Table of Contents
ToggleWhat causes hair loss? This is a common concern affecting millions of people worldwide. Alopecia causes can vary from genetics and hormonal changes to medical conditions and lifestyle factors. Whether it’s gradual thinning or sudden shedding, hair loss can significantly impact confidence and self-esteem.
This article explores alopecia causes, such as genetics, hormones, and medical conditions. You’ll learn about hair loss etiology, what alopecia is, and what medical conditions cause hair loss. We’ll also share tips on how to prevent hair loss in men and highlight effective hair loss treatments. At Kopelman Hair, Dr. Kopelman offers personalized solutions to restore natural-looking hairlines and confidence.
What Causes Hair Loss?
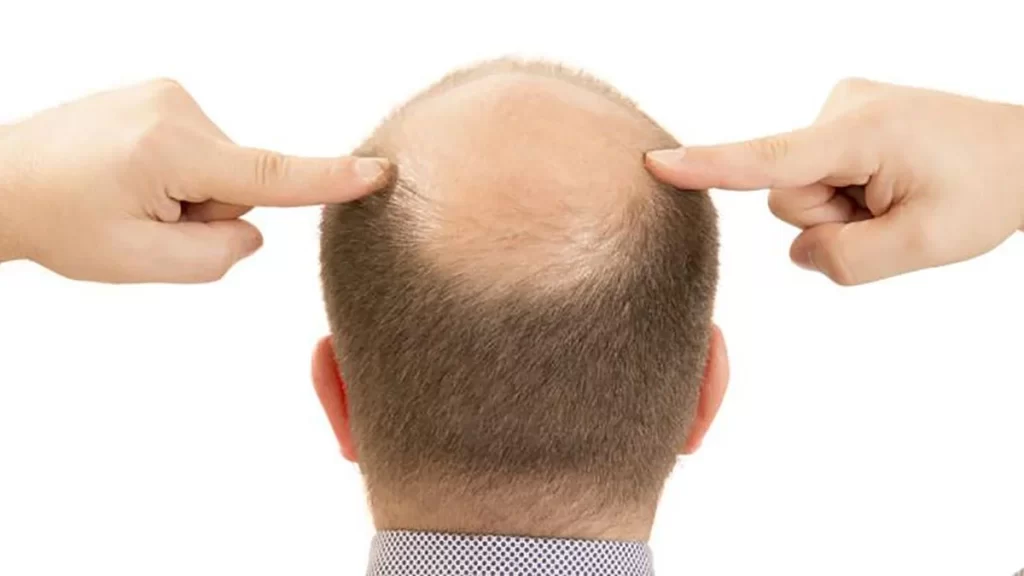
Hair loss, medically known as alopecia, can result from various factors, including genetics, hormonal changes, and health conditions. Understanding the causes of alopecia is essential for effective treatment.
You may be interested in:
- Can mold Cause Hair loss?
- Can Anesthesia Cause Hair Loss?
- Can Metformin Cause Hair Loss?
- Does Mounjaro Cause Hair Fall?
- Does adderall cause hair Fall?
- Can Hair Gel Cause Balding
- Does Dandruff Cause Balding?
- Does Wearing a Hat Cause Balding?
- Berberine and Hair Loss
- Does exercise cause hair loss?
- Do energy drinks cause hair loss
- Can steroids cause hair loss?
- Can creatine cause hair loss?
- Will Phentermine Cause Hair loss?
Genetic Factors and What Causes Alopecia
Androgenetic alopecia is the most common type of hair loss, affecting both men and women. It’s often hereditary, meaning a family history of hair loss increases your risk. Female and male pattern hair loss typically manifests as a thinning hairline or bald patches. Research shows that androgenetic alopecia affects up to 50% of men over 50 and 40% of women by age 70.
Hormonal Changes and Hair Thinning
Hormonal shifts play a significant role in hair thinning. Changes during pregnancy, menopause, or thyroid disease can disrupt the hair growth cycle. For example, many women experience postpartum hair loss due to fluctuating hormone levels.
