Table of Contents
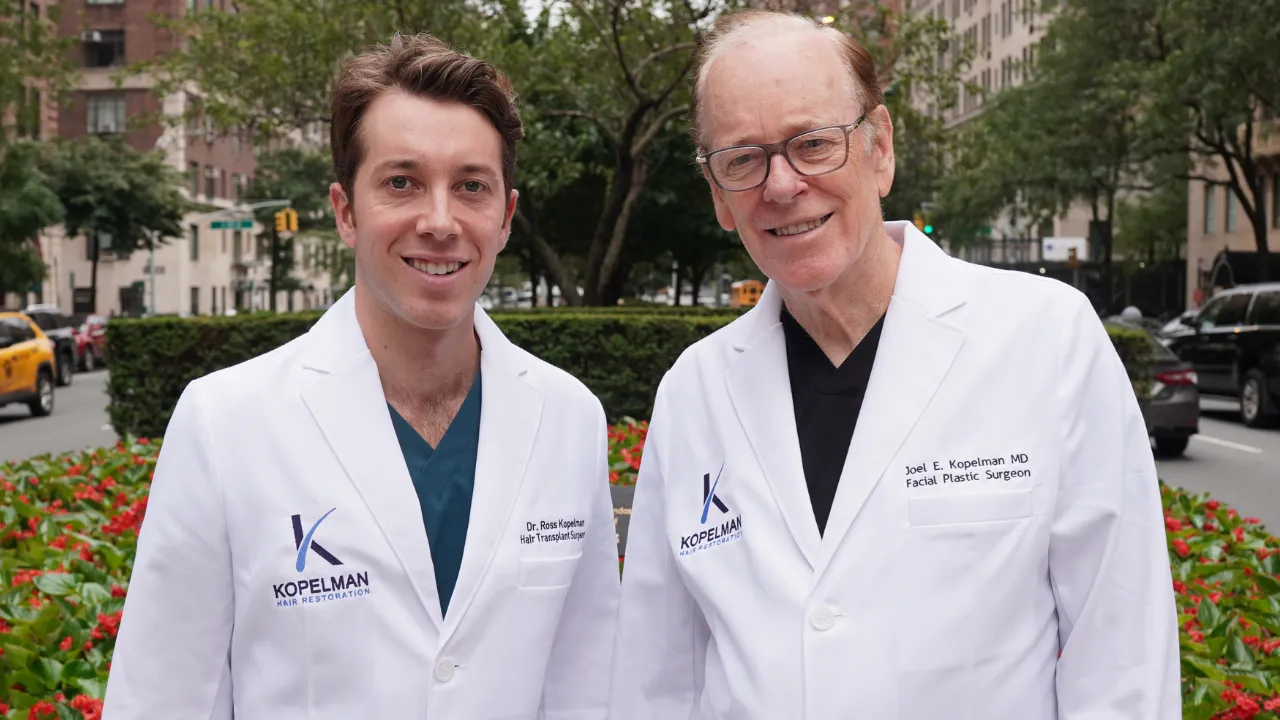
ToggleHair loss affects millions of people worldwide, whether due to male pattern hair loss or female pattern hair loss. Advanced treatments like minoxidil (Rogaine) and finasteride (Propecia) provide effective solutions to combat this issue. Dr. Kopelman is a well-known expert in hair restoration. He focuses on personalized treatments that help restore confidence and promote hair regrowth.
In this guide, we will examine the differences between these treatments, discuss their benefits and possible side effects, and help you choose the best option for your needs.
Understanding Hair Loss and Why It Happens
Hair loss occurs for a variety of reasons, including genetics, stress, aging, and hormonal imbalances. The most common cause is the hormone dihydrotestosterone (DHT), which is derived by converting testosterone. DHT binds to hair follicles, shrinking them and slowing down the hair growth cycle. Over time, this leads to thinning and eventual hair loss.
There are different types of hair loss, such as androgenetic alopecia (commonly known as male pattern hair loss) and female pattern hair loss. Understanding the type of hair loss you’re experiencing helps determine the most effective treatment options, whether it’s minoxidil, finasteride, or a combination of both.
