Table of Contents
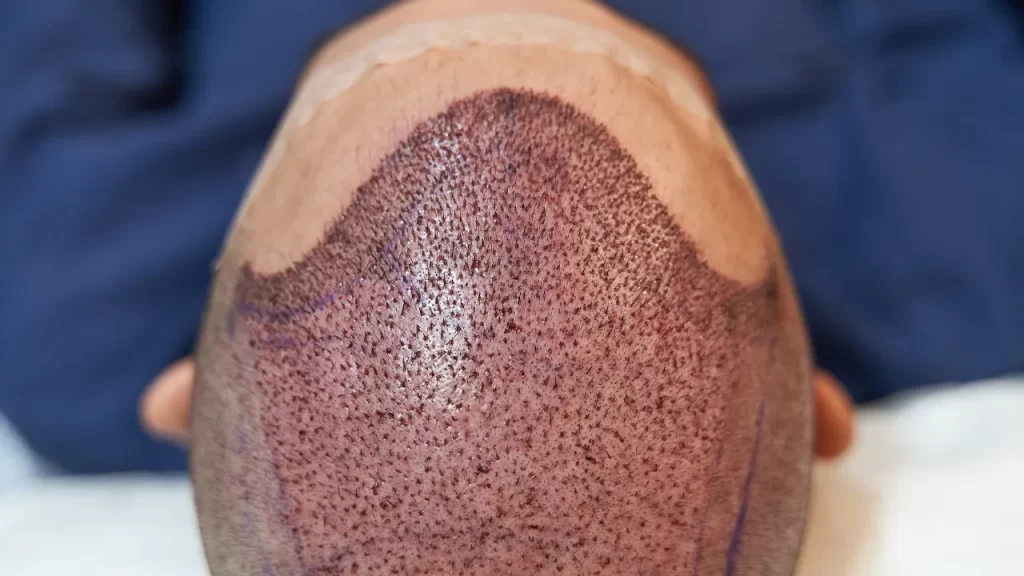
ToggleAfter undergoing a hair transplant, it’s common to experience redness on the scalp. This redness is a normal part of the healing process, signaling that the body is working to repair and adjust to the transplanted hair.
While some level of redness is expected, many hair transplant patients want to know how to reduce it, especially if it persists longer than anticipated.
Why Redness Occurs After a Hair Transplant
Redness after a hair transplant occurs due to the body’s natural response to trauma. During the procedure, tiny incisions are made at both the donor and recipient areas to insert the transplanted grafts, which leads to an increase in blood flow to the recipient site. This increased circulation is necessary for healing, but it also results in visible redness. Patients with sensitive skin tend to experience more noticeable redness, while others may see it fade quicker.
Timeline for Redness to Subside
Most patients ask, “When does hair transplant redness go away?” For the majority, redness improves within two to four weeks. Still, some people wonder how long does redness last after hair transplant, and the answer depends on skin type and healing speed.
For most individuals, the redness subsides within two to four weeks post-op. However, for others, particularly those prone to sensitive skin, the redness may linger for a longer period. If redness persists for more than four weeks, it could indicate irritation or folliculitis after hair transplant surgery, which is common during the healing process. While folliculitis usually resolves on its own, it’s essential to monitor your scalp for signs of infection or persistent inflammation.
Here are some additional causes to look out for not caused by normal healing:
- Cellulitis (skin infection)
- Cysts (small round swelling under the skin)
- Skin necrosis (dead and dying skin)
All of these factors can impact donor areas as well as the recipient areas following a hair transplant, so it’s important to monitor them closely. Below, we outline the typical symptoms and signs to watch for, along with our recommended treatments.
Folliculitis
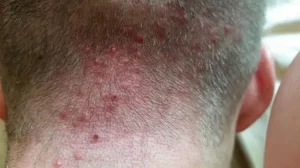
Some patients may develop an infection around the newly transplanted hair follicles. This condition can occur for up to 8 months following surgery. Folliculitis typically presents as small red bumps around each hair follicle, sometimes with a small yellow pus-filled head. It can feel warm, itchy, and painful. This is a relatively common issue after a hair transplant. While it can be caused by bacterial infections (10% of cases), in many instances, no bacteria are detected (23%).
The treatment is generally straightforward and effective. In many cases, folliculitis resolves on its own without intervention. However, it’s advisable to consult your surgeon for a proper evaluation. Warm compresses or a course of antibiotics (oral or topical) may help if bacteria are involved. Maintaining good scalp hygiene is essential to prevent any further complications from infection.
