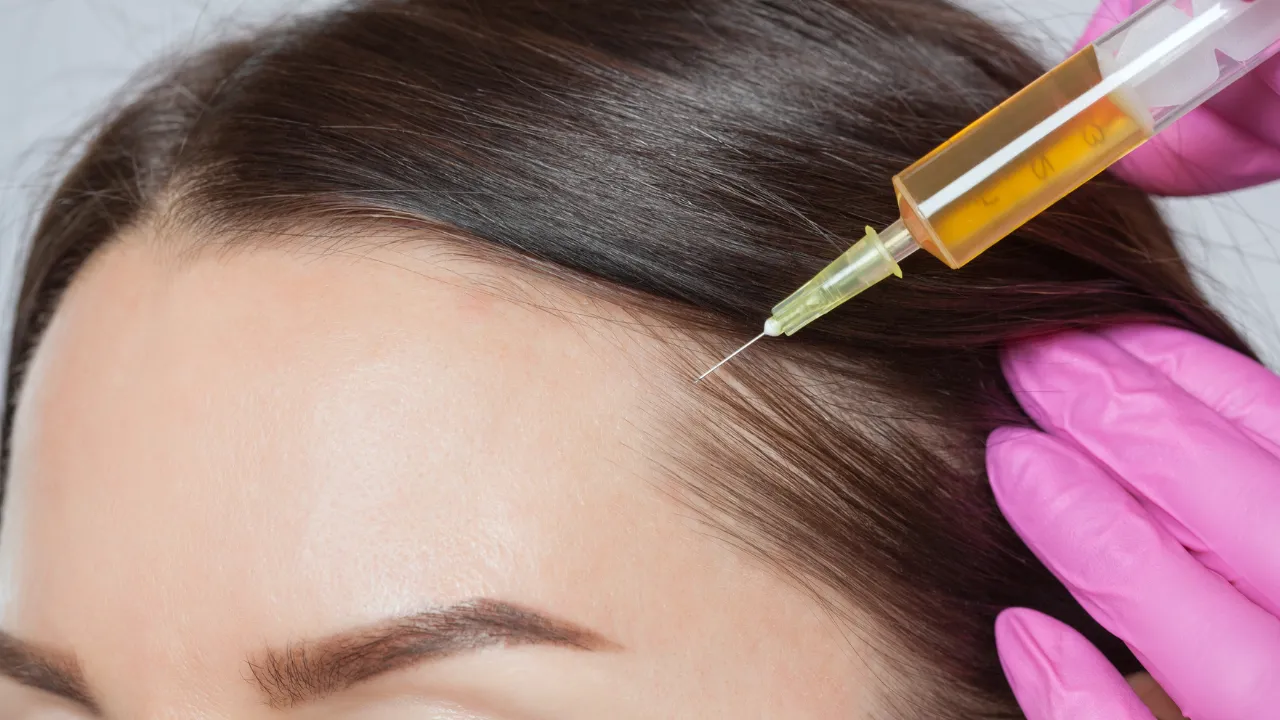
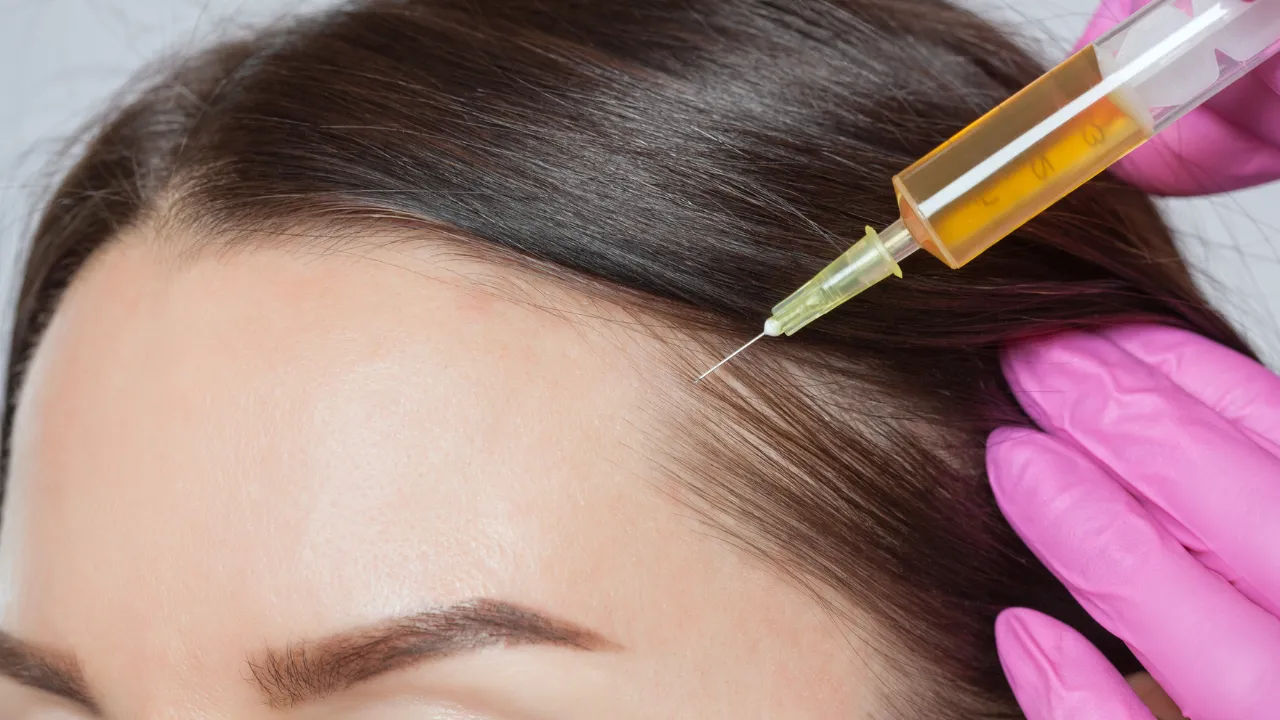
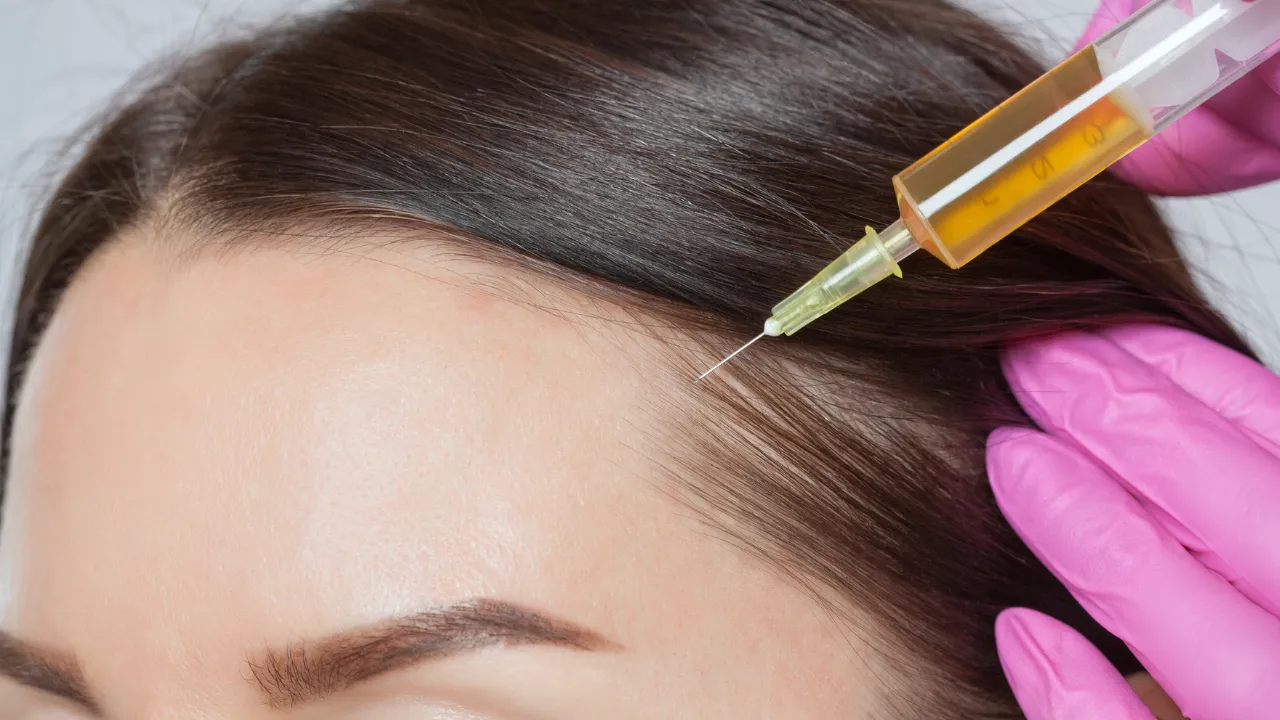
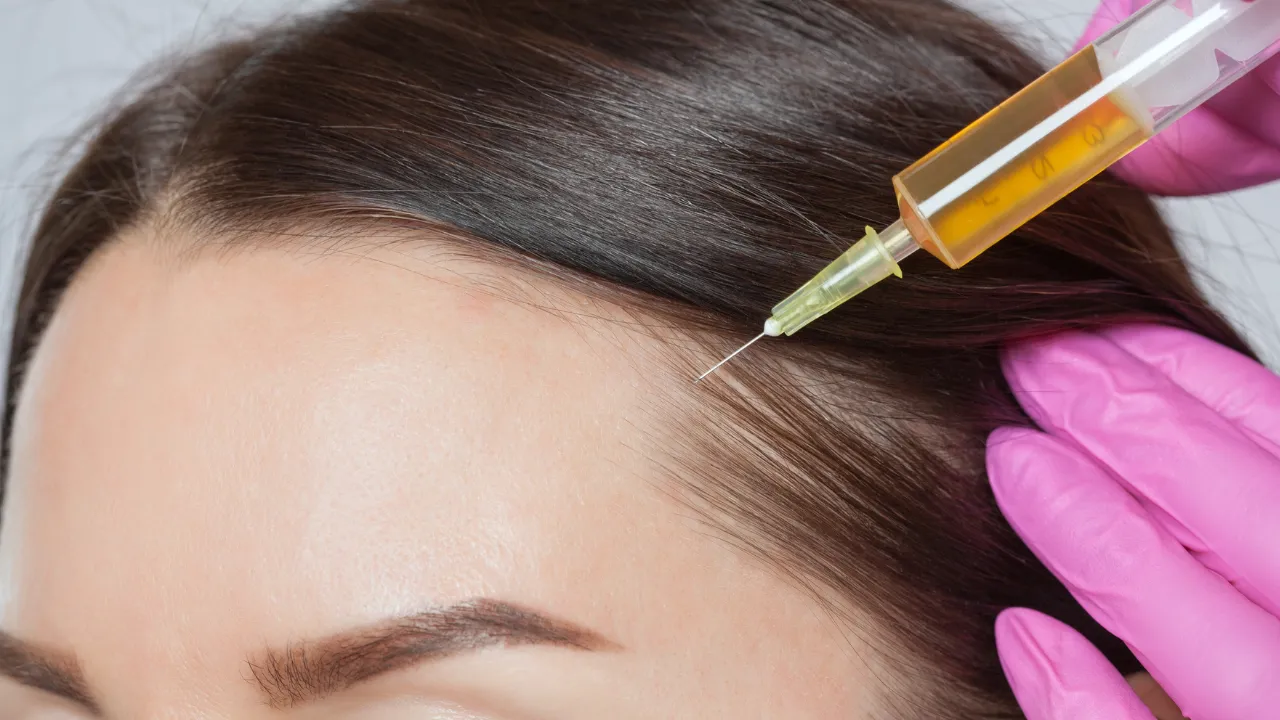
Treatment options include anti-inflammatory medications, topical steroids, and PRP (platelet-rich plasma) therapy, which help reduce inflammation in the scalp and encourage hair regrowth. In some cases, medications like minoxidil are also used to treat hair loss and stimulate growth.