Which hormone causes hair loss in women? Typically, changes in estrogen and progesterone levels contribute to female pattern baldness. Hormonal imbalances can shorten the growth phase of hair, causing more strands to enter the shedding phase.
Medical Conditions and Illnesses That Cause Hair Loss
Several medical conditions can lead to hair loss. Autoimmune diseases like alopecia areata cause the immune system to attack hair follicles, resulting in bald patches. Both hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism disrupt hormone levels, affecting hair growth.
What medical conditions cause hair loss? Lupus, diabetes, and anemia are known contributors. These conditions interfere with hair growth, leading to noticeable thinning.
Medications, Vitamin Deficiencies, and Lifestyle Factors
Certain medications, such as chemotherapy drugs, antidepressants, and blood pressure medications, have side effects that include hair loss. Nutritional gaps, particularly deficiencies in iron, vitamin D, and B12, can weaken hair, making it prone to shedding.
Overusing harsh hair products or excessive styling can lead to traction alopecia, a condition caused by repeated pulling or tension on the hair.
What Causes Hair Loss in Men, Women, and Postpartum?
What causes hair loss in women? Hormonal changes, iron deficiency, and stress are common culprits. In men, androgenetic alopecia remains the primary cause, leading to receding hairlines and bald spots.
Postpartum hair loss is a temporary condition affecting many new mothers due to the sudden drop in pregnancy hormones. Studies show that up to 50% of women experience noticeable hair loss after giving birth.
Recognizing Symptoms of Hair Loss
Identifying the signs of hair loss early can lead to more effective treatments. According to the Cleveland Clinic, early intervention increases the chances of successful hair restoration.
Gradual Thinning Hairline and Sudden Hair Loss
A thinning hairline is often the first noticeable sign of hair loss. You might notice more hair left on your pillow or in the shower drain.
What causes sudden hair loss? Stress, severe illness, or poor nutrition can trigger rapid shedding. Telogen effluvium, often linked to stress or illness, causes hair to fall out suddenly but is usually reversible with proper care.
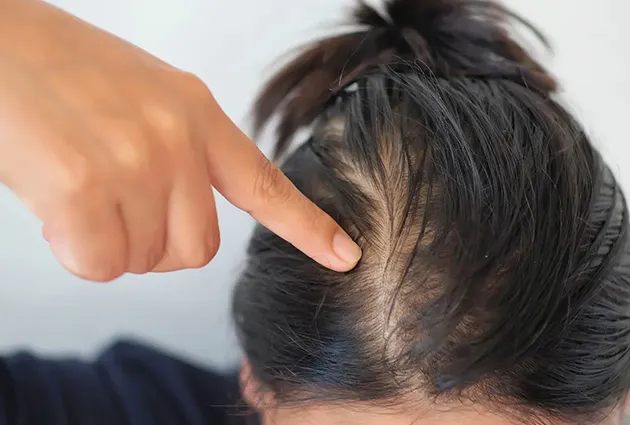
Hair Falling Out in Clumps and Bald Spots
When hair falls out in clumps, it may indicate telogen effluvium or alopecia areata. Bald patches can also result from autoimmune conditions or fungal infections like ringworm.
The AAD notes that fungal infections are common in children and can cause scaly, inflamed patches on the scalp.
Alopecia Definition and Full-Body Hair Loss
What is alopecia? Alopecia is any form of hair loss, from localized patches to full-body hair loss in severe cases like alopecia universalis.
Understanding what causes balding is key to prevention. For many men, androgenetic alopecia — a hereditary condition — is the leading cause. This type of balding occurs when hair follicles shrink due to sensitivity to dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone linked to male pattern baldness.
While genetics can’t be changed, early intervention with medications like finasteride and stress management can slow down the process and maintain hair density longer.
What Diseases Cause Hair Loss?
Several diseases can lead to hair loss by affecting the hair follicles or overall health.
- Autoimmune diseases like alopecia areata cause the immune system to attack hair follicles, resulting in patchy hair loss.