Cellulitis
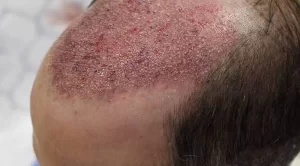
Cellulitis is an infection that affects the skin on your scalp. After a hair transplant, your skin is vulnerable to bacteria, which may enter and cause an infection. Signs of cellulitis include redness that starts spreading, scalp pain, and in some cases, fever.
If you experience these symptoms, it’s critical to see your surgeon immediately. A course of antibiotics and close daily monitoring will typically resolve the issue. Improvement will be evident when the redness stops spreading and gradually disappears.
Cysts
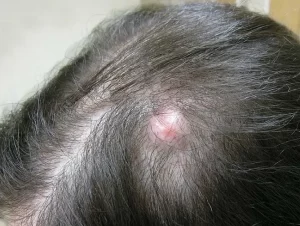
Cysts are small, round sacs that form beneath the skin and can appear in either the donor or recipient areas. They may develop due to improper removal or implantation of grafts, or as part of an abnormal healing process. Cysts are often red, swollen, and painful.
If you suspect you have cysts, it’s important to visit your surgeon. Treatment is simple, and the surgeon may either remove the cyst or recommend warm compresses. Antibiotics might also be prescribed if necessary.
Skin Necrosis
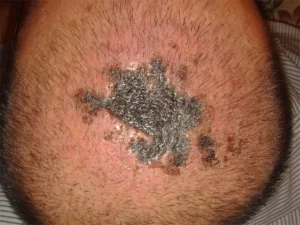
Skin necrosis occurs when the skin tissue dies. This serious complication indicates poor surgical technique and should not occur. It appears as a deep scab and may develop at the back of the head or in the area where hair was transplanted. Necrosis can emerge within 2-4 weeks post-surgery, starting with a dusky or purplish discoloration before the skin turns black and dies.
How to Reduce Redness After Hair Transplant
Reducing redness after a hair transplant and preventing further irritation is all about careful aftercare.
If you’re wondering how to get rid of redness after hair transplant, focus on gentle care, sun protection, hydration, and avoiding scratching. Here are some practical steps:
- Gentle Hair Washing Techniques: Use a mild, non-irritating shampoo to clean the scalp without causing additional inflammation. Avoid scrubbing or applying pressure to the recipient site in the first few weeks.
- Avoid Sun Exposure: The scalp is particularly sensitive after surgery, so it’s crucial to avoid direct sunlight. If you need to be outdoors, wear a hat or apply a sunscreen recommended by your hair transplant surgeon to protect the healing area.
- Hydration and Diet: Staying hydrated and eating a healthy diet can promote faster healing. A diet rich in vitamins A, C, and E, along with omega-3 fatty acids, can help reduce inflammation and redness, which is important for both hair loss prevention and recovery.
- Anti-Inflammatory Treatments: Over-the-counter anti-inflammatory creams or medications, such as corticosteroids, may help soothe the scalp and reduce redness. However, always consult your hair transplant surgeon before applying any topical treatments to avoid interfering with the transplanted grafts.
- Avoid Touching or Scratching: One of the most important steps to avoid prolonging redness is to resist the urge to scratch the healing scalp. Scratching can lead to further irritation or even infection, which would exacerbate redness and delay recovery.
In cases where redness is persistent or accompanied by pimples or bumps, folliculitis after hair transplant surgery may be the cause. This is a relatively common side effect and can be treated with topical or oral antibiotics, depending on the severity.
>> Check out our related articles
Hair Transplant Timeline: A Month-by-Month Guide
Can You Change Your Hair Texture with a Hair Transplant?
When to Be Concerned About Prolonged Redness
While some redness is expected after a FUE hair transplant, prolonged or worsening redness, especially beyond four weeks, should be assessed by your doctor. In rare cases, persistent redness could indicate an infection or severe folliculitis that requires medical treatment. If you notice other symptoms such as swelling, pain, or pus, it’s important to contact your hair transplant clinic promptly.
Your Recovery Goals
Redness after a hair transplant is a natural part of the post-operative healing process, but it can be managed with proper aftercare. By following gentle cleaning routines, avoiding sun exposure, staying hydrated, and monitoring the scalp for signs of complications like folliculitis post hair transplant, most hair transplant patients will see their redness fade within a few weeks. Dr. Kopelman’s after-surgery care services are designed to support your recovery and the healing process. If redness persists or worsens, schedule a consultation with Dr. Kopelman today to ensure that your recovery stays on track.