How Minoxidil and Finasteride Work
Minoxidil: Stimulating Hair Growth
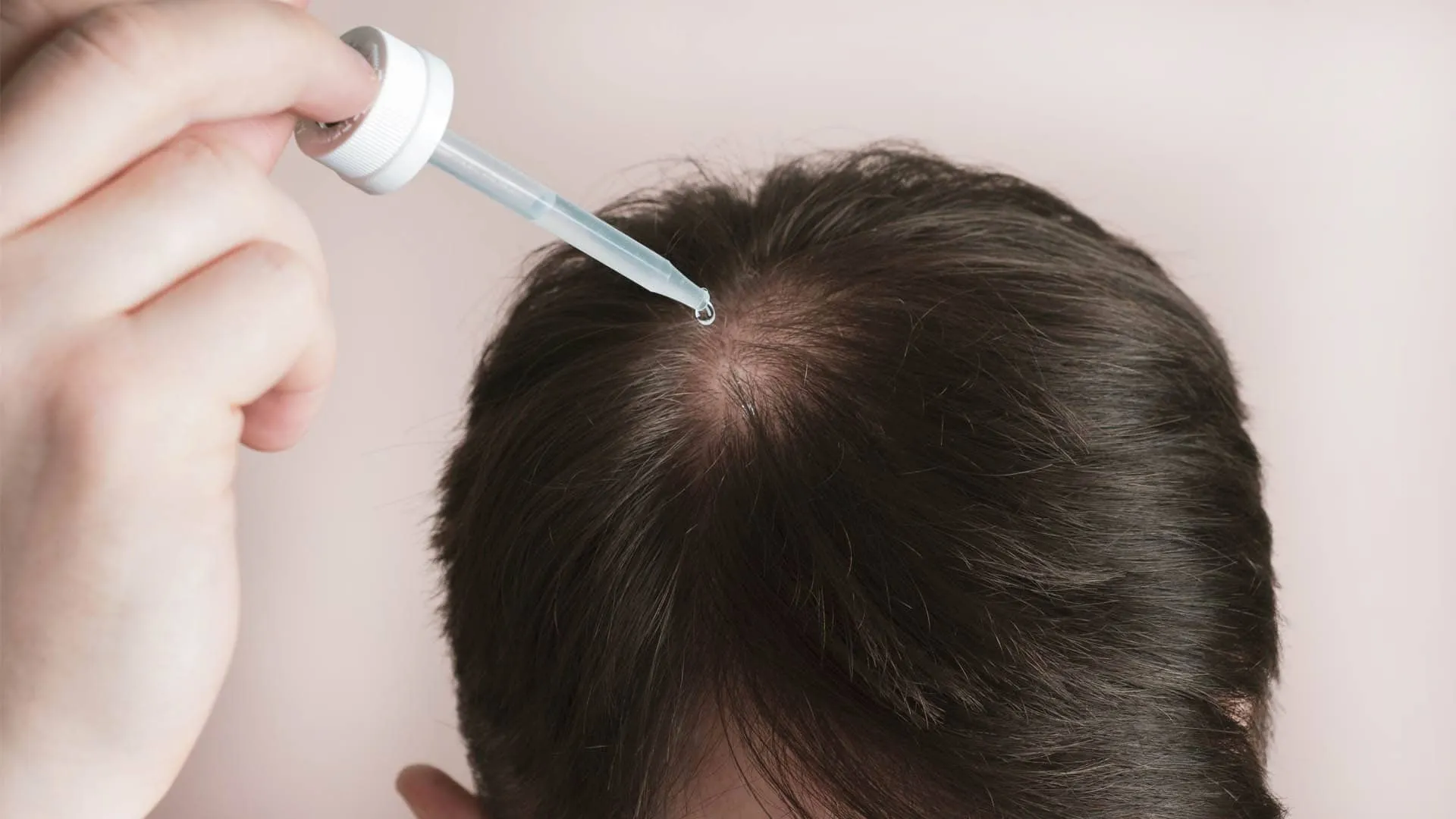
Minoxidil is a topical solution that works by widening blood vessels in the scalp, improving blood flow to hair follicles. This process delivers more oxygen and nutrients, stimulating hair growth and thickening existing strands. Minoxidil is widely used as a first-line treatment for male and female pattern hair loss.
- Available in foam and liquid forms for easy application.
- Best for stimulating hair growth in areas where thinning has occurred.
- Requires consistent use to maintain results, as stopping treatment can reverse progress.
- It may take about 2 to 4 months of regular use to see results with minoxidil.
Finasteride: Blocking DHT
Finasteride is an oral medication designed to stop hair loss by targeting DHT. As a DHT blocker, finasteride prevents testosterone from converting into dihydrotestosterone, which is the primary cause of follicle shrinkage in male pattern hair loss.
- Taken as a daily pill, finasteride is effective for slowing or stopping hair loss.