- Thyroid diseases, including hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism, disrupt hormone levels and lead to noticeable scalp hair loss.
- According to the Mayo Clinic, diabetes can impair blood circulation, weakening hair follicles.
- Anemia, mainly from iron deficiency, reduces oxygen supply to the hair follicles, causing hair thinning and loss.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) triggers hormonal imbalances that contribute to female pattern hair loss.
- Fungal infections like ringworm on the scalp can cause bald patches and brittle hair.
Diagnosing the underlying condition is crucial to restoring healthy hair.
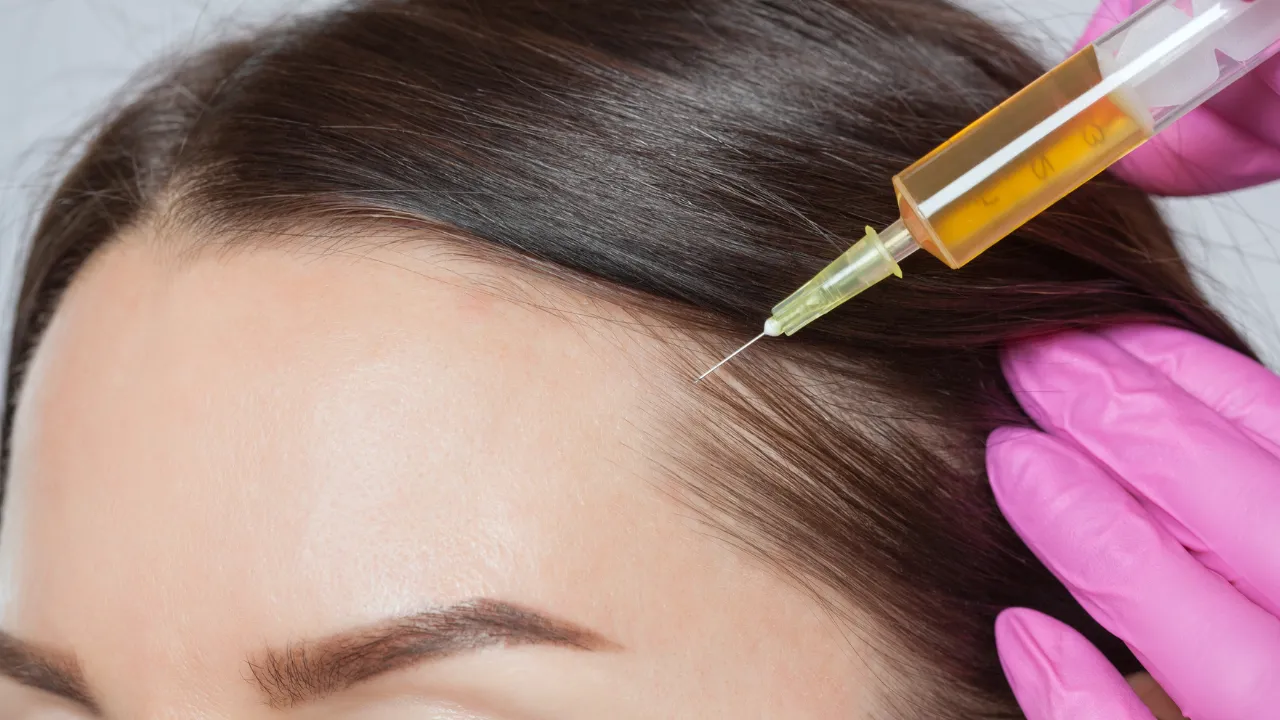
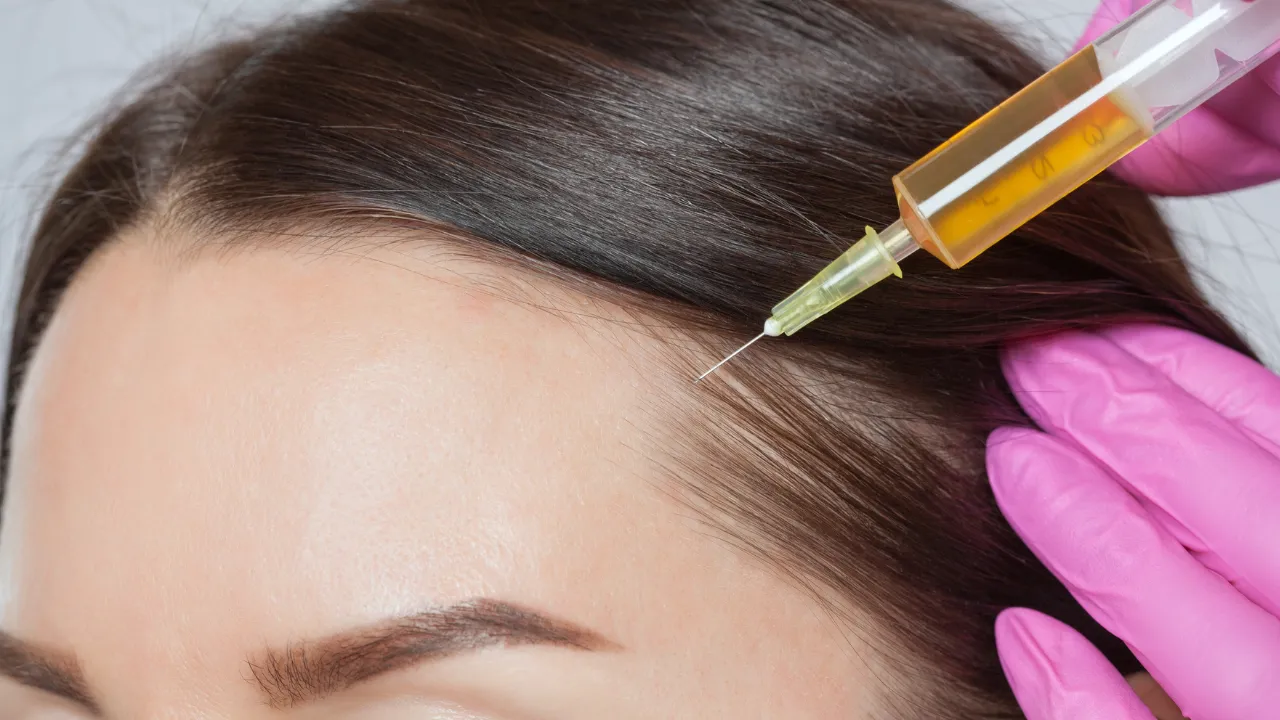
Diagnosing and Treating Hair Loss
Dr. Kopelman’s expertise ensures accurate diagnosis and personalized hair loss treatments. Diagnostic tools such as scalp biopsies, blood tests, and a thorough review of medical history help identify the exact cause of hair loss.
Can You Reverse Hair Loss?
Yes, hair loss can often be slowed or reversed, especially with early intervention. The outcome depends on the reason for losing hair.
Temporary hair loss from stress, illness, or telogen effluvium usually improves once the underlying issue is treated. Conditions like thyroid disease or hormonal imbalances can also be managed to restore hair growth.
Minoxidil and finasteride can slow hair loss and promote regrowth for genetic issues like androgenetic alopecia, though complete reversal may not be possible. In these cases, hair transplants offer a permanent solution.
How Do I Stop My Hair Falling?
- How to Stop Hair Fall Immediately: Reduce stress, maintain a balanced diet, and use gentle hair care products.
- Address underlying causes through medical evaluations, including blood tests for hormonal imbalances or nutritional deficiencies.