Topical Solutions and Anti-Inflammatory Diets
Topical treatments such as corticosteroids or minoxidil are recommended to combat scalp inflammation and encourage hair regrowth. Pairing these with an anti-inflammatory diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and vitamins can support hair health and reduce inflammation.
Is Inflammatory Hair Loss Reversible?
If addressed early, inflammatory hair loss is often reversible. Effective treatments can restore hair growth, especially when inflammation is controlled before causing irreversible damage.
Managing Chronic Inflammation for Hair Regrowth
Chronic inflammation requires ongoing management. Regular use of anti-inflammatory treatments, combined with a balanced diet and stress reduction, can help promote long-term hair regrowth and prevent further hair loss.
The Role of Diet in Inflammation and Hair Loss
Diet plays a crucial role in managing inflammation, which can directly impact hair growth. Foods high in antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids, and vitamins can reduce inflammation and promote a healthy scalp.
- Anti-Inflammatory Foods: Omega-3-rich foods like salmon, flaxseeds, and walnuts help reduce inflammation.
- Vitamins and Minerals: Vitamins A, C, and E support hair health by reducing oxidative stress.
- Foods to Avoid: Consuming processed foods, sugar, and trans fats can contribute to inflammation, which in turn worsens hair loss.
The Link Between Stress and Inflammation-Induced Hair Loss
Stress is a major contributor to inflammation and hair loss. Stress triggers the release of cortisol, which increases inflammation in the scalp, leading to hair thinning and shedding.
- How Stress Affects Hair: Chronic stress can lead to a condition called telogen effluvium, where hair follicles prematurely enter the shedding phase. Inflammation from stress can also contribute to hair loss in women.
- Managing Stress: Practices like yoga, meditation, and regular exercise help reduce stress and its inflammatory effects on hair health.
Preventative Measures for Inflammation and Hair Loss
Preventing inflammation-related hair loss is just as important as treating it. Here are practical steps to reduce inflammation and promote hair health:
- Scalp Care Routine: Keep your scalp clean with gentle shampoos and moisturizing treatments.
- Avoid Irritants: Minimize exposure to harsh chemicals in hair products that can aggravate inflammation.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Obesity increases inflammation. Maintaining a healthy weight through regular exercise and a balanced diet helps reduce inflammation.
- Regular Check-Ups: Routine scalp checks allow early detection and intervention before problems escalate.
The Impact of Hormones on Inflammation and Hair Loss
Hormonal changes, especially those related to thyroid dysfunction, pregnancy, and menopause, can contribute to scalp inflammation and hair loss.
- Thyroid and Hair Loss: Hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism can lead to inflammation in the scalp, resulting in hair thinning.
- Hormonal Fluctuations: Changes in hormones during pregnancy and menopause can increase inflammation, leading to hair shedding.
When to Seek Professional Help for Hair Loss
If you experience persistent hair thinning or scalp discomfort, it’s time to consult a specialist. Dr. Kopelman can help identify the cause of your hair loss and recommend the most effective treatment options.
Consulting Specialists for Inflammation-Induced Hair Loss
A specialist can determine whether inflammation is causing your hair loss. They may recommend treatments like PRP therapy or corticosteroid injections to reduce inflammation and restore hair growth.
Which Autoimmune Diseases Are Linked to Hair Loss?
Autoimmune diseases like alopecia areata and lupus cause scalp inflammation and hair loss. Early intervention is crucial to address both inflammation and the underlying disease.
By following this comprehensive approach to inflammation and hair loss, you can take the necessary steps to address the issue. At Kopelman Hair, we provide personalized care to help you restore your hair and improve your scalp health.
If you’re experiencing symptoms of inflammation-related hair loss, contact us for a consultation and let Dr. Kopelman guide you through effective treatments.