- Studies show it can even promote regrowth in some cases.
- It is also used for treating enlarged prostate, highlighting its versatility as a treatment.
Both minoxidil and finasteride target different aspects of hair loss, making them complementary when used together.
Curious about DHT Blockers? Learn all about them here.
Comparing Effectiveness: Minoxidil vs. Finasteride
Which Treatment is More Effective?
The effectiveness of minoxidil vs. finasteride depends on your goals. Minoxidil is excellent for stimulating hair growth and is suitable for various types of hair loss, including female pattern hair loss. Finasteride, on the other hand, is particularly effective at stopping hair loss caused by DHT.
- Minoxidil focuses on regrowth by improving blood flow to hair follicles.
- Finasteride works to preserve existing hair by targeting the root cause: DHT.
Finasteride and Minoxidil Together: Combining both treatments can provide the best results for those experiencing significant hair loss. The dual approach stimulates hair growth while preventing further loss.
Potential Side Effects of Finasteride and Minoxidil
While these treatments are effective, it’s essential to be aware of their potential side effects.
Side Effects of Minoxidil
- Scalp dryness or irritation due to the topical application.
- Temporary shedding when starting treatment.
- Unwanted facial hair growth if improperly applied.
Side Effects of Finasteride
- Hormonal changes leading to reduced libido or other sexual side effects.
- Risk of dizziness or nausea for some users.
- Side effects include rare cases of breast tenderness or depression.
- Post-Finasteride Syndrome (PFS): In rare cases, some users may experience persistent symptoms such as sexual dysfunction, fatigue, or mood changes even after stopping treatment. While uncommon, PFS highlights the importance of consulting a specialist before starting finasteride to assess individual risks.
Dr. Kopelman emphasizes that while side effects of finasteride and minoxidil are rare, they can vary based on individual sensitivity. Consulting a Hair Restoration specialist ensures you receive the right treatment plan tailored to your needs.
Usage and Dosage Guidelines
Minoxidil Usage
- Apply minoxidil to the scalp twice daily for the best results.
- Avoid washing your hair immediately after application to allow proper absorption.
- Consistent use is key—stopping treatment can lead to hair loss resuming.
Finasteride Dosage
- Take one finasteride pill daily, with or without food.
- Results may take 3-6 months to appear, as it works by gradually reducing DHT levels.
- Adherence is critical, as missing doses can reduce the effectiveness of the treatment.
For those using both treatments, Dr. Kopelman recommends following a strict routine to maximize results.
Cost and Accessibility of Treatments
When comparing finasteride and minoxidil, cost is another factor to consider.
- Minoxidil: Typically more affordable, especially when using generic versions. Monthly costs range from $10 to $30.
- Finasteride: Slightly more expensive, with prices averaging $20 to $50 per month depending on the brand and dosage.
Despite the cost differences, both treatments are considered highly accessible. The right choice depends on your budget, goals, and willingness to commit to a daily routine.
Combination Therapy: Minoxidil and Finasteride
As previously mentioned, using finasteride and minoxidil together is the most effective strategy. This combination leverages the strengths of both treatments:
- Minoxidil improves blood flow and directly stimulates hair growth.
- Finasteride reduces DHT levels, stopping hair loss at its root.
Studies show that patients using both treatments experience better overall results compared to those using only one. Dr. Kopelman often recommends this approach for individuals with significant or long-term hair loss.
Who Should Use Minoxidil or Finasteride?
Minoxidil is Ideal For:
- People experiencing early-stage thinning or patchy hair loss.
- Both men and women seeking a topical solution.
- Those looking for a simple application process.
- Minoxidil also comes in an oral tablet that isn’t approved for treating hair loss. However, a healthcare professional may prescribe lower doses off-label for this use.
Finasteride is Best For:
- Men with moderate to severe male pattern hair loss caused by DHT.
- Individuals comfortable with oral medication.
- Those seeking to stop further hair loss while promoting regrowth.
- Another difference between finasteride and minoxidil is who’s approved to use them for hair loss. Both finasteride and minoxidil are approved for hair loss in men, but only minoxidil is also approved for women.
Whether you choose finasteride or minoxidil—or both—depends on your type of hair loss and personal preferences.
Making the Right Decision
When deciding between minoxidil vs. finasteride, it’s crucial to understand your hair loss type and treatment goals. While both options are effective, their mechanisms differ significantly.
- Topical treatments like minoxidil are great for stimulating hair growth and maintaining thickness.