Medications, Surgical Procedures, and Lifestyle Changes
Treatment options include:
- Minoxidil
- Finasteride
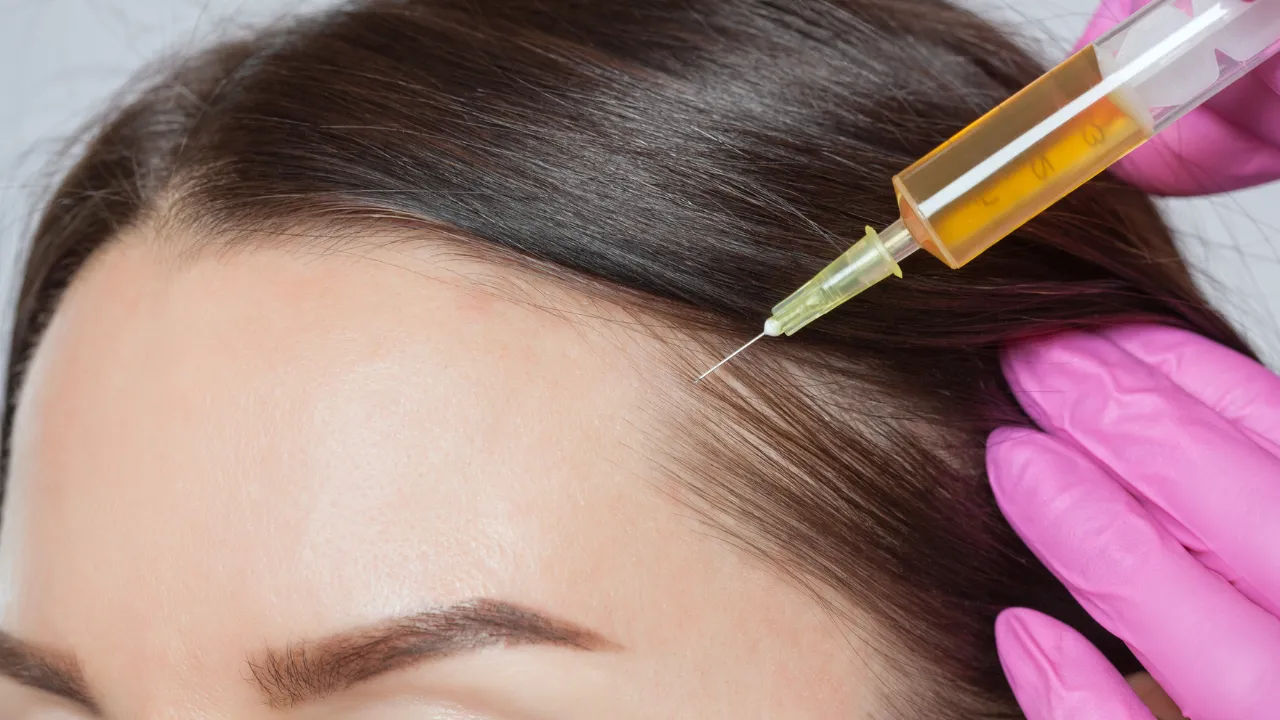
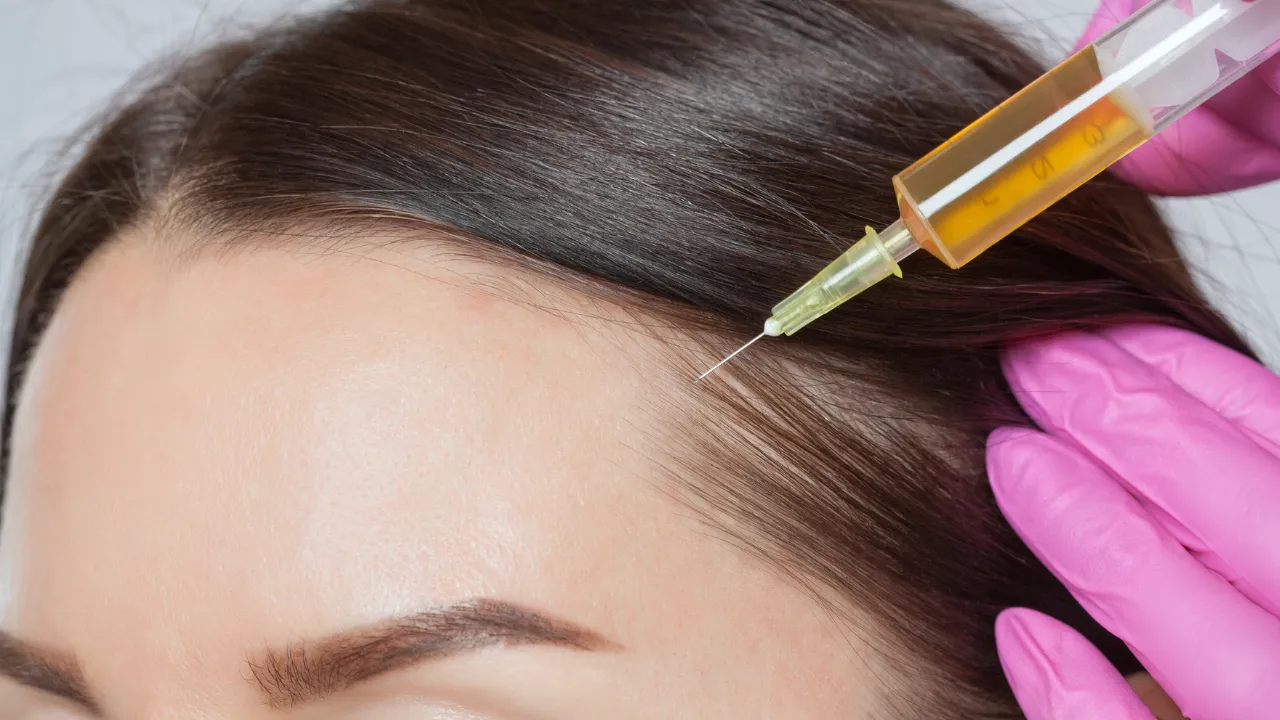
- Corticosteroid injections
Hair transplants provide lasting results for those looking for a more permanent solution. Simple lifestyle changes, like reducing heat styling and improving nutrition, can also support hair health.
How to Prevent Hair Loss in Men: Diet, Hair Care, and Stress Management
Eating a nutrient-rich diet is crucial for maintaining healthy hair. Deficiencies in vitamins like B12, iron, and vitamin D can weaken hair follicles, making them more prone to shedding.
Managing stress is equally important, as chronic stress can trigger conditions like telogen effluvium, leading to noticeable hair loss. Using mild hair products helps prevent damage to the scalp and hair shafts, reducing the risk of breakage and thinning.
When to Seek Medical Advice
Knowing when to consult a specialist like Dr. Kopelman is crucial. Persistent hair thinning, sudden shedding, or the appearance of bald patches warrant professional evaluation.
Early Signs, Rapid Hair Loss, and When to See a Doctor
If hair loss accompanies fatigue, weight changes, or skin issues, underlying conditions like thyroid disease may be involved. Early detection of these symptoms can improve treatment outcomes.
How Does a Bald Spot Form?
Hair follicles shrink due to genetics, autoimmune attacks, or prolonged tension on the hair, leading to bald spots. Identifying the cause early increases the likelihood of successful treatment.
Hair Transplant Solutions with Dr. Kopelman
Hair transplants provide a natural, long-lasting solution to male- and female-pattern hair loss, restoring not just hair but confidence. At Kopelman Hair, Dr. Kopelman utilizes cutting-edge methods like FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction) for minimal scarring and natural results.
What Causes Hair Thinning and Hair Loss: Conclusion
Understanding the causes of hair falling out and recognizing the signs of hair loss are the first steps toward recovery. Whether you’re dealing with androgenetic alopecia, telogen effluvium, or traction alopecia, seeking expert guidance is essential.
Dr. Kopelman’s personalized treatments provide practical solutions tailored to each patient’s needs. With the right approach, hair loss doesn’t have to be permanent—confidence and a fuller hairline are within reach at Kopelman Hair.