- Oral medication such as finasteride targets the hormonal root cause of hair loss, making it ideal for preventing further thinning.
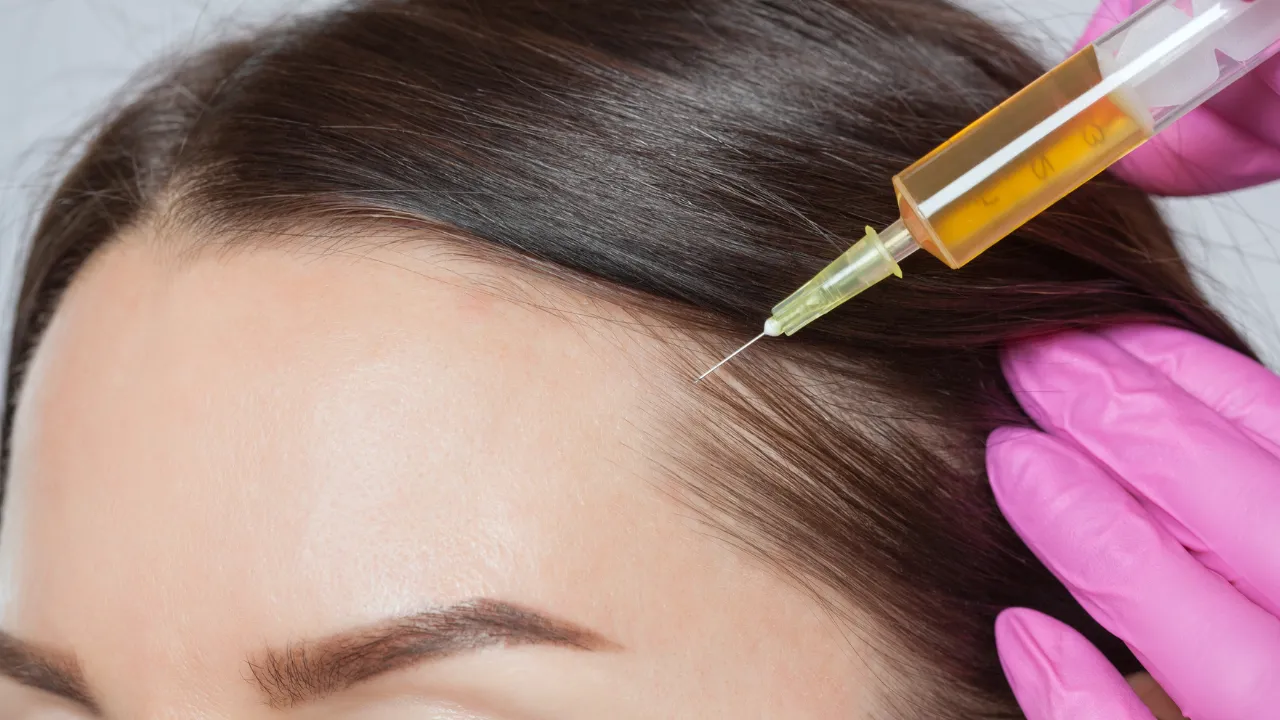
When to Consider Hair Transplants
For individuals experiencing advanced hair loss where medications like minoxidil and finasteride are less effective, hair transplants can provide a permanent solution. Hair transplants are particularly beneficial for addressing bald spots or restoring a receding hairline.
What Are Hair Transplants?
Hair transplants involve relocating healthy hair follicles from donor areas (usually the back or sides of the scalp) to areas affected by thinning or baldness.
Why Consider Hair Transplants?
- Permanent Solution: Transplanted hair is resistant to DHT and won’t fall out.
- Natural Results: Modern Hair Transplant techniques, like FUE, ensure a natural-looking hairline.
- Restores Confidence: This is particularly effective for individuals with extensive hair loss.
Combining Hair Transplants with Medications
While hair transplants address areas of significant hair loss, ongoing treatments like minoxidil or finasteride can help maintain existing hair and prevent further thinning.
Final Thoughts
Hair loss treatments like minoxidil and finasteride have transformed how we address male- and female-pattern hair loss. By targeting blood vessels, stimulating hair growth, and blocking DHT, these treatments provide hope to millions of individuals worldwide.
Dr. Kopelman’s extensive experience ensures patients receive the most effective and personalized care. Whether you’re exploring finasteride and minoxidil pills, topical solutions, or a combination of both, expert guidance can make all the difference. Take the first step toward stopping hair loss and restoring your confidence—schedule a consultation with Dr. Kopelman today.